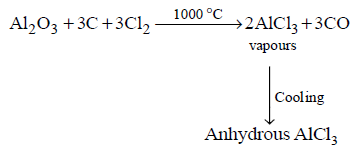481. Trigonal bipyramidal geometry is shown by :
A
$$Xe{O_3}$$
B
$$Xe{O_3}{F_2}$$
C
$$FXeOS{O_2}F$$
D
$${\left[ {Xe{F_8}} \right]^{2 - }}$$
Answer :
$$Xe{O_3}{F_2}$$
482. Which one of the following oxides of chlorine is obtained by passing dry chlorine over silver chlorate at $${90^ \circ }C?$$
A
$$C{l_2}O$$
B
$$Cl{O_3}$$
C
$$Cl{O_2}$$
D
$$Cl{O_4}$$
Answer :
$$Cl{O_2}$$
483. Which of the following statements is not valid for oxoacids of phosphorus?
A
Orthophosphoric acid is used in the manufacture of triple superphosphate
B
Hypophosphorous acid is a diprotic acid
C
All oxoacids contain tetrahedral four coordinated phosphorus
D
All oxoacids contain at least one $$P =O$$ unit and one $$P—OH$$ group
Answer :
Hypophosphorous acid is a diprotic acid
484. Boric acid is the trival name for
A
orthoboric acid
B
metaboric acid
C
pyroboric acid
D
none of these
Answer :
orthoboric acid
485. The shape of $$Xe{O_2}{F_2}$$ molecule is
A
trigonal bipyramidal
B
square planar
C
tetrahedral
D
see-saw
Answer :
see-saw
486. Which one of the following orders is correct for the bond dissociation enthalpy of halogen molecules?
A
$$C{l_2} > B{r_2} > {F_2} > {I_2}$$
B
$$B{r_2} > {I_2} > {F_2} > C{l_2}$$
C
$${F_2} > C{l_2} > B{r_2} > {I_2}$$
D
$${I_2} > B{r_2} > C{l_2} > {F_2}$$
Answer :
$$C{l_2} > B{r_2} > {F_2} > {I_2}$$
487. Anhydrous $$AlC{l_3}$$ cannot be obtained from which of the following reactions ?
A
Heating $$AlC{l_3}.6{H_2}O$$
B
By passing dry $$HCl$$ over hot aluminium powder
C
By passing dry $$C{l_2}$$ over hot aluminium powder
D
By passing dry $$C{l_2}$$ over a hot mixture of alumina and coke
Answer :
Heating $$AlC{l_3}.6{H_2}O$$
488. Blue liquid which is obtained on reacting equimolar amounts of two gases at $${30^ \circ }C$$ is?
A
$${N_2}O\,$$
B
$${N_2}{O_3}\,$$
C
$${N_2}{O_4}$$
D
$${N_2}{O_5}\,$$
Answer :
$${N_2}{O_3}\,$$
489. Dry $$S{O_2}$$ does not bleach dry flowers because
A
nascent hydrogen responsible for bleaching is produced only in presence of moisture
B
water is the actual reducing agent responsible for bleaching
C
water is stronger acid than $$S{O_2}$$
D
the $$O{H^ - }$$ ions produced by water cause bleaching
Answer :
nascent hydrogen responsible for bleaching is produced only in presence of moisture
490. Anhydrous $$AlC{l_3}$$ is prepared from
A
$$conc.\,HCl$$ and $$Al$$ metal
B
aluminium and $$C{l_2}$$
C
dry $$HCl$$ gas + heated $$Al$$ metal
D
$$dil.HCl$$ and $$Al$$ metal
Answer :
dry $$HCl$$ gas + heated $$Al$$ metal