531. Which of the following acids cannot be stored in glass?
A
$$HF$$
B
$$HCl$$
C
$${H_2}S{O_4}$$
D
$$HI$$
Answer :
$$HF$$
532. Ionisation enthalpy $$\left( {{\Delta _i}{H_1}\,kJ\,mo{l^{ - 1}}} \right)$$ for the elements of Group 13 follows the order
A
$$B > Al > Ga > In > Tl$$
B
$$B < Al < Ga < In < Tl$$
C
$$B < Al > Ga < In > Tl$$
D
$$B > Al < Ga > In < Tl$$
Answer :
$$B > Al < Ga > In < Tl$$
533. Phosphine is prepared by the action of
A
$$P\,\,{\text{and}}\,\,{H_2}S{O_4}$$
B
$$P\,\,{\text{and}}\,\,NaOH$$
C
$$P\,\,{\text{and}}\,\,{H_2}S$$
D
$$P\,\,{\text{and}}\,\,HN{O_3}$$
Answer :
$$P\,\,{\text{and}}\,\,NaOH$$
534. Which of the following hydroxides is acidic?
A
$$Al{\left( {OH} \right)_3}$$
B
$$Ga{\left( {OH} \right)_3}$$
C
$$Tl{\left( {OH} \right)_3}$$
D
$$B{\left( {OH} \right)_3}$$
Answer :
$$B{\left( {OH} \right)_3}$$
535.
Boron nitride can be represented by the given structure.
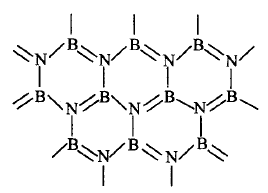
The structure of $$BN$$ is similar to
A
graphite
B
diamond
C
benzene
D
pyridine
Answer :
graphite
536. In $${P_4}{O_{10}}$$ each $$P$$ atom is linked with .......... $$O$$ atoms
A
$$2$$
B
$$3\,$$
C
$$4$$
D
$$5$$
Answer :
$$4$$
537.
\[N{{a}_{2}}{{B}_{4}}{{O}_{7}}\cdot 10{{H}_{2}}O\xrightarrow{\Delta }X\] \[\xrightarrow{\Delta }Y+Z\]
$$X, Y$$ and $$Z$$ in the reaction are
A
$$X = N{a_2}{B_4}{O_7},Y = NaB{O_2},$$ $$Z = {B_2}{O_3}$$
B
$$X = N{a_2}{B_4}{O_7},Y = {B_2}{O_3},$$ $$Z = {H_3}B{O_3}$$
C
$$X = {B_2}{O_3},Y = NaB{O_2},$$ $$Z = B{\left( {OH} \right)_3}$$
D
$$X = NaB{O_2},Y = {B_2}{O_3},$$ $$Z = B{\left( {OH} \right)_3}$$
Answer :
$$X = N{a_2}{B_4}{O_7},Y = NaB{O_2},$$ $$Z = {B_2}{O_3}$$
538. A black powder when heated with conc. $$HCl$$ gives a greenish yellow gas. The gas acts as an oxidising and a bleaching agent. When it is passed over slaked lime, a white powder is formed which is a ready source of the greenish yellow gas. The black powder and white powder respectively are
A
$$KCl{O_3}\,{\text{and}}\,NaCl{O_3}$$
B
$$Mn{O_2}\,{\text{and}}\,Ca{\left( {OCl} \right)_2}$$
C
$$Mn{O_2}\,{\text{and}}\,KCl{O_3}$$
D
$$MnC{l_4}\,{\text{and}}\,COC{l_2}$$
Answer :
$$Mn{O_2}\,{\text{and}}\,Ca{\left( {OCl} \right)_2}$$
539. Aluminium is usually found in $$ + 3$$ oxidation state. In contrast, thallium exists in $$ + 1\,\,{\text{and}} + 3$$ oxidation states. This is due to:
A
inert pair effect
B
diagonal relationship
C
lattice effect
D
lanthanoid contraction
Answer :
inert pair effect
540. In the commercial electrochemical process for aluminium extraction the electrolyte used is
A
$$Al{\left( {OH} \right)_3}$$ in $$NaOH$$ solution
B
an aqueous solution of $$A{l_2}{\left( {S{O_4}} \right)_3}.$$
C
a molten mixture of $$A{l_2}{O_3}$$ and $$N{a_3}Al{F_6}$$
D
a molten mixture of $$AlO\left( {OH} \right)$$ and $$Al{\left( {OH} \right)_3}$$
Answer :
a molten mixture of $$A{l_2}{O_3}$$ and $$N{a_3}Al{F_6}$$