571. In compounds of type $$EC{l_3},$$ where $$E = B,P,$$ $$As$$ or $$Bi,\,$$ the angles $$Cl - E - Cl$$ for different $$E$$ are in the order
A
$$\,B > P = As = Bi$$
B
$$B > P > As > Bi$$
C
$$B < P = As = Bi$$
D
$$B < P < As < Bi$$
Answer :
$$B > P > As > Bi$$
572. Identify $$X$$ and $$Y$$ in the following reaction : \[BC{{l}_{3}}+N{{H}_{4}}Cl\xrightarrow[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}Cl]{{{140}^{\circ }}C}X\] \[\xrightarrow{NaB{{H}_{4}}}Y\]
A
$$X = NaB{O_2},Y = {B_2}{O_3}$$
B
$$X = N{a_2}{B_4}{O_7},Y = {H_3}B{O_3}$$
C
$$X = BN,Y = {\left[ {N{H_4}} \right]^ + }{\left[ {BC{l_4}} \right]^ - }$$
D
$$X = {B_3}{N_3}{H_3}C{l_3},Y = {B_3}{N_3}{H_6}$$
Answer :
$$X = {B_3}{N_3}{H_3}C{l_3},Y = {B_3}{N_3}{H_6}$$
573. Xenon has closed shell configuration but is known to give compounds with fluorine because
A
$$Xe$$ atom has large size and lower ionisation potential as compared to other noble gases
B
$$Xe$$ has unpaired electrons which can form covalent bonds
C
$$Xe$$ has highest boiling point hence it can form compounds with fluorine
D
fluorine is the smallest element hence it can react with all noble gases
Answer :
$$Xe$$ atom has large size and lower ionisation potential as compared to other noble gases
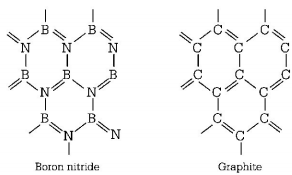
574. Which of the following structure is similar to graphite?
A
$$BN$$
B
$$B$$
C
$${B_4}C$$
D
$${B_2}{H_6}$$
Answer :
$$BN$$
575. The correct order of increasing electron affinity of halogens is
A
$$I < Br < Cl$$
B
$$Br < I < Cl$$
C
$$Cl < Br < I$$
D
$$I < Cl < Br$$
Answer :
$$I < Br < Cl$$
576.
The following acids have been arranged in order of decreasing acid strength. Identify the correct order.
$$\eqalign{
& \left( {\text{i}} \right)ClOH \cr
& \left( {{\text{ii}}} \right)BrOH \cr
& \left( {{\text{iii}}} \right)IOH \cr} $$
A
(i) > (ii) > (iii)
B
(ii) > (i) > (iii)
C
(iii) > (ii) > (i)
D
(i) > (iii) > (ii)
Answer :
(i) > (ii) > (iii)
577.
Match the column I with column II and mark the appropriate choice.
| Column I | Column II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| a. | Coal gas | 1. | $$CO + {H_2}$$ |
| b. | Synthesis gas | 2. | $$C{H_4}$$ |
| c. | Producer gas | 3. | $${H_2} + C{H_4} + CO$$ |
| d. | Natural gas | 4. | $$CO + {N_2}$$ |
A
a - 1, b - 2, c - 3, d - 4
B
a - 3, b - 1, c - 4, d - 2
C
a - 4, b - 3, c - 2, d - 1
D
a - 1, b - 3, c - 2, d - 4
Answer :
a - 3, b - 1, c - 4, d - 2
578. The tendency of group 14 elements to show + 2 oxidation state increases in the order of
A
$$C < Si < Sn < Pb < Ge$$
B
$$C < Si < Ge < Sn < Pb$$
C
$$Ge < Sn < Pb < C < Si$$
D
$$Pb < Sn < Ge < C < Si$$
Answer :
$$C < Si < Ge < Sn < Pb$$
579. In qualitative analysis when $${H_2}S$$ is passed through an aqueous solution of salt acidified with \[dil.HCl,\] a black precipitate is obtained. On boiling the precipitate with \[dil.HN{{O}_{3}},\] it forms a solution of blue colour. Addition of excess of aqueous solution of ammonia to this solution gives _________.
A
deep blue precipitate of $$Cu{\left( {OH} \right)_2}$$
B
deep blue solution of $${\left[ {Cu{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_4}} \right]^{2 + }}$$
C
deep blue solution of $$Cu{\left( {N{O_3}} \right)_2}$$
D
deep blue solution of $$Cu{\left( {OH} \right)_2} \cdot Cu{\left( {N{O_3}} \right)_2}$$
Answer :
deep blue solution of $${\left[ {Cu{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_4}} \right]^{2 + }}$$
580. Which of the following oxides can act as a reducing agent?
A
$$CO$$
B
$$C{O_2}$$
C
$$Sn{O_2}$$
D
$$Pb{O_2}$$
Answer :
$$CO$$