591. Which of the following is a tetrabasic acid?
A
Hypophosphorous acid
B
Metaphosphoric acid
C
Pyrophosphoric acid
D
Orthophosphoric acid
Answer :
Pyrophosphoric acid
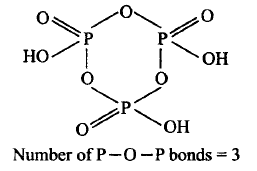
592. How many $$P - O - P$$ bonds appear in cyclotrimetaphosphoric acid?
A
Four
B
Three
C
Two
D
One
Answer :
Three
593. Which of the following shows nitrogen in its increasing order of oxidation number?
A
$${N_2}O < NO < N{O_2} < NO_3^ - < NH_4^ + $$
B
$$NH_4^ + < {N_2}O < NO < N{O_2} < NO_3^ - $$
C
$$NH_4^ + < {N_2}O < N{O_2} < NO_3^ - < NO$$
D
$$NH_4^ + < NO < {N_2}O < N{O_2} < NO_3^ - $$
Answer :
$$NH_4^ + < {N_2}O < NO < N{O_2} < NO_3^ - $$
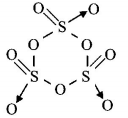
594. Thenumber of $$S - S\,$$ bonds in sulphur trioxide trimer $$\left( {{S_3}{O_9}} \right)$$ is
A
three
B
two
C
one
D
zero
Answer :
zero
595. Which of the following on thermal decomposition gives oxygen gas ?
A
$$A{g_2}O$$
B
$$P{b_3}{O_4}$$
C
$$Pb{O_2}$$
D
$${\text{All of these}}$$
Answer :
$${\text{All of these}}$$
596. On hydrolysis, diborane produces
A
$${H_3}B{O_2} + {H_2}{O_2}$$
B
$${H_3}B{O_3} + {H_2}$$
C
$${B_2}{O_3} + {O_2}$$
D
$${H_3}B{O_3} + {H_2}{O_2}$$
Answer :
$${H_3}B{O_3} + {H_2}$$
597. The tendency of $$B{F_3},BC{l_3}$$ and $$BB{r_3}$$ behave as Lewis acid decreases in the sequence
A
$$BC{l_3} > B{F_3} > BB{r_3}$$
B
$$BB{r_3} > BC{l_3} > B{F_3}$$
C
$$BB{r_3} > B{F_3} > BC{l_3}$$
D
$$B{F_3} > BC{l_3} > BB{r_3}$$
Answer :
$$BB{r_3} > BC{l_3} > B{F_3}$$
598. Carbon shows a maximum covalency of four whereas other members can expand their covalence. It is because of
A
absence of $$d$$ - orbitals in carbon
B
ability of carbon to form $$p\pi - p\pi $$ multiple bonds
C
small size of carbon
D
catenation of carbon
Answer :
absence of $$d$$ - orbitals in carbon
599. Covalency of oxygen cannot exceed 2 unlike sulphur which can show + 4 or + 6 because
A
oxygen atom does not have $$d$$ - orbitals
B
oxygen atom has two unpaired electrons in its valence shell
C
oxygen can form a double bond with another oxygen atom
D
electrons of oxygen atom cannot be promoted to $$d$$ - orbitals due to its small size
Answer :
oxygen atom does not have $$d$$ - orbitals
600. Which of the following is most acidic?
A
$${N_2}{O_5}$$
B
$${P_2}{O_5}$$
C
$$A{s_2}{O_5}$$
D
$$S{b_2}{O_5}$$
Answer :
$${N_2}{O_5}$$