1. Potassium chromate solution is added to an aqueous solution of a metal chloride. The precipitate thus obtained is insoluble in acetic acid. When precipitate is subjected to flame test the colour of the flame is
A
lilac
B
apple green
C
crimson red
D
golden yellow
Answer :
apple green
2. A gas $$“X”$$ is passed through water to form a saturated solution. The aqueous solutions on treatment with the $$AgN{O_3}$$ gives a white preciptate. The saturated aqueous solution also dissolves magnesium ribbon with evolution of a colourless gas $$“Y”.$$ Identify $$'X'$$ and $$'Y'.$$
A
$$X = C{O_2},Y = C{l_2}$$
B
$$X = C{l_2},Y = C{O_2}$$
C
$$X = C{l_2},Y = {H_2}$$
D
$$X = {H_2},Y = C{l_2}$$
Answer :
$$X = C{l_2},Y = {H_2}$$
3. Sodium carbonate cannot be used in place of $${\left( {N{H_4}} \right)_2}C{O_3}$$ for the identification of $$C{a^{2 + }},B{a^{2 + }}$$ and $$S{r^{2 + }}ions$$ ( in group $$V$$ ) during mixture analysis because :
A
$$M{g^{2 + }}\,ions$$ will also be precipitated.
B
Concentration of $$CO_3^{2 - }\,ions$$ is very low.
C
Sodium ions will react with acid radicals.
D
$$N{a^ + }\,ions$$ will interfere with the detection of $$C{a^{2 + }},B{a^{2 + }},S{r^{2 + }}\,ions.$$
Answer :
$$M{g^{2 + }}\,ions$$ will also be precipitated.
4. The sodium extract prepared from sulphanilic acid, contains $$SC{N^ - }.$$ It gives blood red colouration with
A
a mixture of $$N{a_2}S$$ and $$C{S_2}$$
B
$$FeC{l_3}$$
C
$$FeS{O_4}$$
D
$$N{a_2}S{O_3}$$
Answer :
$$FeC{l_3}$$
5. A solution when diluted with $${H_2}O$$ and boiled, gives a white precipitate. On addition of excess $$N{H_4}Cl/N{H_4}OH,$$ the volume of precipitate decreases leaving behind a white gelatinous precipitate. Identify the precipitate which disolves in $$N{H_4}OH/N{H_4}Cl$$
A
$$Al{\left( {OH} \right)_3}$$
B
$$Zn{\left( {OH} \right)_2}$$
C
$$Ca{\left( {OH} \right)_2}$$
D
$$Mg{\left( {OH} \right)_2}$$
Answer :
$$Zn{\left( {OH} \right)_2}$$
6. Prussian blue is formed when
A
ferrous sulphate reacts with $$FeC{l_3}$$
B
ferric sulphate reacts with $$N{a_4}\left[ {Fe{{\left( {CN} \right)}_6}} \right]$$
C
ferrous ammonium sulphate reacts with $$FeC{l_3}$$
D
ammonium sulphate reacts with $$FeC{l_3}$$
Answer :
ferric sulphate reacts with $$N{a_4}\left[ {Fe{{\left( {CN} \right)}_6}} \right]$$
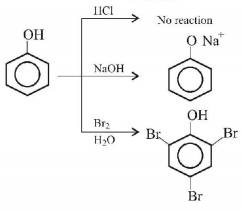
7.
The organic compound that gives following qualitative analysis is:

A
.PNG)
.PNG)
B
.PNG)
.PNG)
C
.PNG)
.PNG)
D
.PNG)
.PNG)
Answer :
.PNG)
.PNG)
8.
A substance on treatment with $$dil.{H_2}S{O_4}$$ liberates a colourless gas which produces
(I) turbidity with baryta water and
(II) turns acidified dichromate solution green.
The reaction indicates the presence of
A
$$CO_3^{2 - }$$
B
$${S^{2 - }}$$
C
$$SO_3^{2 - }$$
D
$$NO_3^ - $$
Answer :
$$SO_3^{2 - }$$
9. Which of the following statements is incorrect ?
A
$$F{e^{2 + }}\,ion$$ also gives blood red colour with $$SC{N^ - }\,ion.$$
B
$$F{e^{3 + }}\,ion$$ also gives blood red colour with $$SC{N^ - }\,ion.$$
C
On passing $${H_2}S$$ into $$N{a_2}Zn{O_2}$$ solution a white ppt of $$ZnS$$ is formed.
D
Cupric ion reacts with excess of ammonia solution to give deep blue colour of $${\left[ {Cu{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_4}} \right]^{2 + }}\,ion.$$
Answer :
$$F{e^{2 + }}\,ion$$ also gives blood red colour with $$SC{N^ - }\,ion.$$
10.
An aqueous solution contains $$H{g^{2 + }},Hg_2^{2 + },P{b^{2 + }}\,{\text{and}}\,C{d^{2 + }}.$$
The addition of $$HCl\left( {6N} \right)$$ will precipitate:
A
$$H{g_2}C{l_2}\,{\text{only}}$$
B
$$PbC{l_2}\,{\text{only}}$$
C
$$PbC{l_2}\,{\text{and}}\,H{g_2}C{l_2}$$
D
$$PbC{l_2}\,{\text{and}}\,HgC{l_2}$$
Answer :
$$PbC{l_2}\,{\text{and}}\,H{g_2}C{l_2}$$