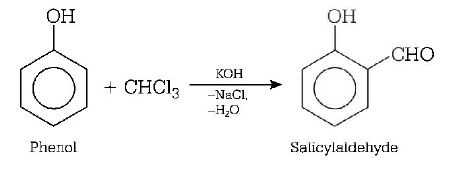
111. When phenol is heated with $$CHC{l_3}$$ and alcoholic $$KOH,$$ salicylaldehyde is produced. This reaction is known as
A
Rosenmund's reaction
B
Reimer-Tiemann reaction
C
Friedel-Craft's reaction
D
Sommelet reaction
Answer :
Reimer-Tiemann reaction
112.
The end product of the following sequence of reactions
 \[OH\xrightarrow[{{H}_{2}}O]{{{K}_{2}}C{{r}_{2}}{{O}_{7}},{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}}\] \[\xrightarrow[{{H}^{+}}\text{(Cat )}]{C{{H}_{3}}OH\text{(excess )}}\,\,\,\xrightarrow[\left( \text{ii} \right)\,{{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}}]{\left( \text{i} \right)\,2C{{H}_{3}}MgBr}\]
\[OH\xrightarrow[{{H}_{2}}O]{{{K}_{2}}C{{r}_{2}}{{O}_{7}},{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}}\] \[\xrightarrow[{{H}^{+}}\text{(Cat )}]{C{{H}_{3}}OH\text{(excess )}}\,\,\,\xrightarrow[\left( \text{ii} \right)\,{{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}}]{\left( \text{i} \right)\,2C{{H}_{3}}MgBr}\]
A


B


C

D
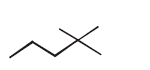

Answer :


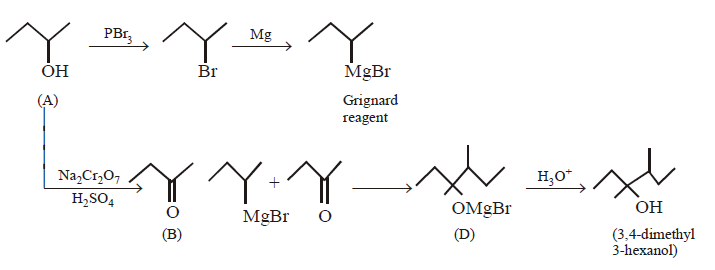
113.
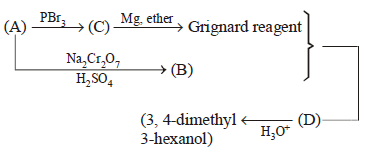
When Grignard reagent reacts with $$(B)$$ product $$(D)$$ will obtained. Reactant $$(A)$$ of the above reaction is :
A
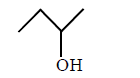

B


C


D


Answer :


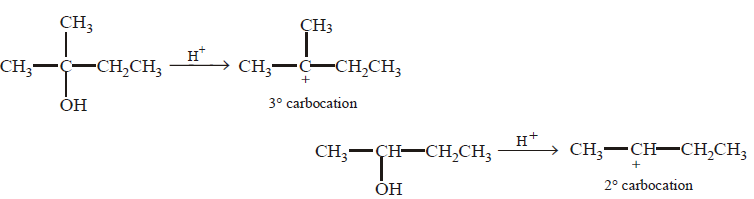
114. In the given pair of alcohol, in which pair second alcohol is more reactive than first towards hydrogen bromide ?
A


B


C
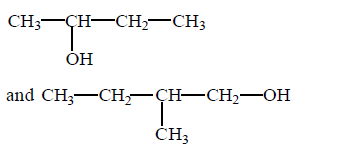

D
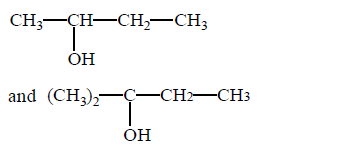

Answer :


115. What amount of bromine will be required to convert $$2g$$ of phenol into 2, 4, 6 - tribromophenol ?
A
4.0
B
6.0
C
10.22
D
20.44
Answer :
10.22
116. Phenyl methyl ether (anisole) reacts with $$HI$$ to give phenol and methyl iodide and not iodobenzene and methyl alcohol because
A
$${I^ - }$$ ion prefers to combine with the smaller group in order to minimise steric hindrance
B
$${I^ - }$$ ion is not reactive towards benzene
C
phenol is formed as a result of hydrolysis of iodobenzene
D
methyl alcohol formed during reaction reacts with $${I^ - }$$ to form methyl iodide
Answer :
$${I^ - }$$ ion prefers to combine with the smaller group in order to minimise steric hindrance
117. Which of the following products are not correctly matched in the given reactions?
A
\[{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OC{{H}_{3}}+HBr\xrightarrow{373\,K}\] \[{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH+C{{H}_{3}}Br\]
B
$${C_2}{H_5}O{C_2}{H_5} + \mathop {2HI}\limits_{{\text{Excess}}} \to $$ $${C_2}{H_5}I + {C_2}{H_5}OH$$
C
\[{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}O{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}+HCl\xrightarrow{\text{Cold}}\] \[\left[ {{\left( {{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}} \right)}_{2}}{{O}^{+}}H \right]C{{l}^{-}}\]
D
\[{{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{3}}CO{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}\xrightarrow{\text{HI}}\] \[{{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{3}}CI+{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH\]
Answer :
$${C_2}{H_5}O{C_2}{H_5} + \mathop {2HI}\limits_{{\text{Excess}}} \to $$ $${C_2}{H_5}I + {C_2}{H_5}OH$$
118.
The reaction,
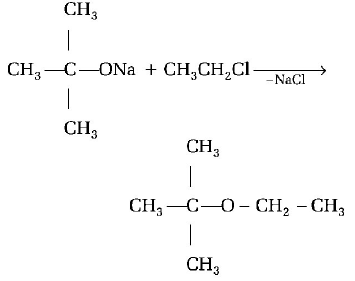
is called
A
Williamson synthesis
B
Williamson continuous etherification process
C
Etard reaction
D
Gatterman-Koch reaction
Answer :
Williamson synthesis
119. Which of the following compounds is oxidised to prepare methyl ethyl ketone?
A
2 - Propanol
B
1 - Butanol
C
2 - Butanol
D
t - Butyl alcohol
Answer :
2 - Butanol
120. The major product $$P$$ in the following reaction is \[{{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{3}}COH+{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH\xrightarrow{{{H}^{+}}}P\]
A
$${\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_3}COC{\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_3}$$
B
$${\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_3}CO{C_2}{H_5}$$
C
$${C_2}{H_5}O{C_2}{H_5}$$
D
$${\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_2}C = C{H_2}$$
Answer :
$${\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_3}CO{C_2}{H_5}$$
 \[OH\xrightarrow[{{H}_{2}}O]{{{K}_{2}}C{{r}_{2}}{{O}_{7}},{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}}\]
\[OH\xrightarrow[{{H}_{2}}O]{{{K}_{2}}C{{r}_{2}}{{O}_{7}},{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}}\]  \[COOH\xrightarrow[{{H}^{+}}]{C{{H}_{3}}OH}\]
\[COOH\xrightarrow[{{H}^{+}}]{C{{H}_{3}}OH}\]  \[COOC{{H}_{3}}\xrightarrow[\text{Excess}/{{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}}]{C{{H}_{3}}MgBr}\]
\[COOC{{H}_{3}}\xrightarrow[\text{Excess}/{{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}}]{C{{H}_{3}}MgBr}\]