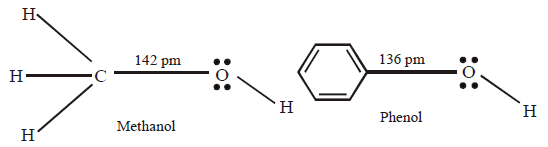
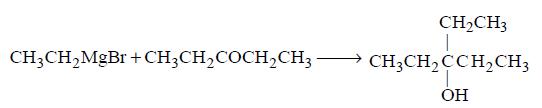121. Which one of the following statements is not correct ?
A
Alcohols are weaker acids than water.
B
Acid strength of alcohols decreases in the following $$RC{H_2}OH > {R_2}CHOH > {R_3}COH.$$
C
Carbon-oxygen bond length in methanol, $$C{H_3}OH$$ is shorter than that of $$C-O$$ bond length in phenol.
D
The bond angle 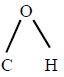 in methanol is $${108.9^ \circ }.$$
in methanol is $${108.9^ \circ }.$$
 in methanol is $${108.9^ \circ }.$$
in methanol is $${108.9^ \circ }.$$
Answer :
Carbon-oxygen bond length in methanol, $$C{H_3}OH$$ is shorter than that of $$C-O$$ bond length in phenol.
122.
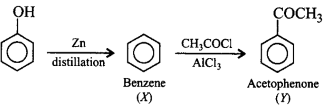
Identify the final product of the reaction sequence.
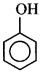 \[\xrightarrow[\text{distillation}]{Zn}X\xrightarrow[AlC{{l}_{3}}]{C{{H}_{3}}COCl}Y\]
\[\xrightarrow[\text{distillation}]{Zn}X\xrightarrow[AlC{{l}_{3}}]{C{{H}_{3}}COCl}Y\]
A
Benzophenone
B
Acetophenone
C
Diphenyl
D
Methyl salicylate
Answer :
Acetophenone
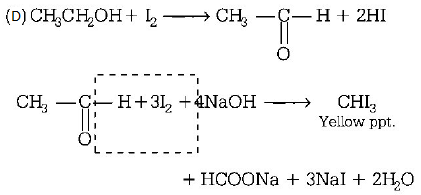
123. Which of the following will not form a yellow precipitate on heating with an alkaline solution of iodine?
A
$$C{H_3}CH\left( {OH} \right)C{H_3}$$
B
$$C{H_3}C{H_2}CH\left( {OH} \right)C{H_3}$$
C
$$C{H_3}OH$$
D
$$C{H_3}C{H_2}OH$$
Answer :
$$C{H_3}OH$$
124. To prepare 3 - ethylpentan - 3 - $$ol,$$ the reagents needed are :
A
$$C{H_3}C{H_2}MgBr + C{H_3}COC{H_2}C{H_3}$$
B
$$C{H_3}MgBr + C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}COC{H_2}C{H_3}$$
C
$$C{H_3}C{H_2}MgBr + C{H_3}C{H_2}COC{H_2}C{H_3}$$
D
$$C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}MgBr + C{H_3}COC{H_2}C{H_3}$$
Answer :
$$C{H_3}C{H_2}MgBr + C{H_3}C{H_2}COC{H_2}C{H_3}$$
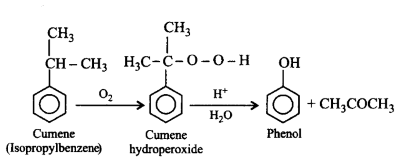
125. Cumene on reaction with oxygen followed by hydrolysis gives
A
$$C{H_3}OH\,\,{\text{and}}\,\,{C_6}{H_5}COC{H_3}$$
B
$${C_6}{H_5}OH\,\,{\text{and}}\,\,{\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_2}O$$
C
$${C_6}{H_5}OC{H_3}\,\,{\text{and}}\,\,C{H_3}OH$$
D
$${C_6}{H_5}OH\,\,{\text{and}}\,\,C{H_3}COC{H_3}$$
Answer :
$${C_6}{H_5}OH\,\,{\text{and}}\,\,C{H_3}COC{H_3}$$
126. Allyl phenyl ether can be prepared by heating :
A
$${C_6}{H_5}Br + C{H_2} = CH - C{H_2} - ONa$$
B
$$C{H_2} = CH - C{H_2} - Br + {C_6}{H_5}ONa$$
C
$${C_6}{H_5} - CH = CH - Br + C{H_3} - ONa$$
D
$$C{H_2} = CH - Br + {C_6}{H_5} - C{H_2} - ONa$$
Answer :
$${C_6}{H_5}Br + C{H_2} = CH - C{H_2} - ONa$$
127. 1 - Propanol and 2 - propanol can be best distinguished by
A
oxidation with alkaline $$KMn{O_4}$$ followed by reaction with Fehling solution
B
oxidation with acidic dichromate followed by reaction with Fehling solution
C
oxidation by heating with copper followed by reaction with Fehling solution
D
oxidation with concentrated $${H_2}S{O_4}$$ , followed by reaction with Fehling solution
Answer :
oxidation by heating with copper followed by reaction with Fehling solution
128. Lucas reagent is
A
$$conc.{\text{ }}HCl{\text{ and }}anhy{\text{.}}\,ZnC{l_2}$$
B
$$conc{\text{.}}\,HN{O_3}\,{\text{and}}\,anhy{\text{.}}\,ZnC{l_2}$$
C
$$conc.{\text{ }}HCl{\text{ and hydrous}}\,ZnC{l_2}$$
D
$$conc{\text{.}}\,HN{O_3}\,{\text{and}}\,{\text{hydrous}}\,ZnC{l_2}$$
Answer :
$$conc.{\text{ }}HCl{\text{ and }}anhy{\text{.}}\,ZnC{l_2}$$
129. Ethers are prepared by the reaction of sodium alkoxides and alkyl halides. Which of the following reagents should be taken to prepare methyl $$tert$$ - butyl ether?
A
$${\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_3}C - Br + NaOC{H_3}$$
B
$$C{H_3}Br + NaOC{\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_3}$$
C
$$C{H_3}C{H_2}Br + NaOC{\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_2}$$
D
$${\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_2}C - Br + NaOC{H_2}C{H_3}$$
Answer :
$$C{H_3}Br + NaOC{\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_3}$$
130.
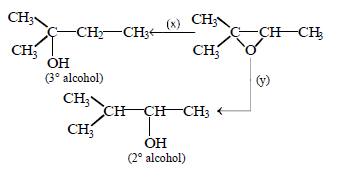
Find missing reagents.
A
$$x = LiAl{H_4},y = NaB{H_4}$$
B
$$x = LiAl{H_4}/AlC{l_3},y = Lial{H_4}$$
C
$$x = LiAl{H_4},y = LiAl{H_4}/AlC{l_3}$$
D
$$x = {H_2}/Ni,y = {H_2}/Pt$$
Answer :
$$x = LiAl{H_4},y = LiAl{H_4}/AlC{l_3}$$