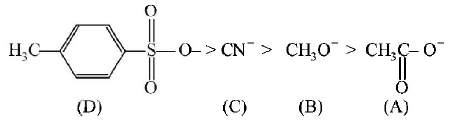11.
The correct IUPAC name of the following compound is 
A
2-ethyl-1-chlorocyclohexanol
B
4-chloro-5-ethylcyclohexanol
C
4-hydroxy-2-ethyl-1-chlorocyclohexane
D
4-chloro-3-ethylcyclohexanol
Answer :
4-chloro-3-ethylcyclohexanol
12. Which of the following acids has the smallest dissociation constant ?
A
$$C{H_3}CHFCOOH$$
B
$$FC{H_2}C{H_2}COOH$$
C
$$BrC{H_2}C{H_2}COOH$$
D
$$C{H_3}CHBrCOOH$$
Answer :
$$BrC{H_2}C{H_2}COOH$$
13. The correct decreasing order of priority for the functional groups of organic compounds in the IUPAC system of nomenclature is
A
$$ - CON{H_2}, - CHO, - S{O_3}H, - COOH$$
B
$$ - COOH, - S{O_3}H, - CON{H_2}, - CHO$$
C
$$ - S{O_3}H, - COOH, - CON{H_2}, - CHO$$
D
$$ - CHO, - COOH, - S{O_3}H, - CON{H_2}$$
Answer :
$$ - COOH, - S{O_3}H, - CON{H_2}, - CHO$$
14.
The decreasing order of nucleophilicity among the nucleophiles

A
(C), (B), (A), (D)
B
(B), (C), (A), (D)
C
(D), (C), (B), (A)
D
(A), (B), (C), (D)
Answer :
(C), (B), (A), (D)
15.
Which of the following names is correct for
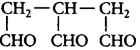 ?
?
A
3-Formylpentane-1, 3-dial
B
1, 2, 3-Triformylpropane
C
2-Formylmethylbutane-1, 4-dial
D
2-Formylmethylbutane-1, 4-dial
Answer :
2-Formylmethylbutane-1, 4-dial
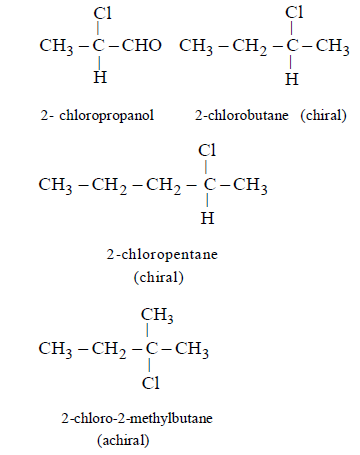
16. The optically inactive compound from the following is :
A
2 - chloropropanal
B
2 - chlorobutane
C
2 - chloropentane
D
2 - chloro - 2- methylbutane
Answer :
2 - chloro - 2- methylbutane
17. Which of the following reactions is elimination reaction ?
A


B
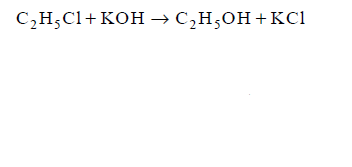
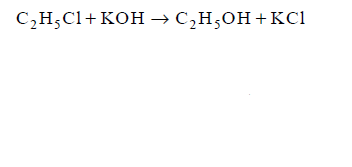
C
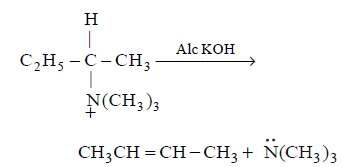
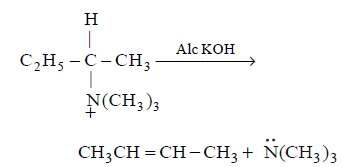
D


Answer :
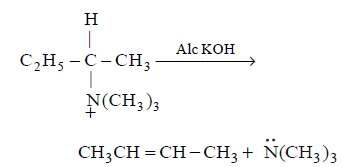
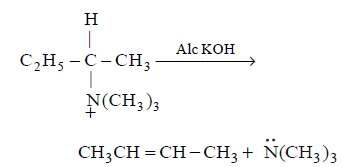
18.
In nucleophilic substitution reaction, order of halogens as incoming (attacking) nucleophile is : $${I^ - } > B{r^ - } > C{l^ - }$$
The order of halogens as departing nucleophile should be :
A
$$B{r^ - } > {I^ - } > C{l^ - }$$
B
$${I^ - } > B{r^ - } > C{l^ - }$$
C
$$C{l^ - } > B{r^ - } > {I^ - }$$
D
$$C{l^ - } > {I^ - } > B{r^ - }$$
Answer :
$${I^ - } > B{r^ - } > C{l^ - }$$
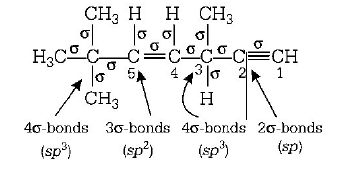
19.
The state of hybridisation of $${C_2},{C_3},{C_5}$$ and $${C_6}$$ of the hydrocarbon,

is in the following sequence
A
$$sp,s{p^3},s{p^2}\,{\text{and}}\,s{p^3}$$
B
$$s{p^3},s{p^2},s{p^2}\,{\text{and}}\,sp$$
C
$$sp,\,s{p^2},s{p^2}\,{\text{and}}\,s{p^3}$$
D
$$sp,s{p^2},s{p^3}\,{\text{and}}\,s{p^2}$$
Answer :
$$sp,s{p^3},s{p^2}\,{\text{and}}\,s{p^3}$$
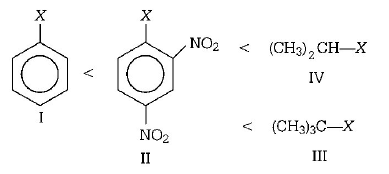
20.
The correct order of increasing reactivity of $$C - X$$ bond towards nucleophile in the following compounds is

A
I < II < IV < III
B
II < III < I < IV
C
IV < III < I < II
D
III < II < I < IV
Answer :
I < II < IV < III