1.
Given below are the structures of few compounds with molecular formula $${C_4}{H_{10}}O.$$ Select metamers from these structures.
\[\begin{align}
& \left( \text{i} \right)C{{H}_{3}}-O-C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}} \\
& \left( \text{ii} \right)C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}OH \\
& \left( \text{iii} \right)C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-O-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{3}} \\
& \left( \text{iv} \right)C{{H}_{3}}\underset{\begin{smallmatrix}
|\,\,\,\,\, \\
OH\,\,
\end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{-CH-}}\,C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{3}} \\
\end{align}\]
A
(i) and (ii)
B
(ii) and (iii)
C
(i) and (iii)
D
(ii) and (iv)
Answer :
(i) and (iii)
2.
Indicate whether each of the following pairs are identical or not ?

A
I - enantiomers; II - diastereomers; III - enantiomers
B
I - identical; II - enantiomers; III - enantiomers
C
I - enantiomers; II - diastereomers; III - identical
D
I - enantiomers; II - identical; III - identical
Answer :
I - enantiomers; II - diastereomers; III - enantiomers
3. Which of the following compounds will exhibit geometrical isomerism ?
A
1 - Phenyl - 2 - butene
B
3 - Phenyl - 1 - butene
C
2 - Phenyl - 1 - butene
D
1,1 - Diphenyl - 1 - propene
Answer :
1 - Phenyl - 2 - butene
4. Allyl isocyanide has
A
$$9\,\sigma \,\,{\text{and}}\,\,4\,\pi {\text{ - bonds}}$$
B
$$8\,\sigma \,\,{\text{and}}\,\,5\,\pi {\text{ - bonds}}$$
C
$$9\,\sigma ,3\,\,\pi \,\,{\text{and}}\,\,2\,\,{\text{non - bonded electrons}}$$
D
$$8\,\sigma ,3\,\pi \,\,{\text{and}}\,\,4\,\,{\text{non - bonded electrons}}$$
Answer :
$$9\,\sigma ,3\,\,\pi \,\,{\text{and}}\,\,2\,\,{\text{non - bonded electrons}}$$
5. Which one of the following acids does not exhibit optical isomerism ?
A
Lactic acid
B
Tartaric acid
C
Maleic acid
D
$$\alpha $$ - amino acids
Answer :
Maleic acid
6. Racemic mixture is formed by mixing two
A
isomeric compounds
B
chiral compounds
C
meso compounds
D
enantiomers with chiral carbon.
Answer :
enantiomers with chiral carbon.
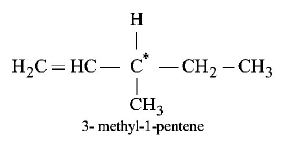
7. Out of the following, the alkene that exhibits optical isomerism is
A
3 - methyl - 2 - pentene
B
4 - methyl - 1 - pentene
C
3 - methyl - 1 - pentene
D
2 - methyl - 2 - pentene
Answer :
3 - methyl - 1 - pentene
8.
Following types of compounds ( as I, II )

are studied in terms of isomerism in :
A
chain isomerism
B
position isomerism
C
conformers
D
stereoisomerism
Answer :
stereoisomerism
9. Maleic acid and fumaric acids are
A
Chain isomers
B
Functional isomers
C
Tautomers
D
Geometrical isomers
Answer :
Geometrical isomers
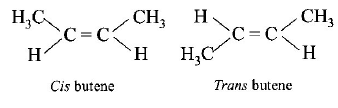
10.
The structure  shows :
shows :
A
geometrical isomersism
B
optical isomerism
C
geometrical & optical isomerism
D
tautomerism.
Answer :
optical isomerism