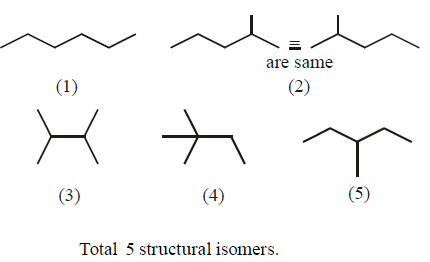
11. The number of structural isomers for $${C_6}{H_{14}}$$ is :
A
4
B
3
C
6
D
5
Answer :
5
12. An isomer of ethanol is :
A
methanol
B
diethyl ether
C
acetone
D
dimethyl ether
Answer :
dimethyl ether
13. 1-Butene and cyclobutane show
A
position isomerism
B
ring-chain isomerism
C
functional isomerism
D
metamerism
Answer :
ring-chain isomerism
14.
The alcohol product$$(s)$$ of the reduction of 2-methyl-3-pentanone with $$LiAl{H_4}$$ is (are)

A
a single enantiomer
B
racemic mixture
C
two diastereoisomers
D
two structural isomers
Answer :
racemic mixture
15. Which of the following is an isomer of ethanol?
A
Methanol
B
Acetone
C
Diethylether
D
Dimethylether
Answer :
Dimethylether
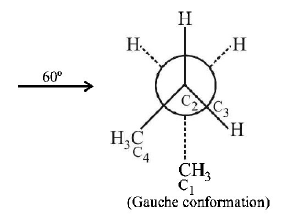
16.
In the given conformation, if $${C_2}$$ is rotated about $${C_2} - {C_3}$$ bond anticlockwise by an angle of $${120^ \circ }$$ then the conformation
obtained is
A
fully eclipsed conformation
B
partially eclipsed conformation
C
gauche conformation
D
staggered conformation
Answer :
gauche conformation
17. The number of stereoisomers possible for a compound of the molecular formula $$C{H_3} - CH = CH - CH\left( {OH} \right) - Me$$ is :
A
2
B
4
C
6
D
3
Answer :
4
18. The number of structural and configurational isomers of a bromo compound, $${C_5}{H_9}Br,$$ formed by the addition of $$HBr$$ to 2-pentyne respectively are
A
1 and 2
B
2 and 4
C
4 and 2
D
2 and 1
Answer :
2 and 4
19.
Which of the following is correct set of physical properties of the geometrical isomers ?


A
(a)
B
(b)
C
(c)
D
(d)
Answer :
(c)
20. The number of isomers for the compound with molecular formula $${C_2}BrClFI$$ is
A
3
B
4
C
5
D
6
Answer :
6