261.
Which one of the following reducing agents is likely to be most effective in bringing about the following change?
\[R\overset{\begin{smallmatrix}
O \\
\parallel
\end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{-C-}}\,N{{H}_{2}}\to RC{{H}_{2}}N{{H}_{2}}\]
A
$${H_2} - Ni$$
B
$$NaB{H_4}$$
C
$$LiAl{H_4}$$
D
$$Na - {\text{Alcohol}}$$
Answer :
$$LiAl{H_4}$$
262.
Benzylamine may be alkylated as shown in the following equation :
$${C_6}{H_5}C{H_2}N{H_2} + R - X \to $$ $${C_6}{H_5}C{H_2}NHR$$
Which of the following alkyl halides is best suited for this reaction through $${S_N}1$$ mechanism?
A
$$C{H_3}Br$$
B
$${C_6}{H_5}Br$$
C
$${C_6}{H_5}C{H_2}Br$$
D
$${C_2}{H_5}Br$$
Answer :
$${C_6}{H_5}C{H_2}Br$$
263.
Predict about the relative boiling point of the following two amines.
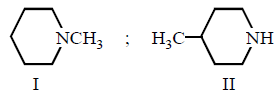
A
Boiling point of I > II
B
Boiling point of II > I
C
Both should have equal boiling points
D
It can’t be predicted
Answer :
Boiling point of II > I
264.
In a reaction of aniline a coloured product $$C$$ was obtained.
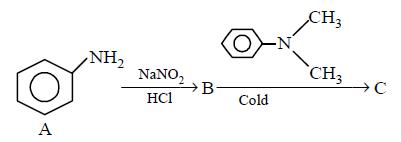
The structure of $$C$$ would be :
A
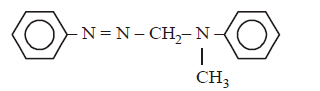
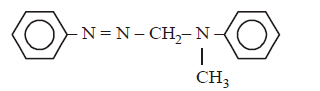
B
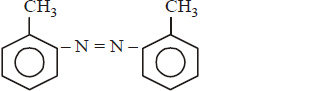

C
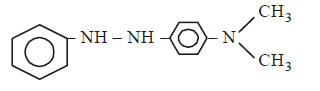

D
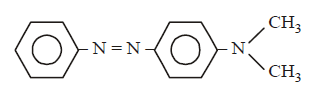

Answer :


265. Which of the following will form isocyanide on reaction with $$CHC{l_3}$$ and $$KOH?$$
A
$${C_6}{H_5}NHC{H_3}$$
B
$$C{H_3}{C_6}{H_4}N{H_2}$$
C
$${C_6}{H_5}NH{C_4}{H_9}$$
D
$${C_6}{H_5}N{\left( {{C_2}{H_5}} \right)_2}$$
Answer :
$$C{H_3}{C_6}{H_4}N{H_2}$$
266.
Identify the reagents $$X, Y$$ and $$Z$$ for the following products.
.PNG)
.PNG)
| $$X$$ | $$Y$$ | $$Z$$ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | $${I_2},$$ warm | $$KCN,$$ warm | $$NaOH,$$ warm |
| (b) | $$CuI$$ | $$NaCN$$ | $$KOH$$ |
| (c) | $$KI,$$ warm | $$CuCN$$ | $${H_2}O,$$ warm |
| (d) | $$AgI,$$ warm | $$AgCN,$$ warm | $$KOH,$$ boil |
A
(a)
B
(b)
C
(c)
D
(d)
Answer :
(c)
267. Considering the basic strength of amines in aqueous solution which one has the smallest $$p{K_b}$$ value?
A
$${\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_2}NH$$
B
$$C{H_3}N{H_2}$$
C
$${\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_3}N$$
D
$${C_6}{H_5}N{H_2}$$
Answer :
$${\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_2}NH$$
268. Primary amines on reaction with nitrous acid form ________. For the test of primary amines ________ reaction is used. Primary amines are ________ basic than ammonia.
A
carboxylic acids, Hoffmann, less
B
alcohols, carbylamine, less
C
alcohols, carbylamine, more
D
hydroxylamines, carbylamine, less
Answer :
alcohols, carbylamine, more
269.
$$'Z'$$ in the following sequence of reactions is
\[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}\xrightarrow[\Delta ]{HN{{O}_{3}}/{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}}W\xrightarrow{Zn/HCl}\] \[X\xrightarrow[HCl]{NaN{{O}_{2}}}Y\xrightarrow{{{H}_{2}}O/{{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{2}}}Z\]
A
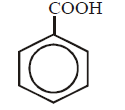

B


C
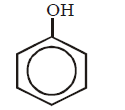

D


Answer :


270. Which of the following is the weakest $${\rm{Br\ddot onsted}}$$ base?
A
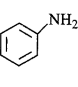

B
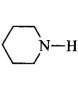

C
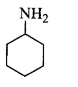

D
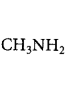
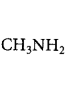
Answer :




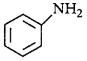 is the weakest $${\rm{Br\ddot onsted}}$$ base due to delocalisation of lone pair of electrons of $$N$$ - atom into the benzene ring.
is the weakest $${\rm{Br\ddot onsted}}$$ base due to delocalisation of lone pair of electrons of $$N$$ - atom into the benzene ring.