231. The solution of $$CuS{O_4}$$ in which copper rod is immersed is diluted to 10 times. The reduction electrode potential
A
Increases by $$30\,m\,V$$
B
Decreases by $$30\,m\,V$$
C
Increases by $$59\,m\,V$$
D
Decreases by $$59\,m\,V$$
Answer :
Decreases by $$30\,m\,V$$
232. Equivalent conductance of $$NaCl,\,HCl$$ and $${C_2}{H_5}COONa $$ at infinete dilution are 126.45, 426.16 and $$91\,{\Omega ^{ - 1}}\,c{m^2},$$ respectively. The equivalent conductance of $${C_2}{H_5}COOH$$ is
A
$$201.28\,{\Omega ^{ - 1}}\,c{m^2}$$
B
$$390.71\,{\Omega ^{ - 1}}\,c{m^2}$$
C
$$698.28\,{\Omega ^{ - 1}}\,c{m^2}$$
D
$$540.48\,{\Omega ^{ - 1}}\,c{m^2}$$
Answer :
$$390.71\,{\Omega ^{ - 1}}\,c{m^2}$$
233. A solution of copper sulphate $$\left( {CuS{O_4}} \right)$$ is electrolysed for 10 minutes with a current of 1.5 amperes. The mass of copper deposited at the cathode $$\left( {at.\,mass\,{\text{of}}\,Cu = 63u} \right)$$ is :
A
$$0.3892\,g$$
B
$$0.2938\,g$$
C
$$0.2398\,g$$
D
$$0.3928\,g$$
Answer :
$$0.2938\,g$$
234.
Given below are two figures of Daniell cell $$(X)$$ and $$(Y).$$ Study the figures and mark the incorrect statement from the following.
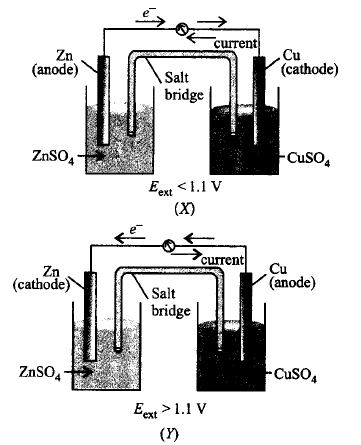
A
In fig. $$(X),$$ electrons flow from $$Zn$$ rod to $$Cu$$ rod hence current flows from $$Cu$$ to $$Zn$$ $$\left( {{E_{{\text{ext}}}} < 1.1\,V} \right).$$
B
In fig. $$(Y),$$ electrons flow from $$Cu$$ to $$Zn$$ and current flows from $$Zn$$ to $$Cu\left( {{E_{{\text{ext}}}} > 1.1\,V} \right).$$
C
In fig. $$(X),$$ $$Zn$$ dissolves at anode and $$Cu$$ deposits at cathode.
D
In fig. $$(Y),$$ $$Zn$$ is deposited at $$Cu$$ and $$Cu$$ is deposited at $$Zn.$$
Answer :
In fig. $$(Y),$$ $$Zn$$ is deposited at $$Cu$$ and $$Cu$$ is deposited at $$Zn.$$
235. Which of the following reactions does not take place during rusting?
A
$${H_2}C{O_3} \rightleftharpoons 2{H^ + } + CO_3^{2 - }$$
B
$$4F{e^{2 + }} + {O_{2\left( {{\text{dry}}} \right)}} \to F{e_2}{O_3}$$
C
$$4F{e^{2 + }} + {O_2} + 4{H_2}O \to $$ $$2F{e_2}{O_3} + 8{H^ + }$$
D
$$F{e_2}{O_3} + x{H_2}O \to F{e_2}{O_3} \cdot x{H_2}O$$
Answer :
$$4F{e^{2 + }} + {O_{2\left( {{\text{dry}}} \right)}} \to F{e_2}{O_3}$$
236.
A battery is constructed of $$Cr$$ and $$N{a_2}C{r_2}{O_7}.$$ The unbalanced chemical equation when such a battery discharges is following :
$$N{a_2}C{r_2}{O_7} + Cr + {H^ + } \to C{r^{3 + }} + {H_2}O + N{a^ + }$$ If one Faraday of electricity is passed through the battery during the charging, the number of moles of $$C{r^{3 + }}$$ removed from the solution is
A
$$\frac{4}{3}$$
B
$$\frac{1}{3}$$
C
$$\frac{3}{3}$$
D
$$\frac{2}{3}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{3}{3}$$
237. The $$EMF$$ of a cell corresponding to the reaction : $$Z{n_{\left( s \right)}} + 2H_{\left( {aq} \right)}^ + \to $$ $$Zn_{\left( {aq} \right)}^{2 + }\left( {0.1\,M} \right) + {H_{2\left( g \right)}}\left( {1\,atm} \right)$$ is 0.28 volt at $${15^ \circ }C.$$ The $$pH$$ of the solution at the hydrogen electrode is $$\left( {{\text{Given:}}\,E_{\frac{{Z{n^{2 + }}}}{{Zn}}}^ \circ = - 0.76\,{\text{volt;}}\,E_{\frac{{{H^ + }}}{{{H_2}}}}^ \circ = 0\,{\text{volt}}} \right)$$
A
7.05
B
8.62
C
8.75
D
9.57
Answer :
8.62
238. If $$x$$ is the specific resistance of the solution and $$N$$ is the normality of the solution, the equivalent conductivity of the solution is given by
A
$$\frac{{1000x}}{N}$$
B
$$\frac{{1000}}{{Nx}}$$
C
$$\frac{{1000N}}{x}$$
D
$$\frac{{Nx}}{{1000}}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{{1000}}{{Nx}}$$
239. Specific conductance of $$0.1\,M$$ sodium chloride solution is $$1.06 \times {10^{ - 2}}oh{m^{ - 1}}c{m^{ - 1}}.$$ Its molar conductance in $$oh{m^{ - 1}}c{m^2}mo{l^{ - 1}}$$ is
A
$$1.06 \times {10^2}$$
B
$$1.06 \times {10^3}$$
C
$$1.06 \times {10^4}$$
D
$$5.3 \times {10^2}$$
Answer :
$$1.06 \times {10^2}$$
240. The molar conductivities $$\Lambda _{NaOAc}^o$$ and $$\Lambda _{HCl}^o$$ at infinite dilution in water at $${25^ \circ }C$$ are $$91.0$$ and $$426.2\,S\,c{m^2}/mol$$ respectively. To calculate $$\Lambda _{HOAc}^o,$$ the additional value required is
A
$$\Lambda _{NaOH}^o$$
B
$$\Lambda _{NaCl}^o$$
C
$$\Lambda _{{H_2}O}^o$$
D
$$\Lambda _{KCl}^o$$
Answer :
$$\Lambda _{NaCl}^o$$