251.
The standard $$EMF$$ of a galvanic cell involving cell reaction with $$n = 2$$ is found to be $$0.295$$ $$V$$ at $${25^ \circ }C.$$ The equilibrium constant of the reaction would be
( Given $${F = 96500\,C\,mo{l^{ - 1}},}$$ $${R = 8.314\,J{K^{ - 1}}\,mo{l^{ - 1}}}$$ )
A
$$2.0 \times {10^{11}}$$
B
$$4.0 \times {10^{12}}$$
C
$$1.0 \times {10^2}$$
D
$$1.0 \times {10^{10}}$$
Answer :
$$1.0 \times {10^{10}}$$
252.
Consider the following standard electrode potentials and calculate the equilibrium constant
at $${25^ \circ }C$$ for the indicated disproportion nation reaction :
$$\eqalign{
& 3M{n^{2 + }}\left( {aq} \right) \to Mn\left( s \right) + 2M{n^{3 + }}\left( {aq} \right) \cr
& M{n^{3 + }}\left( {aq} \right) + {e^ - } \to M{n^{2 + }}\left( {aq} \right);{E^ \circ } = 1.51\,V \cr
& M{n^{2 + }}\left( {aq} \right) + 2{e^ - } \to Mn\left( s \right);{E^ \circ } = - 1.185\,V \cr} $$
A
$$1.2 \times {10^{ - 43}}$$
B
$$2.4 \times {10^{ - 73}}$$
C
$$6.3 \times {10^{ - 92}}$$
D
$$1.5 \times {10^{ - 62}}$$
Answer :
$$6.3 \times {10^{ - 92}}$$
253. Conductivity ( unit Siemen’s $$S$$ ) is directly proportional to area of the vessel and the concentration of the solution in it and is inversely proportional to the length of the vessel then the unit of the constant of proportionality is
A
$$Sm\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
B
$$S{m^2}\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
C
$${S^{ - 2}}{m^2}\,mol$$
D
$${S^2}{m^2}\,mo{l^{ - 2}}$$
Answer :
$$S{m^2}\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
254. What will be the molar conductivity of $$A{l^{3 + }}$$ ions at infinite dilution if molar conductivity of $$A{l_2}{\left( {S{O_4}} \right)_3}$$ is $$858\,S\,c{m^2}\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$ and ionic conductance of $$SO_4^{2 - }$$ is $$160\,S\,c{m^2}\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$ at infinite dilution?
A
$$189\,S\,c{m^2}\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
B
$$698\,S\,c{m^2}\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
C
$$1018\,S\,c{m^2}\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
D
$$429\,S\,c{m^2}\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
Answer :
$$189\,S\,c{m^2}\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
255.
Using the data given below find out in which option the order of reducing power is correct.
$$\eqalign{
& E_{\frac{{C{r_2}O_7^{2 - }}}{{C{r^{3 + }}}}}^ \circ = 1.33\,V;E_{\frac{{C{l_2}}}{{C{l^ - }}}}^ \circ = 1.36\,V \cr
& E_{\frac{{MnO_4^ - }}{{M{n^{2 + }}}}}^ \circ = 1.51\,V;E_{\frac{{C{r^{3 + }}}}{{Cr}}}^ \circ = - 0.74\,V \cr} $$
A
$$C{r^{3 + }} < C{l^ - } < M{n^{2 + }} < Cr$$
B
$$M{n^{2 + }} < C{l^ - } < C{r^{3 + }} < Cr$$
C
$$C{r^{3 + }} < C{l^ - } < C{r_2}O_7^{2 - } < MnO_4^ - $$
D
$$M{n^{2 + }} < C{r^{3 + }} < C{l^ - } < Cr$$
Answer :
$$M{n^{2 + }} < C{l^ - } < C{r^{3 + }} < Cr$$
256. If the \[E_{cell}^{\circ }\] for a given reaction has a negative value, which of the following gives correct relationships for the values of $$\Delta {G^ \circ }$$ and $${K_{eq}}?$$
A
$$\Delta {G^ \circ } > 0;\,{K_{eq}} < 1$$
B
$$\Delta {G^ \circ } > 0;\,{K_{eq}} > 1$$
C
$$\Delta {G^ \circ } < 0;\,{K_{eq}} > 1$$
D
$$\Delta {G^ \circ } < 0;\,{K_{eq}} < 1$$
Answer :
$$\Delta {G^ \circ } > 0;\,{K_{eq}} < 1$$
257.
Label the parts represented by $$(A), (B)$$ and $$(C).$$
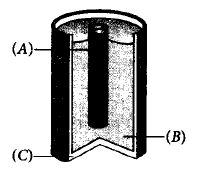
| $$A$$ | $$B$$ | $$C$$ | |
| (a) | Zinc rod | $$N{H_4}Cl + MgC{l_2}$$ | Graphite rod |
| (b) | Carbon rod | $$N{H_4}OH + $$ carbon | Zinc rod |
| (c) | Carbon rod | $$Mn{O_2} + C + N{H_4}Cl$$ | Zinc can |
| (d) | Zinc rod | $$Mn{O_2} + N{H_4}Cl$$ | Carbon |
A
(a)
B
(b)
C
(c)
D
(d)
Answer :
(c)
258. A galvanic cell has electrical potential of $$1.1\,V.$$ If an opposing potential of $$1.1\,V$$ is applied to this cell, what will happen to the cell reaction and current flowing through the cell?
A
The reaction stops and no current flows through the cell.
B
The reaction continuous but current flows in opposite direction.
C
The concentration of reactants becomes unity and current flows from cathode to anode.
D
The cell does not function as a galvanic cell and zinc is deposited on zinc plate.
Answer :
The reaction stops and no current flows through the cell.
259. The $${E^ \circ }_{{M^{3 + }}/{M^{2 + }}}$$ values for $$Cr,Mn,Fe$$ $$Co$$ are $$ - 0.41, + 1.57, + 0.77$$ and $$ + 1.97\,V$$ respectively. For which one of these metals the change in oxidation state from $$+2$$ to $$+3$$ is easiest?
A
$$Fe$$
B
$$Mn$$
C
$$Cr$$
D
$$Co$$
Answer :
$$Cr$$
260. For the galvanic cell, $$Cu\left| {C{u^{2 + }}} \right|\left| {A{g^ + }} \right|Ag.$$ Which of the following observations is not correct?
A
$$Cu$$ acts as anode and $$Ag$$ acts as cathode.
B
$$Ag$$ electrode loses mass and $$Cu$$ electrode gains mass.
C
Reaction at anode, $$Cu \to C{u^{2 + }} + 2{e^ - }.$$
D
Copper is more reactive than silver.
Answer :
$$Ag$$ electrode loses mass and $$Cu$$ electrode gains mass.