161. Which of the following has maximum value of cation/anion ratio?
A
$$KCl$$
B
$$NaCl$$
C
$$Ca{F_2}$$
D
$$MgC{l_2}$$
Answer :
$$Ca{F_2}$$
162. The number of unit cells in $$58.8\,g$$ of $$NaCl$$ is nearly
A
$$6 \times {10^{20}}$$
B
$$3 \times {10^{22}}$$
C
$$1.5 \times {10^{23}}$$
D
$$0.5 \times {10^{24}}$$
Answer :
$$1.5 \times {10^{23}}$$
163. To get a $$n$$ - type semiconductor, the impurity to be added to silicon should have which of the following number of valence electrons
A
1
B
2
C
3
D
5
Answer :
5
164.
How many unit cells are present in a cube-shaped ideal crystal of $$NaCl$$ of mass $$1.00\,g?$$
[ Atomic masses $$:Na = 23,Cl = 35.5$$ ]
A
$$5.14 \times {10^{21}}\,{\text{unit cells}}$$
B
$$1.28 \times {10^{21}}\,{\text{unit cells}}$$
C
$$1.71 \times {10^{21}}\,{\text{unit cells}}$$
D
$$2.57 \times {10^{21}}\,{\text{unit cells}}$$
Answer :
$$2.57 \times {10^{21}}\,{\text{unit cells}}$$
165. In a cubic close packed structure of mixed oxides, the lattice is composed of oxide ions, one-eighth of tetrahedral voids are occupied by divalent cations $$A,$$ while one-half of octahedral voids are occupied by trivalent cations $$B.$$ The formula of the oxide is
A
$${A_2}B{O_4}$$
B
$$A{B_2}{O_3}$$
C
$${A_2}B{O_3}$$
D
$$A{B_2}{O_4}$$
Answer :
$$A{B_2}{O_4}$$
166. For $$fcc,$$ if $$AB$$ is just like the rock salt like structure then, $${A^ + }$$ and $${B^ - }$$ are located at –
A
$${A^ + }$$ - Tetrahedral voids ; $${B^ - }$$ - Corner
B
$${A^ + }$$ - Corner and faces ; $${B^ - }$$ - Octahedral voids
C
$${A^ + }$$ - Octahedral voids ; $${B^ - }$$ - Corner and faces
D
$${A^ + }$$ - Corner and faces ; $${B^ - }$$ - Octahedral and tetrahedral voids
Answer :
$${A^ + }$$ - Octahedral voids ; $${B^ - }$$ - Corner and faces
167. Ferrimagnetism is observed when the magnetic moments of the domains in the substance are
A
oppositely oriented and cancel each other's magnetic moment.
B
aligned in parallel and anti-parallel directions in unequal numbers
C
randomly oriented and their magnetic moments get cancelled
D
in same direction and get aligned in a magnetic field.
Answer :
aligned in parallel and anti-parallel directions in unequal numbers
168. A crystalline solid
A
changes abruptly from solid to liquid when heated.
B
has no definite melting point.
C
undergoes deformation of its geometry easily.
D
has an irregular 3-dimensional arrangements.
Answer :
changes abruptly from solid to liquid when heated.
169. In an antifluorite structure, cations occupy
A
octahedral voids
B
centre of cube
C
tetrahedral voids
D
corners of cube
Answer :
tetrahedral voids
170.
A compound $${M_p}{X_q}$$ has cubic close packing $$\left( {ccp} \right)$$ arrangement of $$X.$$ Its unit cell structure shown below. The empirical formula of the compound is
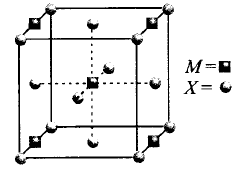
A
$$MX$$
B
$$M{X_2}$$
C
$${M_2}X$$
D
$${M_5}{X_{14}}$$
Answer :
$$M{X_2}$$