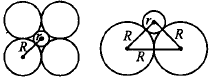61. An alloy of copper, silver and gold is found to have cubic lattice in which $$Cu$$ atoms constitute $$ccp.$$ If $$Ag$$ atoms are located at the edge centres and $$Au$$ atom is present at body centre, the alloy will have the formula
A
$$CuAgAu$$
B
$$C{u_4}A{g_4}Au$$
C
$$C{u_4}A{g_3}Au$$
D
$$C{u_4}A{g_6}Au$$
Answer :
$$C{u_4}A{g_3}Au$$
62. Iodine molecules are held in the crystals lattice by ________.
A
London forces
B
dipole-dipole interactions
C
covalent bonds
D
coulombic forces
Answer :
London forces
63. If the radius of an octahedral void is $$r$$ and radius of atoms in close packing is $$R,$$ the relation between $$r$$ and $$R$$ is
A
$$r = 0.414\,R$$
B
$$R = 0.414r$$
C
$$r = 2R$$
D
$$r = \sqrt 2 R$$
Answer :
$$r = 0.414\,R$$
64. Silver halides generally show
A
Schottky defect
B
Frenkel defect
C
both Frenkel and Schottky defects
D
cation excess defect
Answer :
both Frenkel and Schottky defects
65. What is the coordination number in a square close packed structure in two dimensions ?
A
2
B
3
C
4
D
6
Answer :
4
66. Crystalline $$CsCl$$ has density $$3.988\,g\,c{m^{ - 3}}.$$ The volume occupied by single $$CsCl$$ $$ion$$ pair in the crystal will be
A
$$7.014 \times {10^{ - 3}}\,c{m^3}$$
B
$$7.014 \times {10^{ - 23}}\,c{m^3}$$
C
$$1.014 \times {10^{ - 3}}\,c{m^3}$$
D
$$1.542 \times {10^{ - 5}}\,c{m^3}$$
Answer :
$$7.014 \times {10^{ - 23}}\,c{m^3}$$
67. Total volume of atoms present in a face-centred cubic unit cell of a metal is ( $$r$$ is atomic radius )
A
$$\frac{{12}}{3}\pi {r^3}$$
B
$$\frac{{16}}{3}\pi {r^3}$$
C
$$\frac{{20}}{3}\pi {r^3}$$
D
$$\frac{{24}}{3}\pi {r^3}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{{16}}{3}\pi {r^3}$$
68. The density of mercury is $$13.6\,g/mL.$$ The diameter of an atom of mercury assuming that each atom is occupying a cube of edge length equal to the diameter of the mercury atom is approximately
A
$$3.01\mathop {\text{A}}\limits^{\text{o}} $$
B
$$2.54\mathop {\text{A}}\limits^{\text{o}} $$
C
$$0.29\mathop {\text{A}}\limits^{\text{o}} $$
D
$$2.91\mathop {\text{A}}\limits^{\text{o}} $$
Answer :
$$2.91\mathop {\text{A}}\limits^{\text{o}} $$
69. The radius of a calcium ion is $$94\,pm$$ and of the oxide ion is 146$$\,pm.$$ The possible crystal structure of calcium oxide will be
A
tetrahedral
B
trigonal
C
octahedral
D
pyramidal
Answer :
octahedral
70. Which of the following will have metal deficiency defect ?
A
$$NaCl$$
B
$$FeO$$
C
$$KCl$$
D
$$ZnO$$
Answer :
$$FeO$$