91. A 5.2 molal aqueous solution of methyl alcohol, $$C{H_3}OH,$$ is supplied. What is the mole fraction of methyl alcohol in the solution?
A
0.100
B
0.190
C
0.086
D
0.050
Answer :
0.086
92. $$10\% $$ solution of urea is isotonic with $$6\% $$ solution of a non-volatile solute $$X.$$ What is the molecular mass of solute $$X?$$
A
$$6\,g\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
B
$$60\,g\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
C
$$36\,g\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
D
$$32\,g\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
Answer :
$$36\,g\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
93. $$0.5\,m$$ solution of a complex of iron and cyanide $$ions$$ has the depression of $$f.pt.$$ to be $$3.72\,K$$ ( $${K_f}$$ for water $$ = 1.86\,K\,mola{l^{ - 1}}$$ ). The formula of the complex is :
A
$${K_4}\left[ {Fe{{\left( {CN} \right)}_6}} \right]$$
B
$${K_2}\left[ {Fe{{\left( {CN} \right)}_4}} \right]$$
C
$${K_3}\left[ {Fe{{\left( {CN} \right)}_6}} \right]$$
D
$$Fe{\left( {CN} \right)_4}$$
Answer :
$${K_3}\left[ {Fe{{\left( {CN} \right)}_6}} \right]$$
94. A solution containing $$10\,g$$ per $$d{m^3}$$ of urea ( molecular mass $$ = 60\,g\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$ ) is isotonic with a $$5\% $$ solution of a non-volatile solute. The molecular mass of this non-volatile solute is
A
$$250\,g\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
B
$$300\,g\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
C
$$350\,g\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
D
$$200\,g\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
Answer :
$$300\,g\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
95.
Consider the figure and mark the correct option.
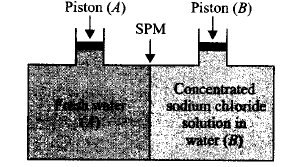
A
Water will move from side $$(A)$$ to side $$(B)$$ if a pressure lower than osmotic pressure is applied on piston $$(B).$$
B
Water will move from side $$(B)$$ to side $$(A)$$ if a pressure greater than osmotic pressure is applied on piston $$(B).$$
C
Water will move from side $$(B)$$ to side $$(A)$$ if a pressure equal to osmotic pressure is applied on piston $$(B).$$
D
Water will move from side $$(A)$$ to side $$(B)$$ if pressure equal to osmotic pressure is applied on piston $$(A).$$
Answer :
Water will move from side $$(B)$$ to side $$(A)$$ if a pressure greater than osmotic pressure is applied on piston $$(B).$$
96. Sea water is desalinated to get fresh water by which of the following methods ?
A
When pressure more than osmotic pressure is applied pure water is squeezed out of sea water by reverse osmosis.
B
When excess pressure is applied on sea water pure water moves in by osmosis.
C
Water moves out from sea water due to osmosis.
D
Salt is precipitated from sea water when kept undisturbed for sometime.
Answer :
When pressure more than osmotic pressure is applied pure water is squeezed out of sea water by reverse osmosis.
97. How many $$N{a^ + }\,ions$$ are present in $$100\,mL$$ of $$0.25\,M$$ of $$NaCl$$ solution ?
A
$$0.025 \times {10^{23}}$$
B
$$1.505 \times {10^{22}}$$
C
$$15 \times {10^{22}}$$
D
$$2.5 \times {10^{23}}$$
Answer :
$$1.505 \times {10^{22}}$$
98. Vapour pressure of solution containing $$2\,mol$$ of liquid $$A\left( {P_A^ \circ = 80\,torr} \right)$$ and $$3\,mol$$ of liquid $$B\left( {P_B^ \circ = 100\,torr} \right)$$ is $$87\,torr.$$ We can conclude that
A
there is negative deviation from Raoult’s law
B
boiling point is higher than that expected for ideal solution
C
molecular attractions between unlike molecules are stronger than those between like molecules
D
All of these statements are correct
Answer :
All of these statements are correct
99. What will be the osmotic pressure in pascals exerted by a solution prepared by dissolving $$1.0\,g$$ of polymer of molar mass $$150,000$$ in $$500\,mL$$ of water at $${37^ \circ }C?$$
A
30.96
B
34.36
C
68.72
D
48.25
Answer :
34.36
100.
Liquid $$'M’$$ and liquid $$'N’$$ form an ideal solution. The vapour
pressures of pure liquids $$'M’$$ and $$'N’$$ are $$450$$ and $$700$$
$$mm\,Hg,$$ respectively, at the same temperature. Then correct statement is :
( $${X_M}$$ = Mole fraction of $$'M’$$ in solution;
$${X_N}$$ = Mole fraction of $$'N’$$ in solution;
$${Y_M}$$ = Mole fraction of $$'M’$$ in vapour phase;
$${Y_N}$$ = Mole fraction of $$'N’$$ in vapour phase )
A
$$\frac{{{x_M}}}{{{x_N}}} = \frac{{{y_M}}}{{{y_N}}}$$
B
$$\left( {{x_M} - {y_M}} \right) < \left( {{x_N} - {y_N}} \right)$$
C
$$\frac{{{x_M}}}{{{x_N}}} < \frac{{{y_M}}}{{{y_N}}}$$
D
$$\frac{{{x_M}}}{{{x_N}}} > \frac{{{y_M}}}{{{y_N}}}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{{{x_M}}}{{{x_N}}} > \frac{{{y_M}}}{{{y_N}}}$$