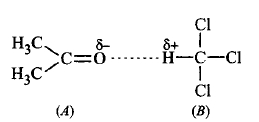251. Intermolecular forces between $$n$$ - hexane and $$n$$ - heptane are nearly same as between hexane and heptane individually. When these two are mixed, which of the following is not true about the solution formed ?
A
It obeys Raoult's law, i.e. $${p_A} = {x_A}p_{\text{A}}^{\text{o}}$$ and $${p_B} = {x_B}p_B^{\text{o}}$$
B
$$\Delta {H_{{\text{mixing}}}}$$ is zero
C
$$\Delta {V_{{\text{mixing}}}}$$ is zero
D
It forms minimum boiling azeotrope.
Answer :
It forms minimum boiling azeotrope.
252. $$25.3\,g$$ of sodium carbonate, $$N{a_2}C{O_3}$$ is dissolved in enough water to make $$250\, mL$$ of solution. If sodium carbonate dissociates completely, molar concentration of sodium ion, $$N{a^ + }$$ and carbonate ion, $$CO_3^{2 - }$$ are respectively ( Molar mass of $$N{a_2}C{O_3} = 106\,g\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$ )
A
$$0.955\,M\,{\text{and}}\,1.910\,M$$
B
$$1.910\,M\,{\text{and}}\,0.955\,M$$
C
$$1.90\,M\,{\text{and}}\,1.910\,M$$
D
$$0.477\,M\,{\text{and}}\,0.477\,M$$
Answer :
$$1.910\,M\,{\text{and}}\,0.955\,M$$
253. The Henry's law constant for the solubility of $${N_2}$$ gas in water at $$298\,K$$ is $$1.0 \times {10^5}\,atm.$$ The mole fraction of $${N_2}$$ in air is $$0.8.$$ The number of moles of $${N_2}$$ from air dissolved in $$10\,moles$$ of water at $$298\,K$$ and $$5\,atm$$ pressure is
A
$$4.0 \times {10^{ - 4}}$$
B
$$4.0 \times {10^{ - 5}}$$
C
$$5.0 \times {10^{ - 4}}$$
D
$$4.0 \times {10^{ - 6}}$$
Answer :
$$4.0 \times {10^{ - 4}}$$
254. A solution has 1 : 4 $$mole$$ ratio of pentane to hexane. The vapour pressure of the pure hydrocarbons at $${20^ \circ }C$$ are $$440\,mm$$ of $$Hg$$ for pentane and $$120$$ $$mm$$ of $$Hg$$ for hexane. The mole fraction of pentane in the vapour phase would be
A
0.549
B
0.200
C
0.786
D
0.478
Answer :
0.478
255. What are the conditions for an ideal solution which obeys Raoult's law over the entire range of concentration ?
A
$${\Delta _{{\text{mix}}}}H = 0,{\Delta _{{\text{mix}}}}V = 0,$$ $${P_{{\text{Total}}}} = p_{\text{A}}^{\text{o}}{x_A} + p_B^{\text{o}}{x_B}$$
B
$${\Delta _{{\text{mix}}}}H = + ve,{\Delta _{{\text{mix}}}}V = 0,$$ $${P_{{\text{Total}}}} = p_{\text{A}}^{\text{o}}{x_A} + p_B^{\text{o}}{x_B}$$
C
$${\Delta _{{\text{mix}}}}H = 0,{\Delta _{{\text{mix}}}}V = + ve,$$ $${P_{{\text{Total}}}} = p_{\text{A}}^{\text{o}}{x_A} + p_B^{\text{o}}{x_B}$$
D
$${\Delta _{{\text{mix}}}}H = 0,{\Delta _{{\text{mix}}}}V = 0,{P_{{\text{Total}}}} = p_B^{\text{o}}{x_B}$$
Answer :
$${\Delta _{{\text{mix}}}}H = 0,{\Delta _{{\text{mix}}}}V = 0,$$ $${P_{{\text{Total}}}} = p_{\text{A}}^{\text{o}}{x_A} + p_B^{\text{o}}{x_B}$$
256. Sea water is $$3.5\% $$ by mass of common salt and has a density $$1.04\,g\,c{m^{ - 3}}$$ at $$293\,K.$$ Assuming the salt to be sodium chloride, then osmotic pressure of sea water will be ( assume complete ionisation of the salt )
A
$$25.45\,atm$$
B
$$11.56\,atm$$
C
$$29.98\,atm$$
D
$$30.20\,atm$$
Answer :
$$29.98\,atm$$
257. If $$0.1\,M$$ solution of glucose and $$0.1\,M$$ solution of urea are placed on two sides of the semipermeable membrane to equal heights, then it will be correct to say that
A
there will be no net movement across the membrane
B
glucose will flow towards urea solution
C
urea will flow towards glucose solution
D
water will flow from urea solution to glucose
Answer :
there will be no net movement across the membrane
258. For which of the following solutes the van't Hoff factor is not greater than one ?
A
$$NaN{O_3}$$
B
$$BaC{l_2}$$
C
$${K_4}\left[ {Fe{{\left( {CN} \right)}_6}} \right]$$
D
$$N{H_2}CON{H_2}$$
Answer :
$$N{H_2}CON{H_2}$$
259. The vapour pressure of two pure liquids $$A$$ and $$B$$ that form an ideal solution, are $$400$$ and $$800$$ $$mm$$ of $$Hg$$ respectively at a temperature $${t^ \circ }C.$$ The $$mole$$ fraction of $$A$$ in a solution of $$A$$ and $$B$$ whose boiling point is $${t^ \circ }C$$ will be
A
0.4
B
0.8
C
0.1
D
0.2
Answer :
0.1
260.
When acetone and chloroform are mixed together, which of the following observations is correct ?
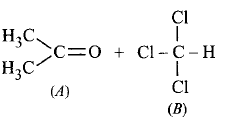
A
$$A - A$$ and $$B - B$$ interactions are stronger than $$A - B$$ interactions.
B
$$A - A$$ and $$B - B$$ interactions are weaker than $$A - B$$ interactions.
C
$$A - A, B - B$$ and $$A - B$$ interactions are equal.
D
The liquids form separate layers and are immiscible.
Answer :
$$A - A$$ and $$B - B$$ interactions are weaker than $$A - B$$ interactions.