1. Schottky defect in a crystal is observed when
A
an ion leaves its normal site and occupies an interstitial site
B
unequal number of cations and anions are missing from the lattice
C
density of the crystal is increased
D
equal number of cations and anions are missing from the lattice
Answer :
equal number of cations and anions are missing from the lattice
2. In a closed flask of $$5\,L,$$ $$1.0\,g$$ of $${H_2}$$ is heated from $$300$$ to $$600 K.$$ Which statement is not correct?
A
Pressure of the gas increases
B
The rate of collision increases
C
The number of moles of gas increases
D
The energy of gaseous molecules increases
Answer :
The number of moles of gas increases
3. If the ratio of masses of $$S{O_3}$$ and $${O_2}$$ gases confined in a vessel is 1 : 1, then the ratio of their partial pressures would be
A
5 : 2
B
2 : 5
C
2 : 1
D
1 : 2
Answer :
2 : 5
4.
Two vessels containing gases $$A$$ and $$B$$ are interconected as shown in the figure. The stopper is opened, the gases are allowed to mix
homogeneously. The partial pressures of $$A$$ and $$B$$ in the mixture will be, respectively
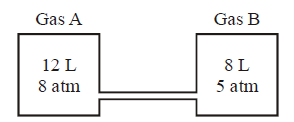
A
8 and 5 atm
B
9.6 and 4 atm
C
4.8 and 2 atm
D
6.4 and 4 atm
Answer :
4.8 and 2 atm
5. $$\alpha ,v$$ and $$u$$ represent most probable velocity, average velocity and root mean square velocity respectively of a gas at a particular temperature. The correct order among the following is
A
$$u > v > \alpha $$
B
$$v > u > \alpha $$
C
$$\alpha > u > v$$
D
$$u > \alpha > v$$
Answer :
$$u > v > \alpha $$
6. Pressure remaining the same, the volume of a given mass of an ideal gas increases for every degree centigrade rise in temperature by definite fraction of its volume at
A
$${0^ \circ }C$$
B
absolute zero
C
its critical temperature
D
its Boyle's temperature
Answer :
$${0^ \circ }C$$
7. A closed container contains equal number of moles of two gases $$X$$ and $$Y$$ at a total pressure of $$710\,mm$$ of $$Hg.$$ If gas $$X$$ is removed from the mixture, the pressure will
A
become double
B
become half
C
remain same
D
become one-fourth.
Answer :
become half
8. A liquid can exist only
A
between triple point and critical temperature
B
at any temperature above the melting point
C
between melting point and critical temperature
D
between boiling and melting temperature
Answer :
between boiling and melting temperature
9. The fraction of total volume occupied by the atoms present in a simple cube is
A
$$\frac{\pi }{6}$$
B
$$\frac{\pi }{{3\sqrt 2 }}$$
C
$$\frac{\pi }{{4\sqrt 2 }}$$
D
$$\frac{\pi }{4}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{\pi }{6}$$
10. The root mean square speeds at $$STP$$ for the gases $${H_2},{N_2},{O_2}$$ and $$HBr$$ are in the order
A
$${H_2} < {N_2} < {O_2} < HBr$$
B
$$HBr < {O_2} < {N_2} < {H_2}$$
C
$${H_2} < {N_2} = {O_2} < HBr$$
D
$$HBr < {O_2} < {H_2} < {N_2}$$
Answer :
$$HBr < {O_2} < {N_2} < {H_2}$$