111. What is the effect on chemical properties and physical properties of water when temperature is changed ?
A
Chemical properties of water remain same but the physical state changes with change in temperature.
B
Chemical properties of water change with change in temperature but physical properties remain same.
C
There is no effect on chemical or physical properties of water when temperature is changed.
D
Both chemical and physical properties of water change with change in temperature.
Answer :
Chemical properties of water remain same but the physical state changes with change in temperature.
112.
Lithium has a $$bcc$$ structure. Its density is $$530\,kg\,{m^{ - 3}}$$ and its atomic mass is $$6.94\,g\,mo{l^{ - 1}}.$$ Calculate the edge length of a unit cell of lithium metal.
$$\left( {{N_A} = 6.02 \times {{10}^{23}}mo{l^{ - 1}}} \right)$$
A
352$$\,pm$$
B
527$$\,pm$$
C
264$$\,pm$$
D
154$$\,pm$$
Answer :
352$$\,pm$$
113. The initial volume of a gas cylinder is $$750.0$$ $$mL.$$ If the pressure of gas inside the cylinder changes from $$840.0\,mm\,Hg$$ to $$360.0\,mm\,Hg,$$ the final volume the gas will be :
A
1.750$$\,L$$
B
3.60$$\,L$$
C
4.032$$\,L$$
D
7.50$$\,L$$
Answer :
1.750$$\,L$$
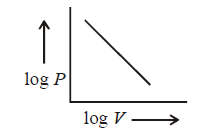
114. For $$1$$ $$mol$$ of an ideal gas at a constant temperature $$T,$$ the plot of $$log\,P$$ against $$log\,V$$ is a ( $$P$$ : Pressure, $$V$$ : Volume )
A
Straight line parallel to $$x$$ - axis.
B
Straight line with a negative slope.
C
Curve starting at origin.
D
Straight line passing through origin.
Answer :
Straight line with a negative slope.
115. Which of the following is not an assumption of the kinetic theory of gases?
A
Gas particles have negligible volume.
B
A gas consists of many identical particles which are in continual motion.
C
At high pressure, gas particles are difficult to compress.
D
Collisions of gas particles are perfectly elastic.
Answer :
At high pressure, gas particles are difficult to compress.
116. For an ideal gas, number of moles per litre in terms of its pressure, temperature and gas constant is
A
$$\frac{{PT}}{R}$$
B
$$\frac{P}{{RT}}$$
C
$$PRT$$
D
$$\frac{{RT}}{P}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{P}{{RT}}$$
117. A bottle of dry ammonia and a bottle of dry hydrogen chloride connected through a long tube are opened simultaneously at both ends the white ammonium chloride ring first formed will be
A
at the centre of the tube.
B
near the hydrogen chloride bottle.
C
near the ammonia bottle.
D
throughout the length of the tube.
Answer :
near the hydrogen chloride bottle.
118. The intermolecular interaction that is dependent on the inverse cube of distance between the molecules is :
A
London force
B
hydrogen bond
C
ion - ion interaction
D
ion - dipole interaction
Answer :
hydrogen bond
119. In a flask of volume $$V$$ litres, $$0.2\,mol$$ of oxygen, $$0.4\,mol$$ of nitrogen, $$0.1\,mol$$ of ammonia and $$0.3\,mol$$ of helium are enclosed at $$27{\,^ \circ }C.$$ If the total pressure exerted by these non-reacting gases is one atmosphere, then partial pressure exerted by nitrogen is
A
0.1 atmosphere
B
0.2 atmosphere
C
0.3 atmosphere
D
0.4 atmosphere
Answer :
0.4 atmosphere
120. If $$NaCl$$ is doped with $${10^{ - 4}}mol\,\,\% $$ of $$SrC{l_2},$$ the concentration of cation vacancies will be $$\left( {{N_A} = 6.023 \times {{10}^{23}}mo{l^{ - 1}}} \right)$$
A
$$6.023 \times {10^{15}}mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
B
$$6.023 \times {10^{16}}mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
C
$$6.023 \times {10^{17}}mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
D
$$6.023 \times {10^{14}}mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
Answer :
$$6.023 \times {10^{17}}mo{l^{ - 1}}$$