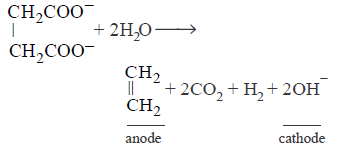71. The drain cleaner, Drainex contains small bits of aluminium which react with caustic soda to produce dihydrogen. What volume of dihydrogen at $$20{\,^ \circ }C$$ and one bar will be released when $$0.15\,g$$ of aluminium reacts ?
A
204$$\,mL$$
B
200$$\,mL$$
C
203$$\,mL$$
D
400$$\,mL$$
Answer :
203$$\,mL$$
72.
Study the following graph and mark the incorrect statement following it.
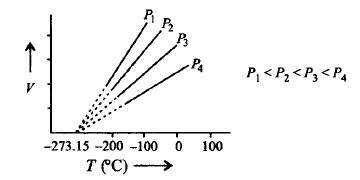
A
At zero volume all lines meet at $$ - 273.15{\,^ \circ }C.$$ This temperature is known as absolute zero.
B
Each line of the volume vs temperature at constant pressure of graph is called isotherm.
C
All gases obey Charles' law at very low pressure and high temperature.
D
Pressure remaining constant, volume of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature
Answer :
Each line of the volume vs temperature at constant pressure of graph is called isotherm.
73. The root mean square speed of $${N_2}$$ molecules in a gas is $$u.$$ If the temperature is doubled and the nitrogen molecules dissociate into nitrogen atoms, the root mean square speed becomes
A
$$\frac{u}{2}$$
B
$$2u$$
C
$$4u$$
D
$$14u$$
Answer :
$$2u$$
74. The correct statement regarding defects in the crystalline solid is
A
Schottky defects have no effect on the density of crystalline solids
B
Frenkel defects decreases the density of crystalline solids
C
Frenkel defect is a dislocation defect
D
Frenkel defect is found in halides of alkaline metals
Answer :
Frenkel defect is a dislocation defect
75. Oxidation of succinate ion produces ethylene and carbon dioxide gases. On passing $$0.2$$ Faraday electricity through an aqueous solution of potassium succinate, the total volume of gases ( at both cathode and anode ) at $$STP$$ (1 atm and $$273\,K$$ ) is :
A
8.96$$\,L$$
B
4.48$$\,L$$
C
6.72$$\,L$$
D
2.24$$\,L$$
Answer :
8.96$$\,L$$
76. According to kinetic theory of gases, the collisions between molecules of a gas
A
occur in a zig-zag path
B
occur in a straight line
C
change velocity and energy
D
result in settling down of molecules.
Answer :
occur in a straight line
77. Which gas shows real behaviour?
A
$$16\,g\,{O_2}$$ at $$1$$ $$atm$$ and $$273$$ $$K$$ occupies $$11.2$$ $$L$$
B
$$1\,g\,{H_2}$$ in $$0.5\,L$$ flask exerts pressure of $$24.63\,atm$$ at $$300\,K$$
C
$$1\,mole\,N{H_3}$$ at $$300\,K$$ and $$1\,atm$$ occupies volume $$22.4\,L$$
D
$$5.6\,L$$ of $$C{O_2}$$ at $$1\,atm$$ and $$273\,K$$ is equal to $$11\,g$$
Answer :
$$1\,mole\,N{H_3}$$ at $$300\,K$$ and $$1\,atm$$ occupies volume $$22.4\,L$$
78. Helium atom is two times heavier than a hydrogen molecule $$at.\,298\,K.$$ The average $$KE$$ of helium is
A
2 times of $${H_2}$$ molecule
B
same as that of $${H_2}$$ molecule
C
4 times that of hydrogen molecule
D
$$\frac{1}{2}$$ that of $${H_2}$$ molecule
Answer :
same as that of $${H_2}$$ molecule
79. Value of gas constant $$R$$ is
A
$$0.082\,{\text{litre}}\,{\text{atm}}$$
B
$$0.987\,cal\,mo{l^{ - 1}}{K^{ - 1}}$$
C
$$8.3\,J\,mo{l^{ - 1}}{K^{ - 1}}$$
D
$$83\,\,erg\,\,mo{l^{ - 1}}{K^{ - 1}}.$$
Answer :
$$8.3\,J\,mo{l^{ - 1}}{K^{ - 1}}$$
80. The appearance of colour in solid alkali metal halides is generally due to
A
$$F$$ - centres
B
Schottky defect
C
Frenkel defect
D
Interstitial positions
Answer :
$$F$$ - centres