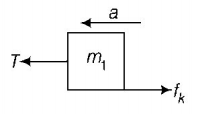
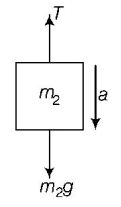
21. A block $$A$$ of mass $${m_1}$$ rests on a horizontal table. A light string connected to it passes over a frictionless pulley at the edge of table and from its other end another block $$B$$ of mass $${m_2}$$ is suspended. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the table is $${\mu _k}.$$ When the block $$A$$ is sliding on the table, the tension in the string is
A
$$\frac{{\left( {{m_2} + {\mu _k}{m_1}} \right)g}}{{\left( {{m_1} + {m_2}} \right)}}$$
B
$$\frac{{\left( {{m_2} - {\mu _k}{m_1}} \right)g}}{{\left( {{m_1} + {m_2}} \right)}}$$
C
$$\frac{{{m_1}{m_2}\left( {1 + {\mu _k}} \right)g}}{{\left( {{m_1} + {m_2}} \right)}}$$
D
$$\frac{{{m_1}{m_2}\left( {1 - {\mu _k}} \right)g}}{{\left( {{m_1} + {m_2}} \right)}}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{{{m_1}{m_2}\left( {1 + {\mu _k}} \right)g}}{{\left( {{m_1} + {m_2}} \right)}}$$
22. A small mass slides down a fixed inclined plane of inclination $$\theta $$ with the horizontal. The coefficient of friction is $$\mu = {\mu _0}x.$$ Where $$x$$ is the distance through which the mass slides down and $${\mu _0}$$ is a constant. Then the speed is maximum after the mass covers a distance of
A
$$\frac{{\cos \theta }}{{{\mu _0}}}$$
B
$$\frac{{\sin \theta }}{{{\mu _0}}}$$
C
$$\frac{{\tan \theta }}{{{\mu _0}}}$$
D
$$\frac{{2\tan \theta }}{{{\mu _0}}}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{{\tan \theta }}{{{\mu _0}}}$$
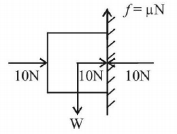
23.
What is the maximum value of the force $$F$$ such that the block shown in the arrangement, does not move?
A
$$20\,N$$
B
$$10\,N$$
C
$$12\,N$$
D
$$15\,N$$
Answer :
$$20\,N$$
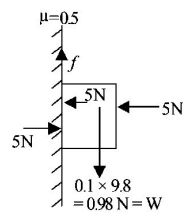
24. A block of mass 0.1 is held against a wall applying a horizontal force of $$5N$$ on the block. If the coefficient of friction between the block and the wall is 0.5, the magnitude of the frictional force acting on the block is :
A
$$2.5N$$
B
$$0.98N$$
C
$$4.9N$$
D
$$0.49N$$
Answer :
$$0.98N$$
25. A block of mass $$m$$ is placed on a surface with a vertical cross section given by $$y = \frac{{{x^3}}}{6}.$$ If the coefficient of friction is 0.5, the maximum height above the ground at which the block can be placed without slipping is:
A
$$\frac{1}{6}m$$
B
$$\frac{2}{3}m$$
C
$$\frac{1}{3}m$$
D
$$\frac{1}{2}m$$
Answer :
$$\frac{1}{6}m$$
26. A block of mass $$10\,kg$$ is placed on a rough horizontal surface having coefficient of friction $$\mu = 0.5.$$ If a horizontal force of $$100\,N$$ is applied on it, then the acceleration of the block will be (Take $$g = 10\,m/{s^2}$$ )
A
$$15\,m/{s^2}$$
B
$$10\,m/{s^2}$$
C
$$5\,m/{s^2}$$
D
$$0.5\,m/{s^2}$$
Answer :
$$5\,m/{s^2}$$
27. The force required to just move a body up the inclined plane is double the force required to just prevent the body from sliding down the plane. The coefficient of friction is $$\mu .$$ The inclination $$\theta $$ of the plane is
A
$${\tan ^{ - 1}}\mu $$
B
$${\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\frac{\mu }{2}} \right)$$
C
$${\tan ^{ - 1}}2\mu $$
D
$${\tan ^{ - 1}}3\mu $$
Answer :
$${\tan ^{ - 1}}3\mu $$
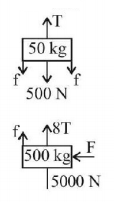
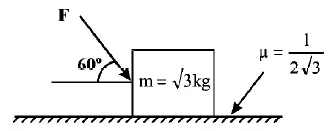
28.
If the coefficient of friction between all surfaces is $$0.5,$$ then find the minimum force $$F$$ to have equilibrium of system. (assume strings and pulleys are massless)

A
$$\frac{{4000}}{{17}}N$$
B
$$\frac{{1000}}{{17}}N$$
C
$$\frac{{2000}}{{17}}N$$
D
$$\frac{{500}}{{17}}N$$
Answer :
$$\frac{{2000}}{{17}}N$$
29. Consider, a car moving along a straight horizontal road with a speed of $$72\,km/h.$$ If the coefficient of static friction between the tyres and the road is 0.5, the shortest distance in which the car can be stopped is (Take $$g = 10\,m/{s^2}$$ )
A
$$30\,m$$
B
$$40\,m$$
C
$$72\,m$$
D
$$20\,m$$
Answer :
$$40\,m$$
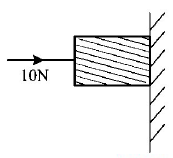
30.
A horizontal force of $$10N$$ is necessary to just hold a block stationary against a wall. The coefficient of friction between the block and the wall is 0.2. The weight of the block is
A
$$20N$$
B
$$50N$$
C
$$100N$$
D
$$2N$$
Answer :
$$2N$$