91. An electron is accelerated through a potential difference of $$V$$ volt. It has a wavelength $$\lambda $$ associated with it. Through what potential difference an electron must be accelerated so that its de Broglie wavelength is the same as that of a proton? Take mass of proton to be 1837 times larger than the mass of electron.
A
$$V\,volt$$
B
$$1837\,V\,volt$$
C
$$\frac{V}{{1837}}volt$$
D
$$\sqrt {1837} \,V\,volt$$
Answer :
$$\frac{V}{{1837}}volt$$
92. A photoelectric cell is illuminated by a point source of light $$1\,m$$ away. When the source is shifted to $$2\,m$$ then
A
number of electrons emitted is a quarter of the initial number
B
each emitted electron carries one quarter of the initial energy
C
number of electrons emitted is half the initial number
D
each emitted electron carries half the initial energy
Answer :
number of electrons emitted is a quarter of the initial number
93. The following particles are moving with the same velocity, then maximum de-Broglie wavelength will be for
A
proton
B
$$\alpha $$-particle
C
neutron
D
$$\beta $$-particle
Answer :
$$\beta $$-particle
94.
A photoelectric surface is illuminated successively by monochromatic light of wavelength $$\lambda $$ and $$\frac{\lambda }{2}.$$ If the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons in the second case is 3 times that in the first case, the work function of the surface of the material is
($$h$$ = Planck’s constant, $$c$$ = speed of light)
A
$$\frac{{hc}}{{2\lambda }}$$
B
$$\frac{{hc}}{\lambda }$$
C
$$\frac{{2hc}}{\lambda }$$
D
$$\frac{{hc}}{{3\lambda }}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{{hc}}{{2\lambda }}$$
95. Which of the following figures represents the variation of particle momentum and the associated de-Broglie wavelength?
A


B
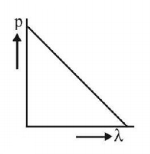

C


D


Answer :


96. A proton has kinetic energy $$E = 100\,keV$$ which is equal to that of a photon. The wavelength of photon is $${\lambda _2}$$ and that of proton is $${\lambda _1}.$$ The ration of $$\frac{{{\lambda _2}}}{{{\lambda _1}}}$$ is proportional to
A
$${E^2}$$
B
$${E^{\frac{1}{2}}}$$
C
$${E^{ - 1}}$$
D
$${E^{ - \frac{1}{2}}}$$
Answer :
$${E^{ - \frac{1}{2}}}$$
97. An atom emits a photon of wavelength $$\lambda = 600\,nm$$ by transition from an excited state of life time $$8 \times {10^{ - 9}}s.$$ If $${\Delta v}$$ represents the minimum uncertainty in the frequency of the photon, the fractional width $$\frac{{\Delta v}}{v}$$ of the spectral line is of the order of
A
$${10^{ - 4}}$$
B
$${10^{ - 6}}$$
C
$${10^{ - 8}}$$
D
$${10^{ - 10}}$$
Answer :
$${10^{ - 6}}$$
98. When the minimum wavelength of X-rays is $$2\mathop {\text{A}}\limits^ \circ $$ then the applied potential difference between cathode and anticathode will be
A
$$6.2\,kV$$
B
$$2.48\,kV$$
C
$$24.8\,kV$$
D
$$62\,kV$$
Answer :
$$6.2\,kV$$
99. The ratio of energies of X-rays of the wavelength $$0.01\,\mathop {\text{A}}\limits^ \circ $$ and $$0.5\,\mathop {\text{A}}\limits^ \circ $$ will be
A
$$1:1$$
B
$$1:2$$
C
$$1:5$$
D
$$50:1$$
Answer :
$$50:1$$
100. Gases begin to conduct electricity at low pressure, because
A
at low pressures gases turn to plasma
B
colliding electrons can acquire higher kinetic energy due to increased mean free path leading to ionisation of atoms
C
atoms break up into electrons and protons
D
the electrons in atoms can move freely at low pressures
Answer :
colliding electrons can acquire higher kinetic energy due to increased mean free path leading to ionisation of atoms