191. A microscope is focussed on a mark on a piece of paper and then a slab of glass of thickness $$3\,cm$$ and refractive index 1.5 is placed over the mark. How should the microscope be moved to get the mark in focus again ?
A
$$1\,cm$$ upward
B
$$4.5\,cm$$ downward
C
$$1\,cm$$ downward
D
$$2\,cm$$ upward
Answer :
$$1\,cm$$ upward
192. A luminous object and a screen are at a fixed distance $$D$$ apart. A converging lens of focal length $$f$$ is placed between the object and screen. A real image of the object in formed on the screen for two lens positions of they are separated by a distance $$d$$ equal to
A
$$\sqrt {D\left( {D + 4f} \right)} $$
B
$$\sqrt {D\left( {D - 4f} \right)} $$
C
$$\sqrt {2D\left( {D - 4f} \right)} $$
D
$$\sqrt {{D^2} + 4f} $$
Answer :
$$\sqrt {D\left( {D - 4f} \right)} $$
193.
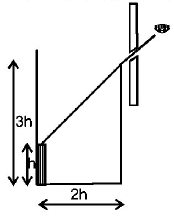
An observer can see through a pin - hole the top end of a thin rod of height h, placed as shown in the figure. The beaker height is $$3\,h$$ and its radius $$h.$$ When the beaker is filled with a liquid up to a height $$2\,h,$$ he can see the lower end of the rod. Then the refractive index of the liquid is
A
$$\frac{5}{2}$$
B
$$\sqrt {\frac{5}{2}} $$
C
$$\sqrt {\frac{3}{2}} $$
D
$$\frac{3}{2}$$
Answer :
$$\sqrt {\frac{5}{2}} $$
194. An electromagnetic wave of frequency $$v = 3.0\,MHz$$ passes from vacuum into a dielectric medium with permittivity $$ \in = 4.0\,.$$ Then
A
wave length is halved and frequency remains unchanged
B
wave length is doubled and frequency becomes half
C
wave length is doubled and the frequency remains unchanged
D
wave length and frequency both remain unchanged.
Answer :
wave length is halved and frequency remains unchanged
195.
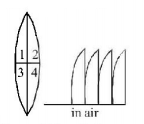
The given lens is broken into four parts and rearranged as shown. If the initial focal length is $$f$$ then after rearrangement the equivalent focal length is -
A
$$f$$
B
$$\frac{f}{2}$$
C
$$\frac{f}{4}$$
D
$$4f$$
Answer :
$$\frac{f}{2}$$
196. A beam of light composed of red and green rays is incident obliquely at a point on the face of a rectangular glass slab. When coming out on the opposite parallel face, the red and green rays emerge from
A
two points propagating in two different non-parallel directions
B
two points propagating in two different parallel directions
C
one point propagating in two different directions
D
one point propagating in the same direction
Answer :
two points propagating in two different parallel directions
197. If $${f_V}$$ and $${f_R}$$ are the focal lengths of a convex lens for violet and red light respectively and $${F_V}$$ and $${F_R}$$ are the focal lengths of concave lens for violet and red light respectively, then we have
A
$${f_V} < {f_R}\,\,{\text{and}}\,\,{F_V} > {F_R}$$
B
$${f_V} < {f_R}\,\,{\text{and}}\,\,{F_V} < {F_R}$$
C
$${f_V} > {f_R}\,\,{\text{and}}\,\,{F_V} > {F_R}$$
D
$${f_V} > {f_R}\,\,{\text{and}}\,\,{F_V} < {F_R}$$
Answer :
$${f_V} < {f_R}\,\,{\text{and}}\,\,{F_V} > {F_R}$$
198. A thin prism having refracting angle $${10^ \circ }$$ is made of glass of refractive index 1.42. This prism is combined with another thin prism of glass of refractive index 1.7. This combination produces dispersion without deviation. The refracting angle of second prism should be
A
$${4^ \circ }$$
B
$${6^ \circ }$$
C
$${8^ \circ }$$
D
$${10^ \circ }$$
Answer :
$${6^ \circ }$$
199. A ray of light is incident at $${50^ \circ }$$ on the middle of one of the two plane mirrors arranged at an angle of $${60^ \circ }$$ between them. The ray then touches the second mirror, get reflected back to the first mirror, making an angle of incidence of
A
$${50^ \circ }$$
B
$${60^ \circ }$$
C
$${70^ \circ }$$
D
$${80^ \circ }$$
Answer :
$${70^ \circ }$$
200. Which of the following phenomenon is not explained by Huygen’s construction of wavefront ?
A
Refraction
B
Reflection
C
Diffraction
D
Origin of spectra
Answer :
Origin of spectra

