221. A telescope has an objective lens of focal length $$150\,cm$$ and an eyepiece of focal length $$5\,cm.$$ If a $$50\,m$$ tall tower at a distance of $$1\,km$$ is observed through this telescope in normal setting, the angle formed by the image of the tower is $$\theta ,$$ then $$\theta $$ is close to:
A
$$6.1\,rad$$
B
$$3.2\,rad$$
C
$$1.5\,rad$$
D
$$0.2\,rad$$
Answer :
$$1.5\,rad$$
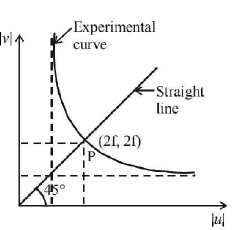
222. In an optics experiment, with the position of the object fixed, a student varies the position of a convex lens and for each position, the screen is adjusted to get a clear image of the object. A graph between the object distance $$u$$ and the image distance $$v,$$ from the lens, is plotted using the same scale for the two axes. A straight line passing through the origin and making an angle of 45° with the $$x$$ - axis meets the experimental curve at $$P.$$ The coordinates of $$P$$ will be:
A
$$\left( {\frac{f}{2},\frac{f}{2}} \right)$$
B
$$\left( {f,f} \right)$$
C
$$\left( {4\,f, 4\,f} \right)$$
D
$$\left( {2\,f, 2\,f} \right)$$
Answer :
$$\left( {2\,f, 2\,f} \right)$$
223. A convex lens is in contact with concave lens. The magnitude of the ratio of their focal length is $$\frac{2}{3}.$$ Their equivalent focal length is $$30\,cm.$$ What are their individual focal lengths?
A
$$- 15,10$$
B
$$- 10, 15$$
C
$$75, 50$$
D
$$- 75, 50$$
Answer :
$$- 15,10$$
224. The image of an illuminated square is obtained on a screen with the help of a converging lens. The distance of the square from the lens is $$40\,cm.$$ The area of the image is 9 times that of the square. The focal length of the lens is :
A
$$36\,cm$$
B
$$27\,cm$$
C
$$60\,cm$$
D
$$30\,cm$$
Answer :
$$30\,cm$$
225. Which of the following is used in optical fibres?
A
total internal reflection
B
scattering
C
diffraction
D
refraction
Answer :
total internal reflection
226. A transparent cube contains a small air bubble. Its apparent distance is $$2\,cm$$ when seen through one face and $$5\,cm$$ when seen through other face. If the refractive index of the material of the cube is $$1.5,$$ the real length of the edge of cube must be
A
$$7\,cm$$
B
$$7.5\,cm$$
C
$$10.5\,cm$$
D
$$\frac{{14}}{3}cm$$
Answer :
$$10.5\,cm$$