21. If the focal length of objective lens is increased, then magnifying power of
A
microscope will increase but that of telescope decrease
B
microscope and telescope both will increase
C
microscope and telescope both will decrease
D
microscope will decrease but that of telescope will increase
Answer :
microscope will decrease but that of telescope will increase
22.
An observer can see through a pin-hole the top end of a thin rod of height $$h,$$ placed as shown in the figure. The beaker height is $$3h$$ and its radius $$h.$$ When the beaker is filled with a liquid up to a height $$2h,$$ he can see the lower end of the rod. Then the refractive index of the liquid is

A
$$\frac{5}{2}$$
B
$$\sqrt {\frac{5}{2}} $$
C
$$\sqrt {\frac{3}{2}} $$
D
$$\frac{3}{2}$$
Answer :
$$\sqrt {\frac{5}{2}} $$
23. Two beams of red and violet colours are made to pass separately through a prism (angle of the prism is 60°). In the position of minimum deviation, the angle of refraction will be
A
30° for both the colours
B
greater for the violet colour
C
greater for the red colour
D
equal but not 30° for both the colours
Answer :
30° for both the colours
24. Two slits in Youngs experiment have widths in the ratio $$1:25.$$ The ratio of intensity at the maxima and minima in the interference pattern $$\frac{{{I_{\max }}}}{{{I_{\min }}}}$$ is
A
$$\frac{9}{4}$$
B
$$\frac{{121}}{{49}}$$
C
$$\frac{{49}}{{121}}$$
D
$$\frac{4}{9}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{9}{4}$$
25. For a parallel beam of monochromatic light of wavelength $$'\lambda '$$ diffraction is produced by a single slit whose width $$'a'$$ is of the order of the wavelength of the light. If $$'D'$$ is the distance of the screen from the slit, the width of the central maxima will be
A
$$\frac{{2D\lambda }}{a}$$
B
$$\frac{{D\lambda }}{a}$$
C
$$\frac{{Da}}{\lambda }$$
D
$$\frac{{2Da}}{\lambda }$$
Answer :
$$\frac{{2D\lambda }}{a}$$
26.
A diverging beam of light from a point source $$S$$ having divergence angle $$\alpha ,$$ falls symmetrically on a glass slab as shown. The angles of incidence of the two extreme rays are equal. If the thickness of the glass slab is $$t$$ and the refractive index $$n,$$ then the divergence angle of the emergent beam is
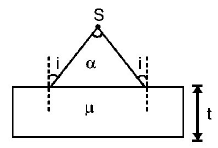
A
zero
B
$$\alpha$$
C
$${\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\frac{1}{n}} \right)$$
D
$$2\,{\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\frac{1}{n}} \right)$$
Answer :
$$\alpha$$
27. A beam of white light is incident on glass air interface from glass to air such that green light just suffers total internal reflection. The colors of the light which will come out to air are
A
Violet, Indigo, Blue
B
All colors except green
C
Yellow, Orange, Red
D
White light
Answer :
Yellow, Orange, Red
28. An observer looks at a distant tree of height $$10\,m$$ with a telescope of magnifying power of 20. To the observer the tree appears:
A
20 times taller
B
20 times nearer
C
10 times taller
D
10 times nearer
Answer :
20 times nearer
29. In Young’s double slit experiment, the slits are $$2\,mm$$ apart and are illuminated by photons of two wavelengths $${\lambda _1} = 12000\,\mathop {\text{A}}\limits^ \circ $$ and $${\lambda _2} = 10000\,\mathop {\text{A}}\limits^ \circ .$$ At what minimum distance from the common central bright fringe on the screen $$2m$$ from the slit will a bright fringe from one interference pattern coincide with a bright fringe from the other?
A
$$8\,mm$$
B
$$6\,mm$$
C
$$4\,mm$$
D
$$3\,mm$$
Answer :
$$6\,mm$$
30. A point object is kept in front of a plane mirror. The plane mirror is doing SHM of amplitude $$2\,cm.$$ The plane mirror moves along the $$x$$-axis which is normal to the mirror. The amplitude of the mirror is such that the object is always in front of the mirror. The amplitude of SHM of the image is
A
0
B
$$2\,cm$$
C
$$4\,cm$$
D
$$1\,cm$$
Answer :
$$4\,cm$$