31.
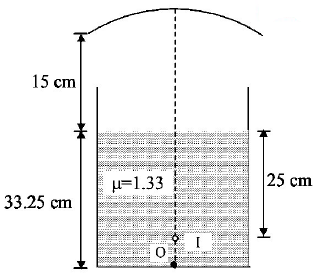
A container is filled with water $$\left( {\mu = 1.33} \right)$$ upto a height of $$33.25\,cm.$$ A concave mirror is placed $$15\,cm$$ above the water level and the image of an object placed at the bottom is formed $$25\,cm$$ below the water level. Focal length of the mirror is
A
$$15\,cm$$
B
$$20\,cm$$
C
$$ - 18.31\,cm$$
D
$$10\,cm$$
Answer :
$$ - 18.31\,cm$$
32. Pick out the longest wavelength from the following types of radiations
A
blue light
B
gamma rays
C
X-rays
D
red light
Answer :
red light
33. At the first minimum adjacent to the central maximum of a single slit diffraction pattern, the phase difference between the Huygen’s wavelet from the edge of the slit and the wavelet from the midpoint of the slit is
A
$$\frac{\pi }{4}\,{\text{radian}}$$
B
$$\frac{\pi }{2}\,{\text{radian}}$$
C
$$\pi \,{\text{radian}}$$
D
$$\frac{\pi }{8}\,{\text{radian}}$$
Answer :
$$\pi \,{\text{radian}}$$
34. A diver looking up through the water sees the outside world contained in a circular horizon. The refractive index of water is $$\frac{4}{3},$$ and the diver’s eyes are $$15\,cm$$ below the surface of water. Then the radius of the circle is :
A
$$15 \times 3 \times \sqrt 5 \,cm$$
B
$$15 \times 3\sqrt 7 \,cm$$
C
$$\frac{{15 \times \sqrt 7 }}{3}\,cm$$
D
$$\frac{{15 \times 3}}{{\sqrt 7 }}\,cm$$
Answer :
$$\frac{{15 \times 3}}{{\sqrt 7 }}\,cm$$
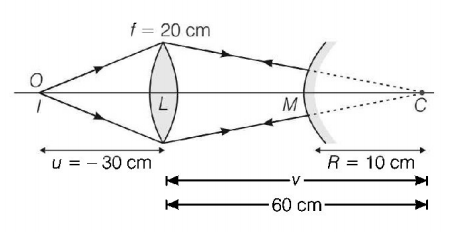
35. A luminous object is placed at a distance of $$30\,cm$$ from the convex lens of focal length $$20\,cm.$$ On the other side of the lens, at what distance from the lens, a convex mirror of radius of curvature $$10\,cm,$$ be placed in order to have an upright image of the object coincident with it ?
A
$$12\,cm$$
B
$$30\,cm$$
C
$$50\,cm$$
D
$$60\,cm$$
Answer :
$$50\,cm$$
36. The angular resolution of a $$10\,cm$$ diameter telescope at a wavelength of $$5000\,\mathop {\text{A}}\limits^ \circ $$ is of the order of
A
$${10^6}\,rad$$
B
$${10^{ - 2}}\,rad$$
C
$${10^{ - 4}}\,rad$$
D
$${10^{ - 6}}\,rad$$
Answer :
$${10^{ - 6}}\,rad$$
37. In an experiment for determination of refractive index of glass of a prism by $$i - \delta ,$$ plot it was found that a ray incident at angle 35°, suffers a deviation of 40° and that it emerges at angle 79°. In that case which of the following is closest to the maximum possible value of the refractive index?
A
1.7
B
1.8
C
1.5
D
1.6
Answer :
1.5
38. In a compound microscope, the intermediate image is
A
virtual, erect and magnified
B
real, erect and magnified
C
real, inverted and magnified
D
virtual, erect and reduced
Answer :
real, inverted and magnified
39. In an experiment to determine the focal length $$(f)$$ of a concave mirror by the $$u - v$$ method, a student places the object pin $$A$$ on the principal axis at a distance $$x$$ from the pole $$P.$$ The student looks at the pin and its inverted image from a distance keeping his/her eye in line with $$PA.$$ When the student shifts his/her eye towards left, the image appears to the right of the object pin. Then,
A
$$x < f$$
B
$$f < x < 2\,f$$
C
$$x = 2\,f$$
D
$$x > 2\,f$$
Answer :
$$f < x < 2\,f$$
40. When a biconvex lens of glass having refractive index 1.47 is dipped in a liquid, it acts as a plane sheet of glass. This implies that the liquid must have refractive index
A
equal to that of glass
B
less than one
C
greater than that of glass
D
less than that of glass
Answer :
equal to that of glass