11.
The angular width of the central maximum in a single slit diffraction pattern is 60°. The width of the slit is $$1\,\mu m.$$ The slit is illuminated by monochromatic plane waves. If another slit of same width is made near it, Young's fringes can be observed on a screen placed at a distance $$50\,cm$$ from the slits. If the observed fringe width is $$1\,cm,$$ what is slit separation distance?
(i.e. distance between the centres of each slit.)
A
$$25\,\mu m$$
B
$$50\,\mu m$$
C
$$75\,\mu m$$
D
$$100\,\mu m$$
Answer :
$$25\,\mu m$$
12. Unpolarised light is incident on a dielectric of refractive index $$\sqrt 3 .$$ What is the angle of incidence if the reflected beam is completely polarised?
A
$${30^ \circ }$$
B
$${45^ \circ }$$
C
$${60^ \circ }$$
D
$${75^ \circ }$$
Answer :
$${60^ \circ }$$
13.
A thin slice is cut out of a glass cylinder along a plane parallel to its axis. The slice is placed on a flat glass plate as shown in Figure.
The observed interference fringes from this combination shall be

A
straight
B
circular
C
equally spaced
D
having fringe spacing which increases as we go outwards
Answer :
straight
14. In the Young’s double slit experiment using a monochromatic light of wavelength $$\lambda ,$$ the path difference (in terms of an integer $$n$$) corresponding to any point having half the peak intensity is
A
$$\left( {2\,n + 1} \right)\frac{\lambda }{2}$$
B
$$\left( {2\,n + 1} \right)\frac{\lambda }{4}$$
C
$$\left( {2\,n + 1} \right)\frac{\lambda }{8}$$
D
$$\left( {2\,n + 1} \right)\frac{\lambda }{16}$$
Answer :
$$\left( {2\,n + 1} \right)\frac{\lambda }{4}$$
15. In a Young’s double slit experiment, if the incident light consists of two wavelengths $${\lambda _1}$$ and $${\lambda _2},$$ the slit separation is $$d,$$ and the distance between the slit and the screen is $$D,$$ the maxima due to the two wavelengths will coincide at a distance from the central maxima, given by :
A
$$\frac{{{\lambda _1}{\lambda _2}}}{{2\,Dd}}$$
B
$$\left( {{\lambda _1} - {\lambda _2}} \right).\frac{{2d}}{D}$$
C
$$LCM\,{\text{of}}\,{\lambda _1}.\frac{D}{d}\,\,{\text{and}}\,\,{\lambda _2}.\frac{D}{d}$$
D
$$HCF\,{\text{of}}\,\frac{{{\lambda _1}D}}{d}\,\,{\text{and}}\,\,\frac{{{\lambda _2}D}}{d}$$
Answer :
$$LCM\,{\text{of}}\,{\lambda _1}.\frac{D}{d}\,\,{\text{and}}\,\,{\lambda _2}.\frac{D}{d}$$
16. A source emits sound of frequency $$600\,Hz$$ inside water. The frequency heard in air will be equal to (velocity of sound in water = $$1500\,m/s,$$ velocity of sound in air = $$300\,m/s$$ )
A
$$3000\,Hz$$
B
$$120\,Hz$$
C
$$600\,Hz$$
D
$$6000\,Hz$$
Answer :
$$600\,Hz$$
17. A beam of monochromatic light is refracted from vacuum into a medium of refractive index $$1.5.$$ The wavelength of refracted light will be
A
dependent on intensity of refracted light
B
same
C
smaller
D
larger
Answer :
smaller
18. The angle of polarisation for any medium is $${60^ \circ }.$$ The critical angle for this is
A
$${\sin ^{ - 1}}\frac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$$
B
$${\cos ^{ - 1}}\sqrt 3 $$
C
$${\sin ^{ - 1}}\sqrt 3 $$
D
$${\tan ^{ - 1}}\sqrt 3 $$
Answer :
$${\sin ^{ - 1}}\frac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$$
19. Monochromatic light of wavelength $$400\,nm$$ and $$560\,nm$$ are incident simultaneously and normally on double slits apparatus whose slits separation is $$0.1\,mm$$ and screen distance is $$1m.$$ Distance between areas of total darkness will be
A
$$4\,mm$$
B
$$5.6\,mm$$
C
$$14\,mm$$
D
$$28\,mm$$
Answer :
$$28\,mm$$
20. In a $$YDSE$$ experiment if a slab whose refraction index can be varied is placed in front of one of the slits then the variation of resultant intensity at midpoint of screen with $$'\mu '$$ will be best represented by $$\left( {\mu \geqslant 1} \right).$$ [Assume slits of equal width and there is no absorption by slab; mid point of screen is the point where waves interfere with zero phase difference in absence of slab]
A


B


C


D
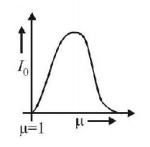

Answer :

