191. Amongst the elements with following electronic configurations, which one may have the highest ionisation energy?
A
$$\left[ {Ne} \right]3{s^2}3{p^3}$$
B
$$\left[ {Ne} \right]3{s^2}3{p^2}$$
C
$$\left[ {Ar} \right]3{d^{10}},4{s^2}4{p^3}$$
D
$$\left[ {Ne} \right]3{s^2}3{p^1}$$
Answer :
$$\left[ {Ne} \right]3{s^2}3{p^3}$$
192. An element $$X$$ has atomic number 19. What will be the formula of its oxide?
A
$${X_2}O$$
B
$$XO$$
C
$$X{O_2}$$
D
$${X_2}{O_3}$$
Answer :
$${X_2}O$$
193. The correct order of decreasing second ionisation enthalpy of $$Ti(22), V(23), Cr(24)$$ and $$Mn(25)$$ is
A
$$Cr > Mn > V > Ti$$
B
$$V > Mn > Cr > Ti$$
C
$$Mn > Cr > Ti > V$$
D
$$Ti > V > Cr > Mn$$
Answer :
$$Cr > Mn > V > Ti$$
194. Which of the following statements regarding an anion is not true?
A
The gain of an electron leads to the formation of an anion.
B
The radius of the anion is larger than the atomic radius of its parent atom.
C
The effective nuclear charge increases when an anion is formed.
D
Electron cloud expands due to increased repulsion among the electrons.
Answer :
The effective nuclear charge increases when an anion is formed.
195. Amongst $${H_2}O,{H_2}S,{H_2}Se\,\,{\text{and}}\,\,{H_2}Te,$$ the one with the highest boiling point is
A
$${H_2}O$$ because of hydrogen bonding
B
$$\,{H_2}Te$$ because of higher molecular weight
C
$${H_2}S$$ because of hydrogen bonding
D
$${H_2}Se$$ because of lower molecular weight
Answer :
$${H_2}O$$ because of hydrogen bonding
196. In which of the following arrangements, the order is not according to the property indicated against it?
A
$$A{l^{3 + }} < M{g^{2 + }} < N{a^ + } < {F^ - }: $$ Ionic size
B
$$B < C < N < O:$$ First ionization enthalpy
C
$$I < Br < F < Cl:$$ Electron gain enthalpy with negative sign
D
$$Li < Na < K < Rb:$$ Metallic radius
Answer :
$$B < C < N < O:$$ First ionization enthalpy
197. Which of the following order is wrong?
A
$$N{H_3} < P{H_3} < As{H_3} - $$ Acidic
B
$$Li < Be < B < C - $$ 1st Ionisation potential
C
$$A{l_2}{O_3} < MgO < N{a_2}O < {K_2}O - $$ Basic
D
$$L{i^ + } < N{a^ + } < {K^ + } < C{s^ + } - $$ Ionic radius
Answer :
$$Li < Be < B < C - $$ 1st Ionisation potential
198. The correct order of acidic strength :
A
$$C{l_2}{O_7} > S{O_2} > {P_4}{O_{10}}$$
B
$${K_2}O > CaO > MgO$$
C
$$C{O_2} > {N_2}{O_5} > S{O_3}$$
D
$$N{a_2}O > MgO > A{l_2}{O_3}$$
Answer :
$$C{l_2}{O_7} > S{O_2} > {P_4}{O_{10}}$$
199. Ionization energies of atoms $$A$$ and $$B$$ are $$400$$ and $$300\,k\,cal\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$ respectively. The electron affinities of these atoms are $$80.0$$ and $$85.0\,k\,cal\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$ respectively. Then which is the correct statement regarding electronegativity $$\chi ?$$
A
$${\chi _A} < {\chi _B}$$
B
$${\chi _A} > {\chi _B}$$
C
$${\chi _A} = {\chi _B}$$
D
$${\text{none of these}}$$
Answer :
$${\chi _A} > {\chi _B}$$
200. Which one of the following is an amphoteric oxide ?
A
$$N{a_2}O$$
B
$$S{O_2}$$
C
$${B_2}{O_3}$$
D
$$ZnO$$
Answer :
$$ZnO$$
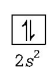 Stable configuration ( due to fully- filled orbital )
Stable configuration ( due to fully- filled orbital ) 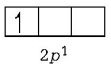 Unstable configuration
Unstable configuration