241. Which of the following sets of examples and geometry of the compounds is not correct?
A
Octahedral $$ - {\left[ {Co{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3 + }},{\left[ {Fe{{\left( {CN} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3 - }}$$
B
Square planar $$ - {\left[ {Ni{{\left( {CN} \right)}_4}} \right]^{2\_}},{\left[ {Cu{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_4}} \right]^{2 + }}$$
C
Tetrahedral $$ - \left[ {Ni{{\left( {CO} \right)}_4}} \right],{\left[ {ZnC{l_4}} \right]^{2 - }}$$
D
Trigonal bipyramidal $$ - {\left[ {Fe{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_6}} \right]^{2 + }},{\left[ {CuC{l_4}} \right]^{2 - }}$$
Answer :
Trigonal bipyramidal $$ - {\left[ {Fe{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_6}} \right]^{2 + }},{\left[ {CuC{l_4}} \right]^{2 - }}$$
242. The oxidation states of $$Cr$$ in $$\left[ {Cr{{\left( {{H_2}O} \right)}_6}} \right]C{l_3},\left[ {Cr{{\left( {{C_6}{H_6}} \right)}_2}} \right]$$ and $${K_2}\left[ {Cr{{\left( {CN} \right)}_2}{{\left( O \right)}_2}{{\left( O \right)}_2}\left( {N{H_3}} \right)} \right]$$ respectively are :
A
$$ + 3, + 4,\,{\text{and}}\, + 6$$
B
$$ + 3, + 2,\,{\text{and}}\, + 4$$
C
$$ + 3,0,\,{\text{and}}\, + 6$$
D
$$ + 3,0,\,{\text{and}}\, + 4$$
Answer :
$$ + 3,0,\,{\text{and}}\, + 6$$
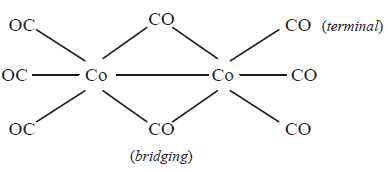
243. $$\left[ {C{o_2}{{\left( {CO} \right)}_8}} \right]$$ displays :
A
one $$Co – Co$$ bond, six terminal $$CO$$ and two bridging $$CO$$
B
one $$Co – Co$$ bond, four terminal $$CO$$ and four bridging $$CO$$
C
no $$Co – Co$$ bond, six terminal $$CO$$ and two bridging $$CO$$
D
no $$Co – Co$$ bond, four terminal $$CO$$ and four bridging $$CO$$
Answer :
one $$Co – Co$$ bond, six terminal $$CO$$ and two bridging $$CO$$
244. The name of complex ion, $${\left[ {Fe{{\left( {CN} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3 - }}$$ is
A
hexacyanoiron (III) ion
B
hexacyanitoferrate (III) ion
C
tricyanoferrate (III) ion
D
hexacyanidoferrate (III) ion
Answer :
hexacyanidoferrate (III) ion
245. Which one of the following octahedral complexes will not show geometrical isomerism? ( $$A$$ and $$B$$ are monodentate ligands )
A
$$\left[ {M{A_4}{B_2}} \right]$$
B
$$\left[ {M{A_5}B} \right]$$
C
$$\left[ {M{A_2}{B_4}} \right]$$
D
$$\left[ {M{A_3}{B_3}} \right]$$
Answer :
$$\left[ {M{A_5}B} \right]$$
246. The degenerate orbitals of $${\left[ {Cr{{\left( {{H_2}O} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3 + }}\,{\text{are:}}$$
A
$${d_{xz}}\,{\text{and}}\,{d_{yz}}$$
B
$${d_{yz}}\,{\text{and}}\,{d_{{z^2}}}$$
C
$${d_{{z^2}}}\,{\text{and}}\,{d_{xz}}$$
D
$${d_{{x^2} - {y^2}\,}}\,{\text{and}}\,{d_{xy}}$$
Answer :
$${d_{xz}}\,{\text{and}}\,{d_{yz}}$$
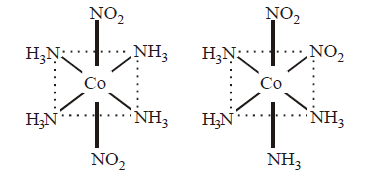
247. $$\left[ {Co{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_4}{{\left( {N{O_2}} \right)}_2}} \right]Cl$$ exhibits
A
linkage isomerism, ionization isomerism and geometrical isomerism
B
ionization isomerism, geometrical isomerism and optical isomerism
C
linkage isomerism, geometrical isomerism and optical isomerism
D
linkage isomerism, ionization isomerism and optical isomerism
Answer :
linkage isomerism, ionization isomerism and geometrical isomerism
248. Which of the following is a tridentate ligand?
A
$$EDT{A^{4 - }}$$
B
$$\left( {COO} \right)_2^{2 - }$$
C
$${\text{dien}}$$
D
$$NO_2^ - $$
Answer :
$${\text{dien}}$$
249. Which of the following compounds is not coloured ?
A
$$N{a_2}\left[ {CuC{l_6}} \right]$$
B
$$N{a_2}\left[ {CdC{l_4}} \right]$$
C
$${K_4}\left[ {Fe{{\left( {CN} \right)}_6}} \right]$$
D
$${K_3}\left[ {Fe{{\left( {CN} \right)}_6}} \right]$$
Answer :
$$N{a_2}\left[ {CdC{l_4}} \right]$$
250. For the reaction of the type $$M + 4L \rightleftharpoons M{L_4}$$
A
larger the stability constant, lower the proportion of $$M{L_4}$$ that exists in solution
B
larger the stability constant, higher the proportion of $$M{L_4}$$ that exists in solution
C
smaller the stability constant, higher the proportion of $$M{L_4}$$ that exists in solution
D
None of the above
Answer :
larger the stability constant, higher the proportion of $$M{L_4}$$ that exists in solution