61. Four successive members of the first row transition elements are listed below with their atomic numbers. Which one of them is expected to have the highest third ionisation enthalpy?
A
Vanadium $$(Z = 23)$$
B
Chromium $$(Z = 24)$$
C
Iron $$(Z = 26)$$
D
Manganese $$(Z = 25)$$
Answer :
Manganese $$(Z = 25)$$
62. The actinoids which shows +7 oxidation state are
A
$$U, Np$$
B
$$Pu, Am$$
C
$$Np, Pu$$
D
$$Am, Cm$$
Answer :
$$Np, Pu$$
63. The color of $$KMn{O_4}$$ is due to :
A
$$L \to M$$ charge transfer transition
B
$$\sigma - {\sigma ^*}$$ transition
C
$$M \to L$$ charge transfer transition
D
$$d - d$$ transition
Answer :
$$L \to M$$ charge transfer transition
64. Transition elements form binary compounds with halogens. Which of the following elements will form $$M{F_3}$$ type compounds?
A
$$Cr$$
B
$$Cu$$
C
$$Ni$$
D
$${\text{All of these}}$$
Answer :
$$Cr$$
65.
Which of the following lanthanoid ions is diamagnetic ?
$$(\,At{\text{ }}nos.{\text{ }}Ce = 58,Sm = 62,Eu = 63,Yb = 70\,)$$
A
$$S{m^{2 + }}$$
B
$$E{u^{2 + }}$$
C
$$Y{b^{2 + }}$$
D
$$C{e^{2 + }}$$
Answer :
$$Y{b^{2 + }}$$
66. Copper sulphate dissolves in excess of $$KCN$$ to give
A
$$CuCN$$
B
$${\left[ {Cu{{\left( {CN} \right)}_4}} \right]^{3 - }}$$
C
$${\left[ {Cu{{\left( {CN} \right)}_4}} \right]^{2 - }}$$
D
$$Cu{\left( {CN} \right)_2}$$
Answer :
$${\left[ {Cu{{\left( {CN} \right)}_4}} \right]^{3 - }}$$
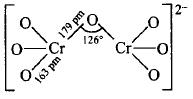
67. In the dichromate anion $$\left( {C{r_2}O_7^{2 - }} \right),$$
A
all $$Cr-O$$ bonds are equivalent
B
$$6\,Cr - O$$ bonds are equivalent
C
$$3\,Cr - O$$ bonds are equivalent
D
no bonds in $$C{r_2}O_7^{2 - }$$ are equivalent
Answer :
$$6\,Cr - O$$ bonds are equivalent
68. Larger number of oxidation states are exhibited by the actinoids than those by the lanthanoids, the main reason being
A
$$4f$$ orbitals more diffused than the $$5f$$ orbitals
B
leasser energy difference between $$5f$$ and $$6d$$ than between $$4f$$ and $$5d$$ orbitals
C
more energy difference between $$5f$$ and $$6d$$ than between $$4f$$ and $$5d$$ orbitals
D
more reactive nature of the actionids than the lanthanoids
Answer :
leasser energy difference between $$5f$$ and $$6d$$ than between $$4f$$ and $$5d$$ orbitals
69. Arrange $$\left( {\text{i}} \right)C{e^{3 + }},\left( {{\text{ii}}} \right)L{a^{3 + }},\left( {{\text{iii}}} \right)P{m^{3 + }}$$ and $$\left( {{\text{iv}}} \right)Y{b^{3 + }}$$ in increasing order of their ionic radii.
A
(iv) < (iii) < (i) < (ii)
B
(i) < (iv) < (iii) < (ii)
C
(iv) < (iii) < (ii) < (i)
D
(iii) < (ii) < (i) < (iv)
Answer :
(iv) < (iii) < (i) < (ii)
70. $$CuS{O_4}$$ is paramagnetic while $$ZnS{O_4}$$ is diamagnetic because
A
$$C{u^{2 + }}$$ ion has $$3{d^9}$$ configuration while $$Z{n^{2 + }}$$ ion has $$3{d^{10}}$$ configuration
B
$$C{u^{2 + }}$$ ion has $$3{d^5}$$ configuration while $$Z{n^{2 + }}$$ ion has $$3{d^6}$$ configuration
C
$$C{u^{2 + }}$$ has half filled orbitals while $$Z{n^{2 + }}$$ has fully filled orbitals
D
$$CuS{O_4}$$ is blue in colour while $$ZnS{O_4}$$ is white
Answer :
$$C{u^{2 + }}$$ ion has $$3{d^9}$$ configuration while $$Z{n^{2 + }}$$ ion has $$3{d^{10}}$$ configuration