111.
In the reaction, $$2X + {B_2}{H_6} \to {\left[ {B{H_2}\left( {{X_2}} \right)} \right]^ + }{\left[ {B{H_4}} \right]^ - }$$
$$'X'$$ cannot be
A
$$N{H_3}$$
B
$$C{H_3}N{H_2}$$
C
$${\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_2}NH$$
D
$${\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_3}N$$
Answer :
$${\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_3}N$$
112. In $$SiO_4^{4 - },$$ the tetrahedral molecule, two oxygen atoms are shared in
A
sheet silicates
B
double-chain silicates
C
chain silicates
D
three-dimensional silicates
Answer :
chain silicates
113. The hybridisation state of the central atom and shape of the molecules is given below. Mark the incorrect combination.
A
$$S{O_3} - s{p^2}$$ hybridisation, planar triangular
B
$$S{O_2} - s{p^2}$$ hybridisation, $$V$$ - shaped
C
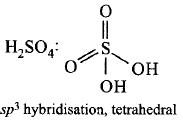
$${H_2}S{O_4} - s{p^2}$$ hybridisation, $$V$$ - shaped
D
$${O_3} - s{p^2}$$ hybridisation, angular
Answer :
$${H_2}S{O_4} - s{p^2}$$ hybridisation, $$V$$ - shaped
114. Which one of the following statements about the zeolite is false?
A
They are used as cation exchangers.
B
Some of the $$SiO_4^{4 - }$$ units are replaced by $$AlO_4^{5 - }$$ and $$AlO_6^{9 - }$$ ions in zeolite.
C
They have open structure which enables them to take up small molecules.
D
Zeolites are aluminosilicates having three dimensional structures.
Answer :
Some of the $$SiO_4^{4 - }$$ units are replaced by $$AlO_4^{5 - }$$ and $$AlO_6^{9 - }$$ ions in zeolite.
115. Which of the following factors would favour the formation of ammonia in Haber's process?
A
High pressure
B
Low temperature
C
High volume
D
Low pressure
Answer :
High pressure
116. In the structure of $$PC{l_5},$$ the $$P - C{l_{{\text{axial}}}}$$ bonds are longer than $$P - C{l_{{\text{equatorial}}}}$$ bond because
A
axial bond pairs suffer more repulsion
B
equatorial bond pairs suffer more repulsion
C
axial bond pairs suffer less repulsion
D
unequal bond lengths are more stable
Answer :
axial bond pairs suffer more repulsion
117. Under hydrolytic conditions, the compounds used for preparation of linear polymer and for chain termination, respectively, are
A
$$C{H_3}SiC{l_3}\,{\text{and}}\,Si{\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_4}$$
B
$${\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_2}SiC{l_2}\,{\text{and}}\,{\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_3}SiCl$$
C
$${\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_2}SiC{l_2}\,{\text{and}}\,C{H_3}SiC{l_3}$$
D
$$SiC{l_4}\,{\text{and}}\,{\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_3}SiCl$$
Answer :
$${\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_2}SiC{l_2}\,{\text{and}}\,{\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_3}SiCl$$
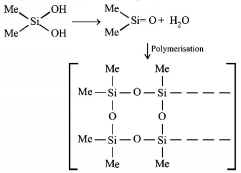
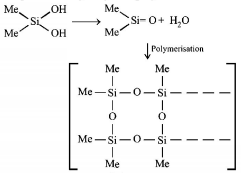
118. $${\left( {Me} \right)_2}SiC{l_2}$$ on hydrolysis will produce
A
$${\left( {Me} \right)_2}Si{\left( {OH} \right)_2}$$
B
$$\,{\left( {Me} \right)_2}Si = O$$
C
$$ - {\left[ { - O - {{\left( {Me} \right)}_2}Si - O - } \right]_n} - $$
D
$${\left( {Me} \right)_2}SiCl\left( {OH} \right)$$
Answer :
$$ - {\left[ { - O - {{\left( {Me} \right)}_2}Si - O - } \right]_n} - $$
119. Nitrogen dioxide cannot be obtained by heating :
A
$$KN{O_3}$$
B
$$Pb{\left( {N{O_3}} \right)_2}$$
C
$$Cu{\left( {N{O_3}} \right)_2}$$
D
$$AgN{O_3}$$
Answer :
$$KN{O_3}$$
120. A metal, $$M$$ forms chlorides in its $$+2$$ and $$+4$$ oxidation states. Which of the following statements about these chlorides is correct ?
A
$$MC{l_2}$$ is more ionic than $$MC{l_4}$$
B
$$MC{l_2}$$ is more easily hydrolysed than $$MC{l_4}$$
C
$$MC{l_2}$$ is more volatile than $$MC{l_4}$$
D
$$MC{l_2}$$ is more soluble in anhydrous ethanol than $$MC{l_4}$$
Answer :
$$MC{l_2}$$ is more ionic than $$MC{l_4}$$