211. The difference of water molecules in gypsum and plaster of Paris is
A
$$\frac{5}{2}$$
B
$$2$$
C
$$\frac{1}{2}$$
D
$$1\frac{1}{2}$$
Answer :
$$1\frac{1}{2}$$
212. The mobility of metal ions in aqueous medium $$\left( {L{i^ + },N{a^ + },{K^ + },R{b^ + }} \right)$$ in the electric field, follows the order
A
$$L{i^ + } > N{a^ + } > {K^ + } > R{b^ + }$$
B
$$R{b^ + } > N{a^ + } = {K^ + } > L{i^ + }$$
C
$$L{i^ + } < N{a^ + } < {K^ + } < R{b^ + }$$
D
$$N{a^ + } = {K^ + } > R{b^ + } > L{i^ + }$$
Answer :
$$L{i^ + } < N{a^ + } < {K^ + } < R{b^ + }$$
213.
The following two figures represent
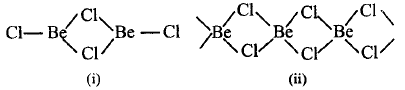
A
$$\left( {\text{i}} \right)BeC{l_2}$$ is a dimer in vapour phase ; $$\left( {{\text{ii}}} \right)BeC{l_2}$$ is chain structure in solid state
B
$$\left( {\text{i}} \right)BeC{l_2}$$ is in solid state ; $$\left( {{\text{ii}}} \right)BeC{l_2}$$ is in vapour phase
C
$$\left( {\text{i}} \right)BeC{l_2}$$ is monomer in solid state ; $$\left( {{\text{ii}}} \right)BeC{l_2}$$ is linear polymer in vapour phase
D
$$\left( {\text{i}} \right)BeC{l_2}$$ is linear monomer ; $$\left( {{\text{ii}}} \right)BeC{l_2}$$ is three dimensional dimer.
Answer :
$$\left( {\text{i}} \right)BeC{l_2}$$ is a dimer in vapour phase ; $$\left( {{\text{ii}}} \right)BeC{l_2}$$ is chain structure in solid state
214. The correct order of the mobility of the alkali metal ions in aqueous solution is
A
$$L{i^ + } > N{a^ + } > {K^ + } > R{b^ + }$$
B
$$N{a^ + } > {K^ + } > R{b^ + } > L{i^ + }$$
C
$${K^ + } > R{b^ + } > N{a^ + } > L{i^ + }$$
D
$$R{b^ + } > {K^ + } > N{a^ + } > L{i^ + }$$
Answer :
$$R{b^ + } > {K^ + } > N{a^ + } > L{i^ + }$$
215. When sodium is dissolved in liquid ammonia, a solution of deep blue colour is obtained. The colour of the solution is due to
A
ammoniated electron
B
sodium ion
C
sodium amide
D
ammoniated sodium ion
Answer :
ammoniated electron
216.
Select the correct statements :
(i) $$C{s^ + }$$ is more highly hydrated than the other alkali metal ions
(ii) Among the alkali metals $$Li,Na,K$$ and $$Rb,$$ lithium has the highest melting point
(iii) Among the alkali metals, only lithium forms a stable nitride by direct combination with nitrogen
A
(i), (ii) and (iii)
B
(i) and (ii)
C
(i) and (iii)
D
(ii) and (iii)
Answer :
(ii) and (iii)
217.
A certain compound $$X$$ imparts a golden yellow flame. When zinc powder is heated with concentrated solution of $$X,{H_2}$$ gas is evolved. $$X$$ combines with $$C{O_2}$$ to give a salt $$Y.$$ $$Y$$ is a hydrated salt which on reaction with $$HCl$$ or excess of $$C{O_2}$$ gives another salt $$Z$$ which is an important part of baking powder. Identify $$X, Y$$ and $$Z.$$
| $$X$$ | $$Y$$ | $$Z$$ | |
| (a) | $$NaOH$$ | $$N{a_2}C{O_3}$$ | $$NaHC{O_3}$$ |
| (b) | $$HCl$$ | $$NaOH$$ | $$NaHC{O_3}$$ |
| (c) | $$KOH$$ | $${K_2}C{O_3}$$ | $$KHC{O_3}$$ |
| (d) | $$NaCl$$ | $$N{a_2}C{O_3}$$ | $$NaOH$$ |
A
(a)
B
(b)
C
(c)
D
(d)
Answer :
(a)
218. A white solid $$X$$ reacts with $$dil.\,HCl$$ to give colourless gas which is used in fire extinguishers. The solid $$X$$ is
A
$$NaCl$$
B
$$C{H_3}COONa$$
C
$$N{a_2}C{O_3}$$
D
$$NaHC{O_3}$$
Answer :
$$NaHC{O_3}$$
219. What are the raw materials used in Solvay's process?
A
$$NaCl,N{H_3},CaC{O_3}$$
B
$$NaOH,C{O_2}$$
C
$$NaCl,CaC{O_3},C,{H_2}S{O_4}$$
D
$$N{H_3},{H_2}O,NaCl$$
Answer :
$$NaCl,N{H_3},CaC{O_3}$$
220. A metal $$M$$ readily forms its sulphate $$MS{O_4}$$ which is water-soluble. It forms its oxide $$MO$$ which becomes inert on heating. It forms an insoluble hyroxide $$M{\left( {OH} \right)_2}$$ which is soluble in $$NaOH$$ solution. Then $$M$$ is
A
$$Mg$$
B
$$Ba$$
C
$$Ca$$
D
$$Be$$
Answer :
$$Be$$