1. Isobutyl magnesium bromide with dry ether and ethyl alcohol gives :
A


B


C
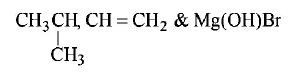
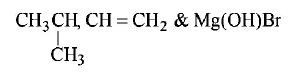
D


Answer :


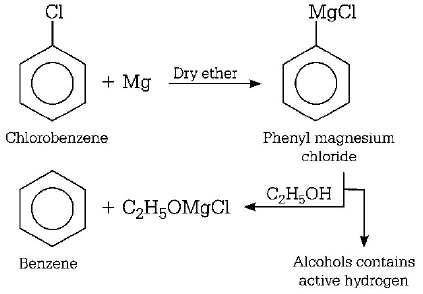
2. Chlorobenzene reacts with $$Mg$$ in dry ether to give a compound $$(A)$$ which further reacts with ethanol to yield
A
phenol
B
benzene
C
ethyl benzene
D
phenyl ether
Answer :
benzene
3.
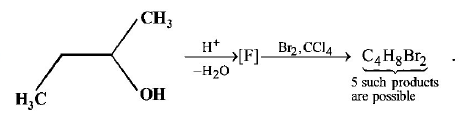
How many structures for $$F$$ are possible?
A
2
B
5
C
6
D
3
Answer :
3
4.
The major product obtained in the following reaction is :
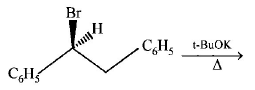
A
$$\left( \pm \right){C_6}{H_5}CH\left( {{O^t}Bu} \right)C{H_2}{C_6}{H_5}$$
B
$${C_6}{H_5}CH = CH{C_6}{H_5}$$
C
$$\left( + \right){C_6}{H_5}CH\left( {{O^t}Bu} \right)C{H_2}{C_6}{H_5}$$
D
$$\left( - \right){C_6}{H_5}CH\left( {{O^t}Bu} \right)C{H_2}{C_6}{H_5}$$
Answer :
$${C_6}{H_5}CH = CH{C_6}{H_5}$$
5.
Which of the following reaction$$(s)$$ can be used for the preparation of alkyl halides?
\[\begin{align}
& \text{(i)}\,C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}OH+HCl\xrightarrow{anh.\,ZnC{{l}_{2}}} \\
& \text{(ii)}\,C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}OH+HCl\to \\
& \text{(iii)}\,{{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{3}}COH+HCl\to \\
& \text{(iv)}{{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}CHOH+HCl\xrightarrow{anh.ZnC{{l}_{2}}} \\
\end{align}\]
A
(i), (iii) and (iv)
B
(i) and (ii)
C
Only (iv)
D
(iii) and (iv)
Answer :
(i), (iii) and (iv)
6. Which of the following is the correct order of decreasing $${S_N}2$$ reactivity?
A
$${R_2}CHX > {R_3}CX > RC{H_2}X$$
B
$$RCHX > {R_3}CX > {R_2}CHX$$
C
$$RC{H_2}X > {R_2}CX > {R_3}CX$$
D
$${R_3}CX > {R_2}CHX > RC{H_2}X$$
Answer :
$$RC{H_2}X > {R_2}CX > {R_3}CX$$
7. Tertiary alkyl halides are practically inert to substitution by \[{{S}_{N}}2\] mechanism because of
A
steric hindrance
B
inductive effect
C
instability
D
insolubility
Answer :
inductive effect
8. The reaction of $${C_6}{H_5}CH = CHC{H_3}$$ with $$HBr$$ produces
A


B


C


D


Answer :


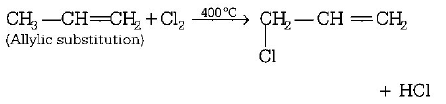
9. When chlorine is passed through propene at $${400^ \circ }C,$$ which of the following is formed?
A
$$PVC$$
B
Allyl chloride
C
Nickel chloride
D
1, 2 - dichloro ethane
Answer :
Allyl chloride
10. Reactivity order of halides for dehydrohalogenation is
A
$$R - F > R - Cl > R - Br > R - I$$
B
$$R - I > R - Br > R - Cl > R - F$$
C
$$R - I > R - Cl > R - Br > R - F$$
D
$$R - F > R - I > R - Br > R - Cl$$
Answer :
$$R - I > R - Br > R - Cl > R - F$$