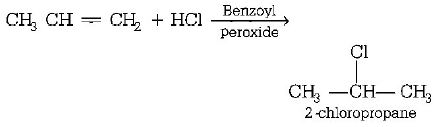41. When $$C{H_3}C{H_2}CHC{l_2}$$ is treated with $$NaN{H_2},$$ the product formed is
A
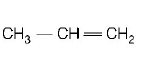
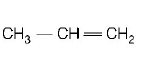
B


C


D


Answer :


42. The organic chloro compound, which shows complete sterochemical inversion during a $${S_N}2$$ reaction, is
A
$$\left( {{C_2}{H_5}} \right)CHCl$$
B
$${\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_3}CCl$$
C
$${\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_2}CHCl$$
D
$$C{H_3}Cl$$
Answer :
$$C{H_3}Cl$$
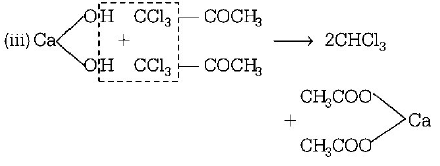
43. Industrial preparation of chloroform employs acetone and
A
phosgene
B
calcium hypochlorite
C
chlorine gas
D
sodium chloride
Answer :
calcium hypochlorite
44. When phenyl magnesium bromide reacts with tert - butanol, the product would be
A
Benzene
B
Phenol
C
ter - butylbenzene
D
ter - butyl phenyl ether
Answer :
Benzene
45. Reaction of phenol with chloroform in the presence of dilute sodium hydroxide finally introduces, which one of the following functional group?
A
$$ - C{H_2}Cl$$
B
$$ - COOH$$
C
$$ - CHC{l_2}$$
D
$$ - CHO$$
Answer :
$$ - CHO$$
46. In a $${S_N}2$$ substitution reaction of the type \[R-Br+C{{l}^{-}}\xrightarrow{DMF}R-Cl+B{{r}^{-}},\] Which one of the following has the highest relative rate?
A


B


C
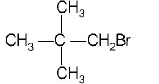

D
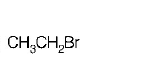
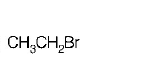
Answer :
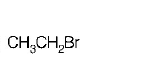
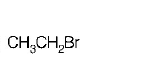
47. Chloropicrin is obtained by the reaction of
A
steam on carbon tetrachloride
B
nitric acid on chlorobenzene
C
chlorine on picric acid
D
nitric acid on chloroform
Answer :
nitric acid on chloroform
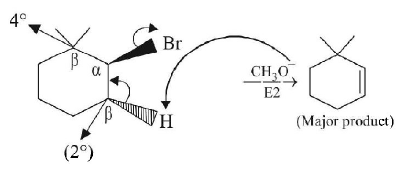
48.
The major product of the following reaction is : 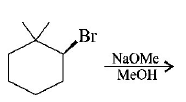
A
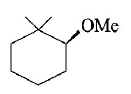

B
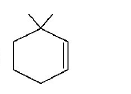

C
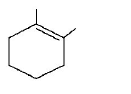

D
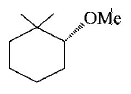

Answer :


49. When hydrochloric acid gas is treated with propene in presence of benzoyl peroxide, it gives
A
2 - chloropropane
B
alkyl chloride
C
no reaction
D
$$n$$ - propyl chloride
Answer :
2 - chloropropane
50.
The reagent $$(s)$$ for the following conversion,

is/are
A
alcoholic $$KOH$$
B
alcoholic $$KOH$$ followed by $$NaN{H_2}$$
C
aqueous $$KOH$$ followed by $$NaN{H_2}$$
D
$$Zn/C{H_3}OH$$
Answer :
alcoholic $$KOH$$ followed by $$NaN{H_2}$$