51. 3 - Methyl - pent - 2 - ene on reaction with $$HBr$$ in presence of peroxide forms an addition product. The number of possible stereoisomers for the product is :
A
Six
B
Zero
C
Two
D
Four
Answer :
Four
52. $${\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_3}CMgCl$$ on reaction with $${D_2}O$$ produces :
A
$${\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_3}CD$$
B
$${\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_3}OD$$
C
$${\left( {C{D_3}} \right)_3}CD$$
D
$${\left( {C{D_3}} \right)_3}OD$$
Answer :
$${\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_3}CD$$
53. The $$Cl-C-Cl$$ angle in 1,1,2,2-tetra-chloroethene and tetrachloromethane will be about
A
$${120^ \circ }\,{\text{and}}\,{109^ \circ }28'$$
B
$${90^ \circ }\,{\text{and}}\,{109.5^ \circ }$$
C
$${109.5^ \circ }\,{\text{and}}\,{90^ \circ }$$
D
$${109.5^ \circ }\,{\text{and}}\,{120^ \circ }$$
Answer :
$${120^ \circ }\,{\text{and}}\,{109^ \circ }28'$$
54. The reaction conditions leading to the best yields of $${C_2}{H_5}Cl$$ are :
A
\[{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}\text{(excess)}+C{{l}_{2}}\xrightarrow{\text{uv}\,\text{light}}\]
B
\[{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}+C{{l}_{2}}\xrightarrow[\text{room temperature}]{\text{dark}}\]
C
\[{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}+C{{l}_{2}}\text{(excess)}\xrightarrow{\text{uv}\,\text{light}}\]
D
\[{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}+C{{l}_{2}}\xrightarrow{\text{uv}\,\text{light}}\]
Answer :
\[{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}\text{(excess)}+C{{l}_{2}}\xrightarrow{\text{uv}\,\text{light}}\]
55. In the following sequence of reactions, \[C{{H}_{3}}-Br\xrightarrow{KCN}A\xrightarrow{{{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}}}B\xrightarrow[\text{ether}]{LiAl{{H}_{4}}}C\] the end product $$C$$ is
A
acetone
B
methane
C
acetaldehyde
D
ethyl alcohol
Answer :
ethyl alcohol
56. Cyclic hydrocarbon $$'A’$$ has all the carbon and hydrogen atoms in a single plane. All the carbon-carbon bonds have the same length, less than $$1.54\mathop {\text{A}}\limits^{\text{o}} ,$$ but more than $$1.34\mathop {\text{A}}\limits^{\text{o}} .$$ The $$C-C-C$$ bond angle will be
A
$${109^ \circ }28'$$
B
$${100^ \circ }$$
C
$${180^ \circ }$$
D
$${120^ \circ }$$
Answer :
$${120^ \circ }$$
57.
\[C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}Cl\xrightarrow{NaCN}X\xrightarrow{\frac{Ni}{{{H}_{2}}}}Y\xrightarrow{\text{Acetic anhydride}}Z\]
In above reaction sequence, $$Z$$ is
A
$$C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}NHCOC{H_3}$$
B
$$C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}N{H_2}$$
C
$$C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}CONHC{H_3}$$
D
$$C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}CONHCOC{H_3}$$
Answer :
$$C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}NHCOC{H_3}$$
58. Phosgene is a common name for
A
phosphonyl chloride
B
thionyl chloride
C
carbon dioxide and phosphine
D
carbonyl chloride
Answer :
carbonyl chloride
59. Which of the following can be used as the halide component for Friedel-Crafts reaction?
A
Chlorobenzene
B
Bromobenzene
C
Chloroethene
D
Isopropyl chloride
Answer :
Isopropyl chloride
60. In which of the following compounds, the $$C-Cl$$ bond ionisation shall give most stable carbonium ion?
A
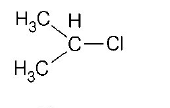

B


C


D
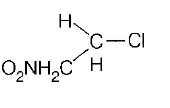

Answer :










