121.
What is the correct order of decreasing stability of the following cations?
$$\eqalign{
& \mathop {C{H_3} - \mathop C\limits^ + H - C{H_3}}\limits_{\left( {\text{I}} \right)} \cr
& \mathop {C{H_3} - \mathop C\limits^ + H - OC{H_3}}\limits_{\left( {{\text{II}}} \right)} \cr
& \mathop {C{H_3} - \mathop C\limits^ + H - C{H_2} - OC{H_3}}\limits_{\left( {{\text{III}}} \right)} \cr} $$
A
(II) > (I) > (III)
B
(II) > (III) > (I)
C
(III) > (I) > (II)
D
(I) > (II) > (III)
Answer :
(II) > (I) > (III)
122. The process of separation of a racemic modification into $$d$$ and $$l$$ -enantiomers is called
A
resolution
B
dehydration
C
revolution
D
dehydrohalogenation
Answer :
resolution
123. 2-methyl-2-butene will be represented as
A


B


C


D


Answer :


124.
Consider the following compounds

hyperconjugation occurs in
A
I only
B
II only
C
III only
D
I and III
Answer :
III only
125. Which of the following represents 3-methylpenta-1, 3-diene?
A
$$C{H_2} = CH{\left( {C{H_2}} \right)_2}C{H_3}$$
B
$$C{H_2} = CHCH\left( {C{H_3}} \right)C{H_2}C{H_3}$$
C
$$C{H_3}CH = C\left( {C{H_3}} \right)CH = C{H_2}$$
D
$$C{H_3}CH = C{\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_2}$$
Answer :
$$C{H_3}CH = C\left( {C{H_3}} \right)CH = C{H_2}$$
126. Which of the following ions is the most resonance stabilised?
A
Ethoxide
B
Phenoxide
C
Butoxide
D
Isopropoxide
Answer :
Phenoxide
127. Which of the following will not show $$cis-trans-isomerism?$$
A


B


C
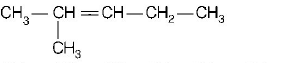
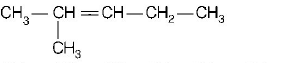
D


Answer :
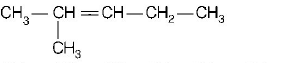
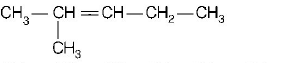
128.
Arrange in order of decreasing trend towards $${S_E}$$ reactions :
$$\mathop {{\text{Chlorobenzene}}}\limits_{\text{I}} {\text{,}}\mathop {{\text{ benzene}}}\limits_{{\text{II}}} {\text{, }}\mathop {{\text{aniliniumchloride}}}\limits_{{\text{III}}} {\text{, }}\mathop {{\text{toluene}}}\limits_{{\text{IV}}} $$
A
II > I > III > IV
B
III > I > II > IV
C
IV > II > I > III
D
I > II > III > IV
Answer :
IV > II > I > III
129.

compound on hydrolysis in aqueous acetone will give

A
Mixture of (i) and (ii)
B
Mixture of (i) and (iii)
C
Only (iii)
D
Only (i)
Answer :
Mixture of (i) and (ii)
130.
The process of separation of an organic compound from its aqueous solution by shaking with a suitable solvent is termed solvent extraction or differential extraction.

The organic compound present in the aqueous layer moves to the organic solvent because
A
the organic substance is more soluble in the organic solvent
B
organic compound being lighter moves in the upper layer
C
organic solvent is insoluble in water hence organic compound moves up
D
from the supersaturated aqueous solution the solute starts diffusing
Answer :
the organic substance is more soluble in the organic solvent




 will not show $$cis-trans$$ isomerism because double bonded carbon atom have two same groups ( $$ - C{H_3},$$ methyl group ).
will not show $$cis-trans$$ isomerism because double bonded carbon atom have two same groups ( $$ - C{H_3},$$ methyl group ). 

