291.
Which is the most suitable reagent among the following to distinguish compound (iii) from rest of the compounds?
$$\eqalign{
& {\text{(i)}}\,C{H_3} - C \equiv C - C{H_3} \cr
& {\text{(ii)}}\,C{H_3} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - C{H_3} \cr
& {\text{(iii)}}\,C{H_3} - C{H_2} - C \equiv CH \cr
& {\text{(iv)}}\,C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2} \cr} $$
A
$$\frac{{B{r_2}}}{{CC{l_4}}}$$
B
$$\frac{{B{r_2}}}{{C{H_3}COOH}}$$
C
$$Alk.\,KMn{O_4}$$
D
$${\text{Ammoniacal}}\,AgN{O_3}$$
Answer :
$${\text{Ammoniacal}}\,AgN{O_3}$$
292.
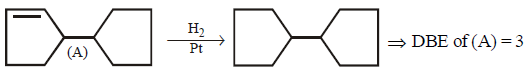
\[\left( A \right)\xrightarrow{{{H}_{2}}\left( 1\,mole \right)/Pt}\] 
Double bond equivalent ( degree of unsaturation ) of $$(A)$$ is :
A
1
B
2
C
3
D
4
Answer :
3
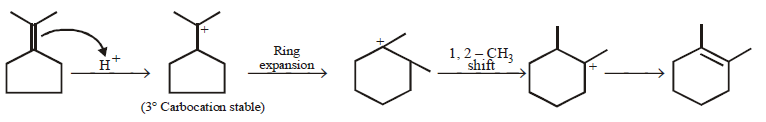
293.
Predict the product $$(A)$$ of the following reaction
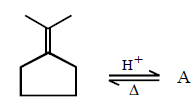
A
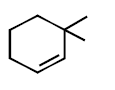

B
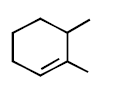

C
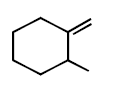

D
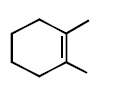

Answer :


294.
Consider the following reaction
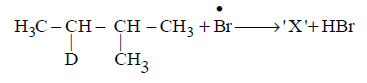
Identify the structure of the major product $$'X'$$
A
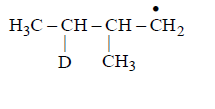
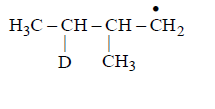
B
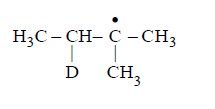
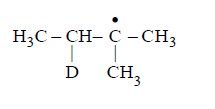
C
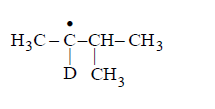
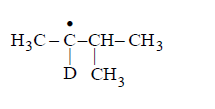
D
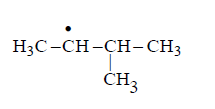
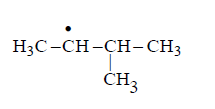
Answer :
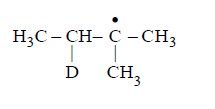
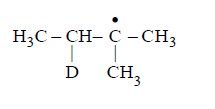
295. Which one of the following gives only one monochloro derivative?
A
$$neo$$ - Pentane
B
$$n$$ - Hexane
C
2 - Methylpentane
D
3 - Methylpentane
Answer :
$$neo$$ - Pentane
296. In the commercial gasolines, the type of hydrocarbons which is more desirable, is
A
branched hydrocarbon
B
straight chain hydrocarbon
C
linear, unsaturated hydrocarbon
D
toluene
Answer :
branched hydrocarbon
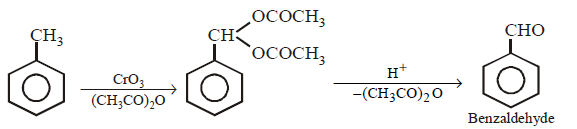
297. Toluene on treatment with $$Cr{O_3}$$ and $${\left( {C{H_3}CO} \right)_2}O$$ followed by hydrolysis with $$dil.HCl$$ gives
A
benzaldehyde
B
benzoic acid
C
phenol
D
phenylacetaldehyde
Answer :
benzaldehyde