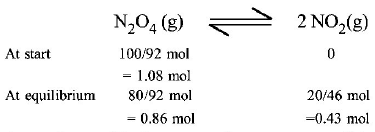211. For real gases, the relation between $$P, V$$ and $$T$$ is given by van der Waals' equation, $$\left( {P + \frac{{a{n^2}}}{{{V^2}}}} \right)\left( {V - nb} \right) = nRT.$$ For the following gases $$C{H_4},C{O_2},{O_2},{H_2}$$ which gas will have (i) highest value of $$a$$ (ii) lowest value of $$b?$$
A
$$\left( {\text{i}} \right)C{O_2},\left( {{\text{ii}}} \right){H_2}$$
B
$$\left( {\text{i}} \right)C{H_4},\left( {{\text{ii}}} \right)C{O_2}$$
C
$$\left( {\text{i}} \right){H_2},\left( {{\text{ii}}} \right)C{O_2}$$
D
$$\left( {\text{i}} \right){O_2},\left( {{\text{ii}}} \right){H_2}$$
Answer :
$$\left( {\text{i}} \right)C{O_2},\left( {{\text{ii}}} \right){H_2}$$
212. Boiling point of hydrogen fluoride is highest amongst $$HF, HCl, HBr$$ and $$HI.$$ Which type of intermolecular forces are present in hydrogen fluoride ?
A
$$H-F$$ has highest van der Waals forces and dipole moment.
B
$$H - F$$ has highest London forces.
C
$$H - F$$ has highest dipole moment hence has dipole-dipole, London forces and hydrogen bonding.
D
$$H -F$$ has strong intermolecular interactions like dipole-induced dipole.
Answer :
$$H - F$$ has highest dipole moment hence has dipole-dipole, London forces and hydrogen bonding.
213. If $${10^{ - 4}}d{m^3}$$ of water is introduced into a $$1.0\,d{m^3}$$ flask at $$300 K,$$ how many moles of water are in the vapour phase when equilibrium is established ? ( Given : Vapour pressure of $${H_2}O$$ at $$300 K$$ is $$3170 pa;$$ $$R = 8.314J\,{K^{ - 1}}mo{l^{ - 1}})$$
A
$$5.56 \times {10^{ - 3}}mol$$
B
$$1.53 \times {10^{ - 2}}mol$$
C
$$4.46 \times {10^{ - 2}}mol$$
D
$$1.27 \times {10^{ - 3}}mol$$
Answer :
$$1.27 \times {10^{ - 3}}mol$$
214. One mole of $${N_2}{O_2}\left( g \right)$$ at $$300K$$ is kept in a closed container under one atmosphere. It is heated to $$600K$$ when $$20\% $$ by mass of $${N_2}{O_4}\left( g \right)$$ decomposes to $$N{O_2}\left( g \right).$$ The resultant pressure is :
A
1.2 atm
B
2.4 atm
C
2.0 atm
D
1.0 atm
Answer :
2.4 atm
215. As the temperature increases, average kinetic energy of molecules increases. What would be the effect of increase of temperature on pressure provided the volume is constant ?
A
Increases
B
Decreases
C
Remains same
D
Becomes half
Answer :
Increases
216. By how many folds the temperature of a gas would increase when the root mean square velocity of the gas molecules in a container of fixed volume is increased from $$5 \times {10^4}\,cm/s$$ to $$10 \times {10^4}\,cm/s?$$
A
Two
B
Three
C
Six
D
Four
Answer :
Four
217. The value of van der waals constant $$'a’$$ for gases $${O_2},{N_2},N{H_3}$$ and $$C{H_4}$$ are 1.360, 1.390, 4.170 and 2.253 $$litr{e^2}atm\,\,mo{l^{ - 2}}$$ respectively. The gas which can most easily be liquefied is :
A
$${O_2}$$
B
$${N_2}$$
C
$$N{H_3}$$
D
$$C{H_4}$$
Answer :
$$N{H_3}$$
218.
The graphs representing distribution of molecular speeds at $$300\,K$$ for gases $$C{l_2}$$ and $${N_2}:$$

Select the correct option.
A
I graph is for $${N_2}$$ and II is for $$C{l_2}$$
B
II graph is for $${N_2}$$ and I is for $$C{l_2}$$
C
Either graph can be taken for $${N_2}$$ or $$C{l_2}$$
D
Information is not sufficient.
Answer :
II graph is for $${N_2}$$ and I is for $$C{l_2}$$
219.
Two closed bulbs of equal volume $$(V)$$ containing an ideal gas initially at pressure $${P_i}$$ and temperature $${T_1}$$ are connected through a narrow tube of negligible volume as shown in the figure below. The temperature of one of the bulbs is then raised to $${T_2}.$$ The final pressure $${P_f}$$ is :

A
$$2{p_i}\left( {\frac{{{T_2}}}{{{T_1} + {T_2}}}} \right)$$
B
$$2{p_i}\left( {\frac{{{T_1}{T_2}}}{{{T_1} + {T_2}}}} \right)$$
C
$${p_i}\left( {\frac{{{T_1}{T_2}}}{{{T_1} + {T_2}}}} \right)$$
D
$$2{p_i}\left( {\frac{{{T_1}}}{{{T_1} + {T_2}}}} \right)$$
Answer :
$$2{p_i}\left( {\frac{{{T_2}}}{{{T_1} + {T_2}}}} \right)$$
220.
Consider the van der Waals constants, $$a$$ and $$b,$$ for the following gases,
| Gas | $$Ar$$ | $$Ne$$ | $$Kr$$ | $$Xe$$ |
| a/(atm dm6 mol−2) | 1.3 | 0.2 | 5.1 | 4.1 |
| b/(10−2 dm3 mol−1) | 3.2 | 1.7 | 1.0 | 5.0 |
A
$$Kr$$
B
$$Ne$$
C
$$Xe$$
D
$$Ar$$
Answer :
$$Kr$$