251. It is easier to liquefy ammonia than oxygen because
A
it is easier to compress oxygen than $$N{H_3}$$
B
$$N{H_3}$$ has a very low critical temperature as compared to $${O_2}$$
C
$${O_2}$$ has a higher value of van der Waals constant $$a$$ and higher critical temperature than $$N{H_3}$$
D
$$N{H_3}$$ has a higher value of van der Waals constant $$a$$ and higher critical temperature than oxygen.
Answer :
$$N{H_3}$$ has a higher value of van der Waals constant $$a$$ and higher critical temperature than oxygen.
252.
What is the value of $$X$$ in $$^ \circ C$$ for given volume vs temperature curve ?
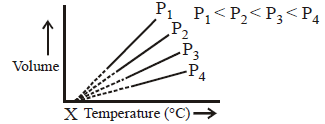
A
$${0^ \circ }C$$
B
$${273.15^ \circ }C$$
C
$$ - {273.15^ \circ }C$$
D
$${300^ \circ }C$$
Answer :
$$ - {273.15^ \circ }C$$
253. Equal masses of methane and oxygen are mixed in an empty container at $${25^ \circ }C.$$ The fraction of the total pressure exerted by oxygen is
A
$$\frac{1}{2}$$
B
$$\frac{2}{3}$$
C
$$\frac{1}{3} \times \frac{{273}}{{298}}$$
D
$$\frac{1}{3}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{1}{3}$$
254. Liquids are similar to gases because
A
both possess the property of flowing and take the volume of the containers
B
both diffuse and take the shape of the containers
C
both are readily compressible and diffuse
D
both are capable of infinite expansion.
Answer :
both diffuse and take the shape of the containers
255. At what temperature will the molar kinetic energy of $$0.3\,mol$$ of $$He$$ be the same as that of $$0.4\,mol$$ of $$Ar$$ at $$400\,K?$$
A
700$$\,K$$
B
500$$\,K$$
C
800$$\,K$$
D
400$$\,K$$
Answer :
400$$\,K$$
256.
The qualitative sketches I, II and III given below show the variation of surface tension with molar concentration of three different aqueous solutions of $$KCl,$$ $$C{H_3}OH$$ and $$C{H_3}{\left( {C{H_2}} \right)_{11}}OSO_3^ - N{a^ + }$$ at room temperature.
The correct assignment of the sketches is
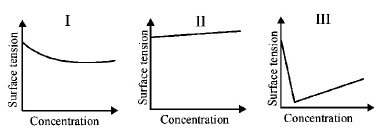
A
$$I:\,KCl\,\,\,II:C{H_3}OH\,\,\,III:C{H_3}{\left( {C{H_2}} \right)_{11}}OSO_3^ - N{a^ + }$$
B
$$I:C{H_3}{\left( {C{H_2}} \right)_{11}}OSO_3^ - N{a^ + }\,\,II:C{H_3}OH\,\,III:KCl$$
C
$$I:KCl\,\,\,II:C{H_3}{\left( {C{H_2}} \right)_{11}}OSO_3^ - N{a^ + }\,\,\,III:C{H_3}OH$$
D
$$I:C{H_3}OH\,\,\,II:KCl\,\,\,\,\,III:C{H_3}{\left( {C{H_2}} \right)_{11}}OSO_3^ - N{a^ + },$$
Answer :
$$I:C{H_3}OH\,\,\,II:KCl\,\,\,\,\,III:C{H_3}{\left( {C{H_2}} \right)_{11}}OSO_3^ - N{a^ + },$$
257. In van der Waals’ equation of state for a non-ideal gas, the term that accounts for inter molecular forces is
A
$$\left( {V - b} \right)$$
B
$${\left( {RT} \right)^{ - 1}}$$
C
$$\left( {p + \frac{a}{{{V^2}}}} \right)$$
D
$$RT$$
Answer :
$$\left( {p + \frac{a}{{{V^2}}}} \right)$$
258.
Atmospheric pressures recorded in different cities are as follows :
| Cities | Shimla | Bangalore | Delhi | Mumbai |
| $$P\,{\text{in}}\,N/{m^2}$$ | $$1.01 \times {10^5}$$ | $$1.2 \times {10^5}$$ | $$1.02 \times {10^5}$$ | $$1.21 \times {10^5}$$ |
Consider the above data and mark the place at which liquid will boil first.
A
Shimla
B
Bangalore
C
Delhi
D
Mumbai
Answer :
Shimla
259.
A 20 litre container at $$400\,K$$ contains $$C{O_2}\left( g \right)$$ at pressure $$0.4\,atm$$ and an excess of $$SrO$$ ( neglect the volume of solid $$SrO$$ ). The volume of the container is now decreased by moving the movable piston fitted in the container. The maximum volume of the container, when pressure of $$C{O_2}$$ attains its maximum value, will be
( Given that : $$SrC{O_3}\left( s \right) \rightleftharpoons SrO\left( s \right) + C{O_2}\left( g \right),$$ $${K_p} = 1.6\,\left. {atm} \right)$$
A
5$$\,L$$
B
10$$\,L$$
C
4$$\,L$$
D
2$$\,L$$
Answer :
5$$\,L$$
260. Weight of $$C{O_2}$$ in a $$10\,L$$ cylinder at $$5\,atm$$ and $$27{\,^ \circ }C$$ is
A
200$$\,g$$
B
224$$\,g$$
C
44$$\,g$$
D
89.3$$\,g$$
Answer :
89.3$$\,g$$