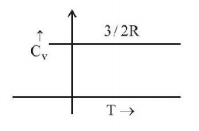
51. Graph of specific heat at constant volume for a monatomic gas is
A
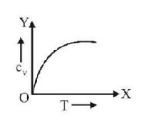

B
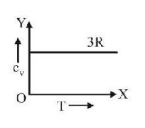

C
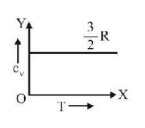

D
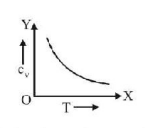

Answer :


52. The specific heats at constant pressure is greater than that of the same gas at constant volume because
A
at constant pressure work is done in expanding the gas
B
at constant volume work is done in expanding the gas
C
the molecular attraction increases more at constant pressure
D
the molecular vibration increases more at constant pressure
Answer :
at constant pressure work is done in expanding the gas
53. The quantity of gas in a closed vessel is halved and the velocities of its molecules are doubled. The final pressure of the gas will be
A
$$P$$
B
$$2P$$
C
$$\frac{P}{2}$$
D
$$4P$$
Answer :
$$2P$$
54. The temperature of an air bubble while rising from bottom to surface of a lake remains constant but its diameter is doubled if the pressure on the surface is equal to $$h$$ meter of mercury column and relative density of mercury is $$\rho $$ then the depth of lake in metre is
A
$$2\rho h$$
B
$$4\rho h$$
C
$$8\rho h$$
D
$$7\rho h$$
Answer :
$$7\rho h$$
55. The degree of freedom of a molecule of a triatomic gas is
A
2
B
4
C
6
D
8
Answer :
6
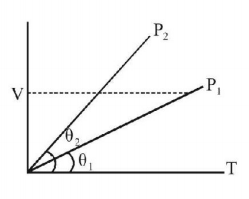
56.
In the given $$\left( {V - T} \right)$$ diagram, what is the relation between pressure $${P_1}$$ and $${P_2}$$ ?
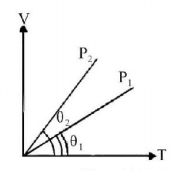
A
$${P_2} > {P_1}$$
B
$${P_2} < {P_1}$$
C
Cannot be predicted
D
$${P_2} = {P_1}$$
Answer :
$${P_2} < {P_1}$$
57. The amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of $$1g$$ of Helium at $$NTP,$$ from $${T_1}K$$ to $${T_2}K$$ is
A
$$\frac{3}{2}{N_a}{k_B}\left( {{T_2} - {T_1}} \right)$$
B
$$\frac{3}{4}{N_a}{k_B}\left( {{T_2} - {T_1}} \right)$$
C
$$\frac{3}{4}{N_a}{k_B}\frac{{{T_2}}}{{{T_1}}}$$
D
$$\frac{3}{8}{N_a}{k_B}\left( {{T_2} - {T_1}} \right)$$
Answer :
$$\frac{3}{8}{N_a}{k_B}\left( {{T_2} - {T_1}} \right)$$
58. The speed of sound in oxygen $$\left( {{O_2}} \right)$$ at a certain temperature is $$460\,\,m\,{s^{ - 1}}.$$ The speed of sound in helium $$\left( {{He}} \right)$$ at the same temperature will be (assume both gases to be ideal)
A
$$1421\,\,m\,{s^{ - 1}}$$
B
$$500\,\,m\,{s^{ - 1}}$$
C
$$650\,\,m\,{s^{ - 1}}$$
D
$$330\,\,m\,{s^{ - 1}}$$
Answer :
$$1421\,\,m\,{s^{ - 1}}$$
59. At what temperature is the $$r.m.s$$ velocity of a hydrogen molecule equal to that of an oxygen molecule at $${47^ \circ }C$$ ?
A
$$80\,K$$
B
$$-73\,K$$
C
$$3\,K$$
D
$$20\,K$$
Answer :
$$20\,K$$
60. The molar specific heat at constant pressure of an ideal gas is $$\left( {\frac{9}{2}} \right)R.$$ The ratio of specific heat at constant pressure to that at constant volume is
A
1.58
B
1.82
C
1.28
D
1.44
Answer :
1.28