71. For a gas, difference between two specific heats is $$5000\,J/mol{e^ \circ }C.$$ If the ratio of specific heat is $$1.6,$$ the two specific heats are in $$J/mol{e-^ \circ }C$$
A
$${C_P} = 1.33 \times {10^4},{C_V} = 2.66 \times {10^4}$$
B
$${C_P} = 13.3 \times {10^4},{C_V} = 8.33 \times {10^3}$$
C
$${C_P} = 1.33 \times {10^4},{C_V} = 8.33 \times {10^3}$$
D
$${C_P} = 2.6 \times {10^4},{C_V} = 8.33 \times {10^4}$$
Answer :
$${C_P} = 1.33 \times {10^4},{C_V} = 8.33 \times {10^3}$$
72.
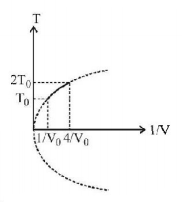
Figure shows a parabolic graph between $$T$$ and $$\frac{1}{V}$$ for a mixture of a gas undergoing an adiabatic process. What is the ratio of $${V_{rms}}$$ of molecules and speed of sound in mixture?
A
$$\sqrt {\frac{3}{2}} $$
B
$$\sqrt 2 $$
C
$$\sqrt {\frac{2}{3}} $$
D
$$\sqrt 3 $$
Answer :
$$\sqrt 2 $$
73. Two vessels separately contain two ideal gases $$A$$ and $$B$$ at the same temperature. The pressure of $$A$$ being twice that of $$B.$$ Under such conditions, of $$A$$ being twice that of $$B.$$ Under such conditions, the density of $$A$$ is found to be 1.5 times the density of $$B.$$ The ratio of molecular weight of $$A$$ and $$B$$ is:
A
$$\frac{3}{4}$$
B
$$2$$
C
$$\frac{1}{2}$$
D
$$\frac{2}{3}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{3}{4}$$
74. A gas mixture consists of molecules of type 1, 2 and 3, with molar masses $${m_1} > {m_2} > {m_3}.{v_{rms}}$$ and $$\overline K $$ are the $$r.m.s.$$ speed and average kinetic energy of the gases. Which of the following is true?
A
$${\left( {{v_{rms}}} \right)_1} < {\left( {{v_{rms}}} \right)_2} < {\left( {{v_{rms}}} \right)_3}\,{\text{and}}\,{\left( {\overline K } \right)_1} = {\left( {\overline K } \right)_2} = {\left( {\overline K } \right)_3}$$
B
$${\left( {{v_{rms}}} \right)_1} = {\left( {{v_{rms}}} \right)_2} = {\left( {{v_{rms}}} \right)_3}\,{\text{and}}\,{\left( {\overline K } \right)_1} = {\left( {\overline K } \right)_2} > {\left( {\overline K } \right)_3}$$
C
$${\left( {{v_{rms}}} \right)_1} > {\left( {{v_{rms}}} \right)_2} > {\left( {{v_{rms}}} \right)_3}\,{\text{and}}\,{\left( {\overline K } \right)_1} < {\left( {\overline K } \right)_2} > {\left( {\overline K } \right)_3}$$
D
$${\left( {{v_{rms}}} \right)_1} > {\left( {{v_{rms}}} \right)_2} > {\left( {{v_{rms}}} \right)_3}\,{\text{and}}\,{\left( {\overline K } \right)_1} < {\left( {\overline K } \right)_2} < {\left( {\overline K } \right)_3}$$
Answer :
$${\left( {{v_{rms}}} \right)_1} < {\left( {{v_{rms}}} \right)_2} < {\left( {{v_{rms}}} \right)_3}\,{\text{and}}\,{\left( {\overline K } \right)_1} = {\left( {\overline K } \right)_2} = {\left( {\overline K } \right)_3}$$
75. Consider a collection of a large number of dust particles each with speed $$v.$$ The direction of velocity is randomly distributed in the collection. What is the magnitude of the relative velocity between a pairs in the collection ?
A
$$\frac{{3v}}{\pi }$$
B
$$\frac{{4v}}{\pi }$$
C
$$\frac{{2v}}{\pi }$$
D
$$\frac{{v}}{\pi }$$
Answer :
$$\frac{{4v}}{\pi }$$
76. Which of the following will have maximum total kinetic energy at temperature $$300K$$ ?
A
$$1\,kg\,{H_2}$$
B
$$1\,kg\,He$$
C
$$\frac{1}{2}kg\,{H_2} + \frac{1}{2}kg\,He$$
D
$$\frac{1}{2}kg\,{H_2} + \frac{3}{4}kg\,He$$
Answer :
$$1\,kg\,{H_2}$$
77. From the following statements concerning ideal gas at any given temperature $$T,$$ select the correct one(s)
A
The co-efficient of volume expansion at constant pressure is the same for all ideal gases
B
The average translational kinetic energy per molecule of oxygen gas is $$3kT, k$$ being Boltzmann constant
C
The mean - free path of molecules increases with increases in the pressure
D
In a gaseous mixture, the average translational kinetic energy of the molecules of each component is different
Answer :
The co-efficient of volume expansion at constant pressure is the same for all ideal gases
78. The molar specific heat at constant pressure of an ideal gas is $$\left( {\frac{7}{2}} \right)R.$$ The ratio of specific heat at constant pressure to that at constant volume is
A
$$\frac{8}{7}$$
B
$$\frac{5}{7}$$
C
$$\frac{9}{7}$$
D
$$\frac{7}{5}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{7}{5}$$
79. At constant volume, temperature is increased then
A
collision on walls will be less
B
number of collisions per unit time will increase
C
collisions will be in straight lines
D
collisions will not change
Answer :
number of collisions per unit time will increase
80. The internal energy of monatomic and diatomic gases are respectively due to
A
linear motion and rolling motion
B
rolling motion and linear motion
C
linear motion and rotatory motion
D
rotatory motion and linear motion
Answer :
linear motion and rolling motion