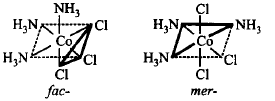31. Which of the following complexes exists as pair of enantiomers?
A
$$trans - {\left[ {Co{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_4}C{l_2}} \right]^ + }$$
B
$${\left[ {Cr{{\left( {en} \right)}_3}} \right]^{3 + }}$$
C
$$trans - {\left[ {Co{{\left( {en} \right)}_2}C{l_2}} \right]^ + }$$
D
$${\text{All}}\,\,{\text{of}}\,\,{\text{these}}$$
Answer :
$${\left[ {Cr{{\left( {en} \right)}_3}} \right]^{3 + }}$$
32.
Match the complex ions given in column I with their colour given in column II and mark the appropriate choice.
| Column I | Column II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| a. | $${\left[ {Co{F_6}} \right]^{3 - }}$$ | 1. | Blue-green |
| b. | $${\left[ {Co{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3 + }}$$ | 2. | Pale yellow |
| c. | $${\left[ {Co{{\left( {{H_2}O} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3 + }}$$ | 3. | Green |
| d. | $${\left[ {Co{{\left( {CN} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3 - }}$$ | 4. | Yellow-orange |
A
a - 3, b - 4, c - 1, d - 2
B
a - 3, b - 4, c - 2, d - 1
C
a - 1, b - 3, c - 4, d - 2
D
a - 4, b - 1, c - 3, d - 2
Answer :
a - 3, b - 4, c - 1, d - 2
33.
Two isomers of a compound $$Co{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)_3}C{l_3}\left( {M{A_3}{B_3}\,{\text{type}}} \right)$$ are shown in the figures.
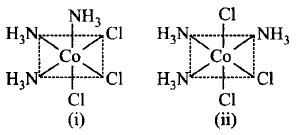
The isomers can be classified as
A
(i) $$fac$$ - isomer (ii) $$mer$$ - isomer
B
(i) optical-isomer (ii) $$trans$$ - isomer
C
(i) $$mer$$ - isomer (ii) $$fac$$ - isomer
D
(i) $$trans$$ -isomer (ii) $$cis$$ -isomer
Answer :
(i) $$fac$$ - isomer (ii) $$mer$$ - isomer
34. Which of the following ligands is expected to be bidentate ?
A
$$C{H_3}N{H_2}$$
B
$$C{H_3}C \equiv N$$
C
$$Br$$
D
$${C_2}O_4^{2 - }$$
Answer :
$${C_2}O_4^{2 - }$$
35. The structure of which of the following chloro species can be explained on the basis of $$ds{p^2}$$ hybridization ?
A
$${\left[ {PdC{l_4}} \right]^{2 - }}$$
B
$${\left[ {FeC{l_4}} \right]^{2 - }}$$
C
$${\left[ {CoC{l_4}} \right]^{2 - }}$$
D
$${\left[ {NiC{l_4}} \right]^{2 - }}$$
Answer :
$${\left[ {PdC{l_4}} \right]^{2 - }}$$
36. The spin only magnetic moment value (in Bohr magneton units) of $$Cr{\left( {CO} \right)_6}$$ is
A
$$0$$
B
$$2.84$$
C
$$4.90$$
D
$$5.92$$
Answer :
$$0$$
37. Which of the following is not a neutral ligand ?
A
$${H_2}O$$
B
$$N{H_3}$$
C
$$ONO$$
D
$$CO$$
Answer :
$$ONO$$
38. In metal carbonyl having general formula $$M{\left( {CO} \right)_x}$$ where, $$M =$$ metal, $$x= 4$$ and the metal is bonded to
A
carbon and oxygen
B
$$C \equiv O$$
C
oxygen
D
carbon
Answer :
carbon
39.
The charges $$x$$ and $$y$$ on the following ions are
$$\eqalign{
& \left( {\text{i}} \right){\left[ {Co{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_2}C{l_4}} \right]^x} \cr
& \left( {{\text{ii}}} \right){\left[ {Fe{{\left( {CN} \right)}_6}} \right]^y} \cr} $$
( Oxidation state of $$Co$$ is +3 and $$Fe$$ is +2 in their respective complexes. )
A
$$x = + 1,y = - 1$$
B
$$x = - 1,y = + 3$$
C
$$x = - 1,y = - 4$$
D
$$x = - 2,y = - 3$$
Answer :
$$x = - 1,y = - 4$$
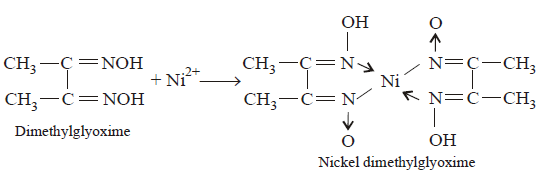
40.
Red precipitate is obtained when ethanol solution of dimethylglyoxime is added to ammoniacal $$Ni\left( {{\text{II}}} \right){\text{.}}$$ Which of the following statements is not true ?
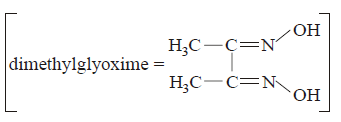
A
Red complex has a square planar geometry.
B
Complex has symmetrical $$H$$ - bonding
C
Red complex has a tetrahedral geometry.
D
Dimethylglyoxime functions as bidentate ligand.
Answer :
Red complex has a tetrahedral geometry.