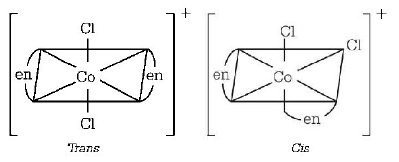
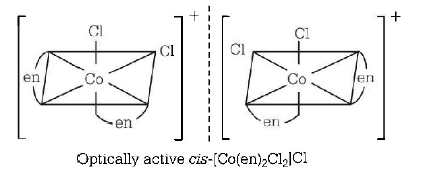
51. Which one of the following complexes will have four isomers ?
A
$$\left[ {Co{{\left( {en} \right)}_3}} \right]C{l_3}$$
B
$$\left[ {Co{{\left( {en} \right)}_2}C{l_2}} \right]Cl$$
C
$$\left[ {Co{{\left( {PP{h_3}} \right)}_2}\left( {N{H_3}} \right)C{l_2}} \right]Cl$$
D
$$\left[ {Co{{\left( {PP{h_3}} \right)}_3}Cl} \right]C{l_2}$$
Answer :
$$\left[ {Co{{\left( {en} \right)}_2}C{l_2}} \right]Cl$$
52. $$50\,mL$$ of $$0.2\,M$$ solution of a compound with empirical formula $$CoC{l_3}.4N{H_3}$$ on treatment with excess of $$AgN{O_3}\left( {aq} \right)$$ yields $$1.435g$$ of $$AgCl.$$ Ammonia is not removed by treatment with concentrated $${H_2}S{O_4}.$$ The formula of the compound is :
A
$$\left[ {Co{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_4}} \right]C{l_3}$$
B
$$\left[ {Co{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_4}C{l_2}} \right]Cl$$
C
$$\left[ {Co{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_4}} \right]C{l_3}$$
D
$$\left[ {CoC{l_3}\left( {N{H_3}} \right)} \right]{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)_3}$$
Answer :
$$\left[ {Co{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_4}C{l_2}} \right]Cl$$
53. For the square planar complex $$\left[ {M\,abcd} \right]$$ where $$M$$ is the central atom and $$a,b,c,d$$ are monodentate ligands, the number of possible geometrical isomers are
A
one
B
two
C
three
D
four
Answer :
three
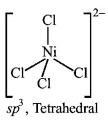
54. The species having tetrahedral shape is
A
$${\left[ {PdC{l_4}} \right]^{2 - }}$$
B
$${\left[ {Ni{{\left( {CN} \right)}_4}} \right]^{2 - }}$$
C
$${\left[ {Pd{{\left( {CN} \right)}_4}} \right]^{2 - }}$$
D
$${\left[ {NiC{l_4}} \right]^{2 - }}$$
Answer :
$${\left[ {Ni{{\left( {CN} \right)}_4}} \right]^{2 - }}$$
55. Which of the following complex will show geometrical as well as optical isomerism ( $$en=$$ ethylenediammine )
A
$$\left[ {Pt{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_2}C{l_2}} \right]$$
B
$$\left[ {Pt\left( {en} \right)C{l_4}} \right]$$
C
$${\left[ {Pt{{\left( {en} \right)}_3}} \right]^{4 + }}$$
D
$$\left[ {Pt{{\left( {en} \right)}_2}C{l_2}} \right]$$
Answer :
$$\left[ {Pt{{\left( {en} \right)}_2}C{l_2}} \right]$$
56. When aqueous solution of potassium fluoride is added to the blue coloured aqueous $$CuS{O_4}$$ solution, a green precipitate is formed. This observation can be explained as
A
on adding $$KF,{H_2}O$$ is replaced by $${F^ - }$$ ions forming $${\left[ {Cu{F_4}} \right]^{2 - }}$$ which is green in colour.
B
potassium is coordinated to $${\left[ {Cu{{\left( {{H_2}O} \right)}_4}} \right]^{2 + }}$$ ion present in $$CuS{O_4}$$ and gives green colour.
C
on adding $$KF,C{u^{2 + }}$$ are replaced by $${K^ + }$$ forming a green complex.
D
blue colour of $$CuS{O_4}$$ and yellow colour of $$KI$$ form green colour on mixing.
Answer :
on adding $$KF,{H_2}O$$ is replaced by $${F^ - }$$ ions forming $${\left[ {Cu{F_4}} \right]^{2 - }}$$ which is green in colour.
57. The correct order of the stoichiometrics of $$AgCl$$ formed when $$AgN{O_3}$$ in excess is treated with the complexes : $$CoC{l_3} \cdot 6N{H_3},CoC{l_3} \cdot 5N{H_3},CoC{l_3} \cdot 4N{H_3}$$ respectively is
A
$$1AgCl,3AgCl,2AgCl$$
B
$$3AgCl,1AgCl,2AgCl$$
C
$$3AgCl,2AgCl,1AgCl$$
D
$$2AgCl,3AgCl,1AgCl$$
Answer :
$$3AgCl,2AgCl,1AgCl$$
58. How many $$EDTA$$ (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) molecules are required to make an octahedral complex with a $$C{a^{2 + }}$$ ion?
A
One
B
Two
C
Sx
D
Three
Answer :
One
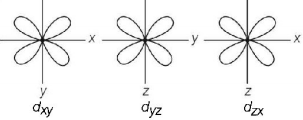
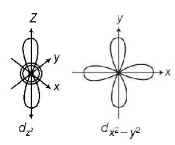
59. Which of the following pairs of $$d$$ - orbitals will have electron density along the axis ?
A
$${d_{{z^2}}},{d_{xz}}$$
B
$${d_{xz}},{d_{yz}}$$
C
$${d_{{z^2}}},{d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}$$
D
$${d_{xy}},{d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}$$
Answer :
$${d_{{z^2}}},{d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}$$
60. Ammonia acts as a very good ligand but ammonium ion does not form complexes because
A
$$N{H_3}$$ is a gas while $$NH_4^ + $$ is in liquid form
B
$$N{H_3}$$ undergoes $$s{p^3}$$ hybridisation while $$NH_4^ + $$ undergoes $$s{p^3}d$$ hybridisation
C
$$NH_4^ + $$ ion does not have any lone pair of electrons
D
$$NH_4^ + $$ ion has one unpaired electron while $$N{H_3}$$ has two unpaired electrons.
Answer :
$$NH_4^ + $$ ion does not have any lone pair of electrons