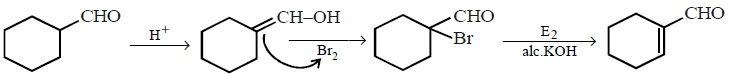
131.

Identify appropriate reagents for the above reaction :
A
\[a=B{{r}_{2}}/CC{{l}_{4}},\,\,b=aq.\,KOH\]
B
\[a=B{{r}_{2}}/{{H}^{+}},\,\,b=aq.\,KOH\]
C
\[a=B{{r}_{2}}/{{H}^{+}},\,\,b=alc.\,KOH\]
D
\[a=B{{r}_{2}}/H{{O}^{-}},\,\,b=aq.\,KOH\]
Answer :
\[a=B{{r}_{2}}/{{H}^{+}},\,\,b=alc.\,KOH\]
132. Which is major product formed when acetone is heated with iodine and potassium hydroxide ?
A
Iodoacetone
B
Acetic acid
C
Iodoform
D
Acetophenone
Answer :
Iodoform
133. Which of the following on oxidation followed by hydrolysis gives pyruvic acid ?
A
Acetaldehyde cyanohydrin
B
Acetone cyanohydrin
C
Formaldehyde cyanohydrin
D
None of these
Answer :
Acetaldehyde cyanohydrin
134.
Aldehydes that do not undergo aldol condensation are
(1) propanal
(2) trichloroethanal
(3) 2-phenylethanal
(4) ethanal
(5) benzaldehyde
A
3 and 4 only
B
2 and 5 only
C
1, 2 and 3 only
D
2, 3 and 5 only
Answer :
2 and 5 only
135. lodoform can be prepared from all except :
A
Ethyl methyl ketone
B
Isopropyl alcohol
C
3 - Methyl 2 - butanone
D
Isobutyl alcohol
Answer :
Isobutyl alcohol
136. Benzoyl chloride on reduction with $$\frac{{{H_2}}}{{Pd{\text{ - }}BaS{O_4}}}$$ produces
A
benzoic acid
B
benzyl alcohol
C
benzoyl sulphate
D
benzaldehyde
Answer :
benzaldehyde
137. Which of following compound is hemiacetal ?
A


B


C


D


Answer :


138. Which is the correct method of synthesising acetamide from acetone?
A
\[C{{H}_{3}}COC{{H}_{3}}\xrightarrow{\frac{Pb}{Bas{{O}_{4}}}}C{{H}_{3}}CHO\] \[\xrightarrow{N{{H}_{3}}}C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}N{{H}_{2}}\xrightarrow{{{H}_{2}}O}\] \[C{{H}_{3}}CON{{H}_{2}}\]
B
\[C{{H}_{3}}COC{{H}_{3}}\xrightarrow[NaOH]{{{I}_{2}}}C{{H}_{3}}COONa\] \[\xrightarrow[N{{H}_{3}}]{{{H}^{+}}}C{{H}_{3}}COON{{H}_{4}}\xrightarrow{\Delta }\] \[C{{H}_{3}}CON{{H}_{2}}\]
C
\[C{{H}_{3}}COC{{H}_{3}}\xrightarrow{Cr{{O}_{3}}}C{{H}_{3}}COOH\] \[\xrightarrow{N{{H}_{3}}}C{{H}_{3}}CON{{H}_{2}}\]
D
\[C{{H}_{3}}COC{{H}_{3}}\xrightarrow[NaOH]{{{I}_{2}}}C{{H}_{3}}COOH\] \[\xrightarrow{HCl}C{{H}_{3}}COCl\xrightarrow{N{{H}_{3}}}\] \[C{{H}_{3}}CON{{H}_{2}}\]
Answer :
\[C{{H}_{3}}COC{{H}_{3}}\xrightarrow[NaOH]{{{I}_{2}}}C{{H}_{3}}COONa\] \[\xrightarrow[N{{H}_{3}}]{{{H}^{+}}}C{{H}_{3}}COON{{H}_{4}}\xrightarrow{\Delta }\] \[C{{H}_{3}}CON{{H}_{2}}\]
139. Nucleophilic addition reaction will be most favoured in
A


B


C


D


Answer :


140. Reaction of cyclohexanone with dimethylamine in the presence of catalytic amount of an acid forms a compound if water during the reaction is continuously removed. The compound formed is generally known as
A
an amine
B
an imine
C
an anemine
D
a Schiff’s base
Answer :
an anemine
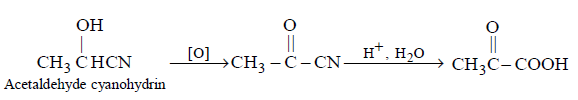

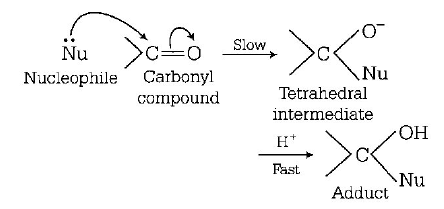
 group. In aldehyde
group. In aldehyde  group is present with at least one alkyl group ( except formaldehyde ) which has $$ + I$$ - effect ( electron donating effect ) and which decreases the positive charge of carbon, thereby making the attack to nucleophile difficult. The nucleophilic attack becomes more difficult in ketones having minimum of two alkyl groups.
group is present with at least one alkyl group ( except formaldehyde ) which has $$ + I$$ - effect ( electron donating effect ) and which decreases the positive charge of carbon, thereby making the attack to nucleophile difficult. The nucleophilic attack becomes more difficult in ketones having minimum of two alkyl groups.

