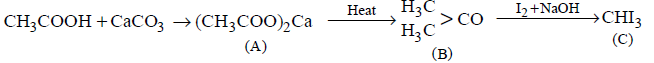121.
Consider the following transformations :
\[C{{H}_{3}}COOH\xrightarrow{CaC{{O}_{3}}}A\xrightarrow{\text{heat}}B\xrightarrow[NaOH]{{{I}_{2}}}C\]
The molecular formula of $$C$$ is
A
\[C{{H}_{3}}\underset{\begin{smallmatrix}
| \\
I
\end{smallmatrix}}{\overset{\begin{smallmatrix}
\,\,\,OH \\
|
\end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{-C-}}}\,C{{H}_{3}}\]
B
$$IC{H_2} - COC{H_3}$$
C
$$CH{I_3}$$
D
$$C{H_3}I$$
Answer :
$$CH{I_3}$$
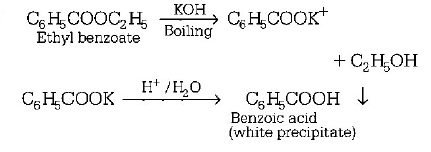
122. An ester is boiled with $$KOH.$$ The product is cooled and acidified with $$conc.$$ $$HCl.$$ A white crystalline acid separates. The ester is
A
methyl acetate
B
ethyl acetate
C
ethyl formate
D
ethyl benzoate
Answer :
ethyl benzoate
123. The compound used as a preservative, for food products such as tomato ketchup and fruit juices, is
A
sodium salicylate
B
sodium benzoate
C
sodium acetate
D
formic acid
Answer :
sodium benzoate
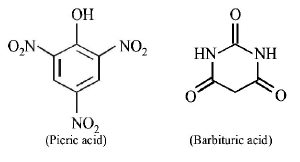
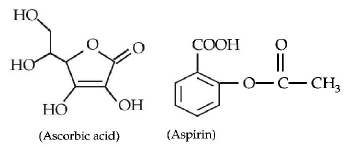
124. The carboxyl functional group $$\left( { - COOH} \right)$$ is present in
A
picric acid
B
barbituric acid
C
ascorbic acid
D
aspirin
Answer :
aspirin
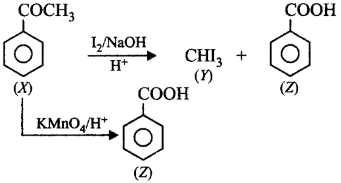
125. An aromatic compound $$\left( X \right)\left( {{C_8}{H_8}O} \right)$$ gives positive 2, 4-$$DNP$$ test. It gives a yellow precipitate of compound $$(Y)$$ on reaction with iodine and sodium hydroxide solution. $$(X)$$ does not give Tollens' test on oxidation under drastic conditions. It gives a carboxylic acid $$\left( Z \right)\left( {{C_7}{H_6}{O_2}} \right).$$ $$(Z)$$ is also formed with $$(Y)$$ during the reaction. $$(X), (Y)$$ and $$(Z)$$ respectively are
A
$${C_6}{H_5}COC{H_3},CH{I_3},{C_6}{H_5}COOH$$
B
$$C{H_3}COC{H_3},CH{I_3},C{H_3}COOH$$
C
$${C_6}{H_5}COC{H_3},CH{I_3},C{H_3}COOH$$
D
$$C{H_3}CHO,CH{I_3},{C_6}{H_5}COOH$$
Answer :
$${C_6}{H_5}COC{H_3},CH{I_3},{C_6}{H_5}COOH$$
126.
In a set of reactions propionic acid yielded a compound $$D.$$
\[C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}COOH\xrightarrow{SOC{{l}_{2}}}\] \[B\xrightarrow{N{{H}_{3}}}C\xrightarrow[B{{r}_{2}}]{KOH}D\]
The structure of $$D$$ would be
A
$$C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}N{H_2}$$
B
$$C{H_3}C{H_2}CON{H_2}$$
C
$$C{H_3}C{H_2}NHC{H_3}$$
D
$$C{H_3}C{H_2}N{H_2}$$
Answer :
$$C{H_3}C{H_2}N{H_2}$$
127. Benzoyl chloride is prepared from benzoic acid by
A
$$C{l_2},hv$$
B
$$S{O_2}C{l_2}$$
C
$$SOC{l_2}$$
D
$$C{l_2},{H_2}O$$
Answer :
$$SOC{l_2}$$
128. The compound that undergoes decarboxylation most readily under mild condition is
A
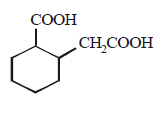

B
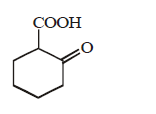

C
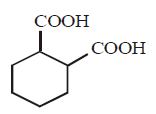

D
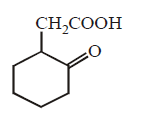

Answer :


129.
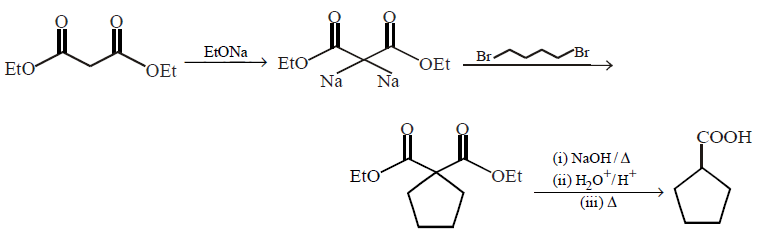
What is the missing reagent in the synthesis shown below
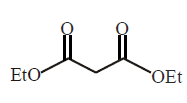 \[\xrightarrow[\left( \text{ii} \right)\,\text{Reagant}]{\left( \text{i} \right)\,EtONa}\]
\[\xrightarrow[\Delta ]{NaOH,{{H}_{2}}O}\,\,\,\xrightarrow[\left( \text{ii} \right)\,\Delta ]{\left( \text{i} \right)\,{{H}_{2}}O,{{H}^{+}}}\]
\[\xrightarrow[\left( \text{ii} \right)\,\text{Reagant}]{\left( \text{i} \right)\,EtONa}\]
\[\xrightarrow[\Delta ]{NaOH,{{H}_{2}}O}\,\,\,\xrightarrow[\left( \text{ii} \right)\,\Delta ]{\left( \text{i} \right)\,{{H}_{2}}O,{{H}^{+}}}\] 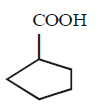
A
bromocyclopentane
B
1, 5 - dibromo pentane
C
1, 4 - dibromo butane
D
1, 1 - dibromo cyclopentane
Answer :
1, 4 - dibromo butane
130. The correct decreasing order for acid strength is :
A
$$N{O_2}C{H_2}COOH > FC{H_2}COOH > $$ $$CNC{H_2}COOH > ClC{H_2}COOH$$
B
$$FC{H_2}COOH > NCC{H_2}COOH > $$ $$N{O_2}C{H_2}COOH > ClC{H_2}COOH$$
C
$$CNC{H_2}COOH > N{O_2}C{H_2}COOH > $$ $$FC{H_2}COOH > ClC{H_2}COOH$$
D
$$N{O_2}C{H_2}COOH > NCC{H_2}COOH > $$ $$FC{H_2}COOH > ClC{H_2}COOH$$
Answer :
$$N{O_2}C{H_2}COOH > NCC{H_2}COOH > $$ $$FC{H_2}COOH > ClC{H_2}COOH$$