51.

The compound $$(X)$$ is
A
$$C{H_3}COOH$$
B
$$BrC{H_2} - COOH$$
C
$${\left( {C{H_3}CO} \right)_2}O$$
D
$$CHO - COOH$$
Answer :
$${\left( {C{H_3}CO} \right)_2}O$$
52. A compound $$(X)$$ with a molecular formula $${C_5}{H_{10}}O$$ gives a positive 2, 4-$$DNP$$ test but a negative Tollens' test. On oxidation it gives a carboxylic acid $$(Y)$$ with a molecular formula $${C_3}{H_6}{O_2}.$$ Potassium salt of $$(Y)$$ undergoes Kolbe's reaction and gives a hydrocarbon $$(Z).$$ $$(X), (Y)$$ and $$(Z)$$ respectively are
A
pentan-3-one, propanoic acid, butane
B
pentanal, pentanoic acid, octane
C
2-methylbutanone, butanoic acid, hexane
D
2, 2-dimethylpropanone, propanoic acid, hexane
Answer :
pentan-3-one, propanoic acid, butane
53. The compound formed when malonic acid is heated with urea, is
A
cinnamic acid
B
butyric acid
C
barbituric acid
D
crotonic acid
Answer :
barbituric acid
54. Which of the following will not undergo $$HVZ$$ reaction?
A
Propanoic acid
B
Ethanoic acid
C
2-Methylpropanoic acid
D
2, 2-Dimethylpropanoic acid
Answer :
2, 2-Dimethylpropanoic acid
55.
In the following sequence of reactions, what is $$D?$$
 \[\xrightarrow{\left[ O \right]}A\]
\[\xrightarrow{\left[ O \right]}A\]
\[A\xrightarrow{SOC{{l}_{2}}}B\xrightarrow{Na{{N}_{3}}}C\xrightarrow{\text{heat}}D\]
A
Primary amine
B
An amide
C
Phenyl isocyanate
D
A higher hydrocarbon
Answer :
Phenyl isocyanate
56. The major product $$H$$ of the given reaction sequence is \[C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-CO-C{{H}_{3}}\xrightarrow{\overset{\Theta }{\mathop{C}}\,N}\] \[G\xrightarrow[{{\text{Heat}}}]{{95\% \,\,{H_2}S{O_4}}}H\]
A
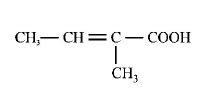

B


C
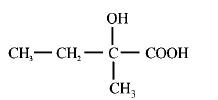

D


Answer :


57. When acetaldehyde is heated with Fehling’s solution it gives a precipitate of
A
$$Cu$$
B
$$CuO$$
C
$$C{u_2}O$$
D
$$Cu + C{u_2}O + CuO$$
Answer :
$$C{u_2}O$$
58.
Which of the following represent the correct decreasing order of acidic strength of
following?
(i) Methanoic acid
(ii) Ethanoic acid
(ii) Propanoic acid
(iv) Butanoic acid
A
(i) > (ii) > (iii) > (iv)
B
(ii) > (iii) > (iv) > (i)
C
(i) > (iv) > (iii) > (i)
D
(iv) > (i) > (iii) > (ii)
Answer :
(i) > (ii) > (iii) > (iv)
59.
\[C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}COOH\xrightarrow[\text{Red}\,P]{B{{r}_{2}}}X\xrightarrow{N{{H}_{3}}\left( alc. \right)}Y\]
$$Y$$ in the above reactions is
A
lactic acid
B
ethylamine
C
propylamine
D
alanine
Answer :
alanine
60. Which of the following compounds will react with \[NaHC{{O}_{3}}\] solution to give sodium salt and carbon dioxide ?
A
Acetic acid
B
$$n$$ - Hexanol
C
Phenol
D
Both (B) and (C)
Answer :
Acetic acid

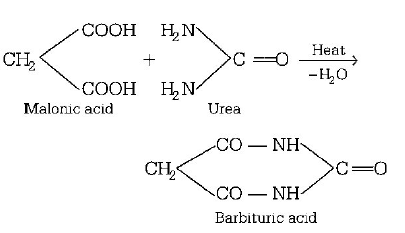
 \[\underset{\text{Phenyl isocyanate,}\left[ D \right]}{\mathop{\to {{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}NCO}}\,\]
\[\underset{\text{Phenyl isocyanate,}\left[ D \right]}{\mathop{\to {{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}NCO}}\,\] 