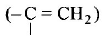211. Ozonolysis of an organic compound gives formaldehyde as one of the products. This confirms the presence of :
A
two ethylenic double bonds
B
a vinyl group
C
an isopropyl group
D
an acetylenic triple bond
Answer :
a vinyl group
212. The distance between two adjacent carbon atoms is largest in
A
benzene
B
ethene
C
butane
D
ethyne
Answer :
butane
213.
Complete the reaction with suitable reagents and compounds.

A
$$\left( A \right){\text{ - }}C{H_4},\left( B \right){\text{ - }}{C_6}{H_5}CHO,$$ $$\left( C \right){\text{ - }}{C_6}{H_5}COONa,\left( D \right){\text{ - }}C{H_4}$$
B
$$\left( A \right){\text{ - }}C{H_3}Cl,\left( B \right){\text{ - }}{C_6}{H_5}COOH,$$ $$\left( C \right){\text{ - }}{C_6}{H_5}COONa,\left( D \right){\text{ - alc}}{\text{.}}\,KOH$$
C
$$\left( A \right){\text{ - }}C{H_3}Cl,\left( B \right){\text{ - }}{C_6}{H_5}COOH,$$ $$\left( C \right){\text{ - }}{C_6}{H_5}COONa,\left( D \right){\text{ - }}NaOH + CaO$$
D
$$\left( A \right){\text{ - }}C{H_3}COCl,\left( B \right){\text{ - }}{C_6}{H_5}CHO,$$ $$\left( C \right){\text{ - }}{C_6}{H_5}COONa,\left( D \right){\text{ - }}AlC{l_3}$$
Answer :
$$\left( A \right){\text{ - }}C{H_3}Cl,\left( B \right){\text{ - }}{C_6}{H_5}COOH,$$ $$\left( C \right){\text{ - }}{C_6}{H_5}COONa,\left( D \right){\text{ - }}NaOH + CaO$$
214. In the reaction, \[C{{l}_{2}}+C{{H}_{4}}\xrightarrow{H\upsilon }C{{H}_{3}}Cl+HCl\] presence of a small amount of oxygen
A
increases the rate of reaction for a brief period of time
B
decreases the rate of reaction for a brief period of time
C
does not affect the rate of reaction
D
completely stops the reaction
Answer :
decreases the rate of reaction for a brief period of time
215. Which of the following has the lowest boiling point?
A
2-Methylbutane
B
2-Methylpropane
C
2, 2-Dimethylpropane
D
$$n$$ - Pentane
Answer :
2-Methylpropane
216.
Arrange the following in decreasing order of reactivity towards $$EAS$$ ( electrophilic aromatic substitution )
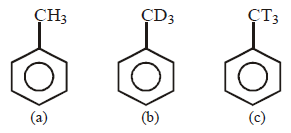
A
$$a > b > c$$
B
$$c > b > a$$
C
$$a > c > b$$
D
$$c > a > b$$
Answer :
$$a > b > c$$
217. When propyne is treated with aqueous $${H_2}S{O_4}$$ in presence of $$HgS{O_4}$$ the major product is
A
propanal
B
propyl hydrogensulphate
C
acetone
D
propanol
Answer :
acetone
218. Which of the following reactions does not show the correct products of the reaction?
A
\[C{{H}_{3}}-CH=C{{H}_{2}}\xrightarrow[\text{peroxide}]{HBr}\] \[C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}Br\]
B
\[C{{H}_{3}}-CH=C{{H}_{2}}\xrightarrow[\text{peroxide}]{HCl}\] \[C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}Cl\]
C
\[C{{H}_{3}}-CH=C{{H}_{2}}\xrightarrow{HBr}C{{H}_{3}}\overset{\begin{smallmatrix}
Br\,\, \\
|\,\,\,\,
\end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{-CH-}}\,C{{H}_{3}}\]
D
\[C{{H}_{3}}-CH=C{{H}_{2}}\xrightarrow{HCl}C{{H}_{3}}\underset{\begin{smallmatrix}
|\,\,\,\,\,\,\, \\
Cl\,\,\,\,\,\,
\end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{-CH-}}\,C{{H}_{3}}\]
Answer :
\[C{{H}_{3}}-CH=C{{H}_{2}}\xrightarrow[\text{peroxide}]{HCl}\] \[C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}Cl\]
219. Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding dehydrohalogenation of alkenes ?
A
During the reaction hydrogen atom is eliminated from the $$\beta {\text{ - }}$$ carbon atom.
B
Rate of reaction for same alkyl group; Iodine > Bromine > Chlorine
C
Rate of reaction; $${\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_3}C - > {\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_2}CH - > C{H_3}C{H_2} - $$
D
Only nature of halogen atom determine rate of the reaction.
Answer :
Only nature of halogen atom determine rate of the reaction.
220. Which of the following compounds does not dissolve in conc. $${H_2}S{O_4}$$ even on warming ?
A
ethylene
B
benzene
C
hexane
D
aniline
Answer :
hexane