51. For the reaction, $$2{N_2}{O_5} \to 4N{O_2} + {O_2}$$ rate and rate constant are $$1.02 \times {10^{ - 4}}\,mol\,{L^{ - 1}}{s^{ - 1}}$$ and $$3.4 \times {10^{ - 5}}\,{s^{ - 1}}$$ respectively. The concentration of $${N_2}{O_5}$$ in $$mol\,{L^{ - 1}}$$ will be
A
$$3.4 \times {10^{ - 4}}$$
B
$$3.0$$
C
$$5.2$$
D
$$3.2 \times {10^{ - 5}}$$
Answer :
$$3.0$$
52. Units of rate constant of first and zero order reactions in terms of molarity $$M$$ unit are respectively
A
$${\sec ^{ - 1}},M{\sec ^{ - 1}}$$
B
$${\sec ^{ - 1}},M$$
C
$$M{\sec ^{ - 1}},{\sec ^{ - 1}}$$
D
$$M,{\sec ^{ - 1}}$$
Answer :
$${\sec ^{ - 1}},M{\sec ^{ - 1}}$$
53. Plots showing the variation of the rate constant $$(k)$$ with temperature $$(T)$$ are given below. The plot that follows Arrhenius equation is
A


B
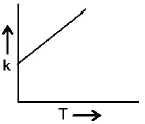

C
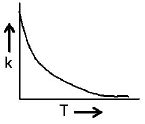

D


Answer :


54. The half life period of a first order chemical reaction is 6.93 minutes. The time required for the completion of 99% of the chemical reaction will be ( log 2 = 0.301 )
A
23.03 minutes
B
46.06 minutes
C
460.6 minutes
D
230.03 minutes
Answer :
46.06 minutes
55.
In the reaction, $$P + Q → R + S.$$ The time taken for $$75\% $$ reaction of $$P$$ is twice the time taken for $$50\% $$ reaction of $$P.$$ The concentration of $$Q$$ varies with reaction time as shown in the figure. The overall order of the
reaction is
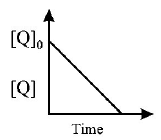
A
2
B
3
C
0
D
1
Answer :
1
56. The rate constant of a reaction depends on
A
temperature
B
initial concentration of the reactants
C
time of reaction
D
extent of reaction
Answer :
temperature
57. For a reaction, $${I^ - } + OC{l^ - } \to I{O^ - } + C{l^ - }$$ in an aqueous medium, the rate of reaction is given by $$\frac{{d\left[ {I{O^ - }} \right]}}{{dt}} = k\frac{{\left[ {{I^ - }} \right]\left[ {OC{l^ - }} \right]}}{{\left[ {O{H^ - }} \right]}}.$$ The overall or der of reaction is
A
-1
B
0
C
1
D
2
Answer :
1
58. When a catalyst is used in an equilibrium process,
A
it increases the rate of forward reaction
B
it decreases the rate of backward reaction
C
it decreases activation energy of both forward and backward processes
D
it fastens the attainment of equilibrium by lowering activation energy
Answer :
it fastens the attainment of equilibrium by lowering activation energy
59.
Which of the following graphs represents exothermic reaction?
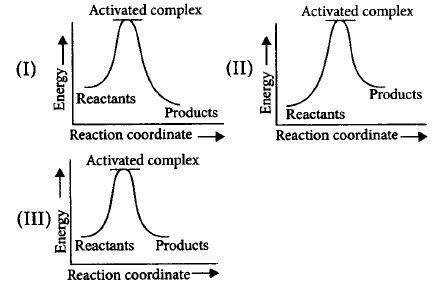
A
(I) only
B
(II) only
C
(III) only
D
(I) and (II)
Answer :
(I) only
60. The unit of rate and rate constant are same for a
A
zero order reaction
B
first order reaction
C
second order reaction
D
third order reaction
Answer :
zero order reaction