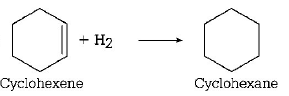
101. The enthalpy of combustion of $${H_2},$$ cyclohexene $$\left( {{C_6}{H_{10}}} \right)$$ and cyclohexane $$\left( {{C_6}{H_{12}}} \right)$$ are $$-241, -3800$$ and $$-3920$$ $$kJ$$ per $$mol$$ respectively. Heat of hydrogenation of cyclohexene is
A
$$ - 121\,kJ\,{\text{per}}\,mol$$
B
$$ + 121\,kJ\,{\text{per}}\,mol$$
C
$$ + 242\,kJ\,{\text{per}}\,mol$$
D
$$ - 242\,kJ\,{\text{per}}\,mol$$
Answer :
$$ - 121\,kJ\,{\text{per}}\,mol$$
102.
Among the following, the set of parameters that represents path functions, is :
$$\eqalign{
& \left( {\text{i}} \right)q + w \cr
& \left( {{\text{ii}}} \right)q \cr
& \left( {{\text{iii}}} \right)w \cr
& \left( {{\text{iv}}} \right)H - TS \cr} $$
A
(ii) and (iii)
B
(ii), (iii) and (iv)
C
(i) and (iv)
D
(i), (ii) and (iii)
Answer :
(ii) and (iii)
103. If for a given substance melting point is $${T_B}$$ and freezing point is $${T_A},$$ then correct variation shown by, graph between entropy change and temperature is
A
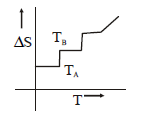

B


C
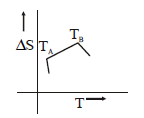

D


Answer :


104.
What will be the enthalpy of combustion of carbon to produce carbon monoxide on the basis of data given below ?
$$\eqalign{
& {C_{\left( s \right)}} + {O_{2\left( g \right)}} \to C{O_{2\left( g \right)}} - 393.4\,kJ \cr
& C{O_{\left( g \right)}} + \frac{1}{2}{O_{2\left( g \right)}} \to C{O_{2\left( g \right)}} - 283.0\,kJ \cr} $$
A
$$ + 676.4\,kJ$$
B
$$ - 676.4\,kJ$$
C
$$ - 110.4\,kJ$$
D
$$ + 110.4\,kJ$$
Answer :
$$ - 110.4\,kJ$$
105. The work done during the expansion of a gas from a volume of $$4\,d{m^3}$$ to $$6\,d{m^3}$$ against a constant external pressure of $$3\,atm,$$ is
A
$$ - 6\,J$$
B
$$ - 608\,J$$
C
$$ + 304\,J$$
D
$$ - 304\,J$$
Answer :
$$ - 608\,J$$
106.
For the reaction given below the values of standard Gibbs free energy of formation at $$298\,K$$ are given. What is the nature of the reaction ?
$${I_2} + {H_2}S \to 2HI + S$$
$$\Delta G_f^ \circ \left( {HI} \right) = 1.8\,kJ\,mo{l^{ - 1}},$$ $$\Delta G_f^ \circ \left( {{H_2}S} \right) = 33.8\,kJ\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
A
Non-spontaneous in forward direction.
B
Spontaneous in forward direction.
C
Spontaneous in backward direction.
D
Non-spontaneous in both forward and backward directions.
Answer :
Spontaneous in forward direction.
107. For the reaction of one mole of zinc dust with one $$mole$$ of sulphuric acid in a bomb calorimeter, $$\Delta U$$ and $$w$$ correspond to
A
$$\Delta U < 0,w = 0$$
B
$$\Delta U < 0,w < 0$$
C
$$\Delta U > 0,w = 0$$
D
$$\Delta U > 0,w > 0$$
Answer :
$$\Delta U < 0,w = 0$$
108. A chemical reaction will be spontaneous if it is accompanied by a decrease in
A
entropy of the system
B
enthalpy of the system
C
internal energy of the system
D
free energy of the system
Answer :
free energy of the system
109. Equal volumes of methanoic acid and sodium hydroxide are mixed. If $$x$$ is the heat of formation of water, then heat evolved on neutralization is
A
more than $$x$$
B
equal to $$x$$
C
less than $$x$$
D
twice $$x$$
Answer :
less than $$x$$
110. For which one of the processes represented by the following equations the enthalpy (heat) change is likely to be negative
A
$$C{l^ - }\left( g \right) + aq \to C{l^ - }\left( {aq} \right)$$
B
$$Cl\left( g \right) \to C{l^ + }\left( g \right) + {e^ - }$$
C
$$\frac{1}{2}C{l_2}\left( g \right) \to Cl\left( g \right)$$
D
$$C{l_2}\left( l \right) \to C{l_2}\left( g \right)$$
Answer :
$$C{l^ - }\left( g \right) + aq \to C{l^ - }\left( {aq} \right)$$