291. A system changes from state $$X$$ to $$Y$$ with a change in internal energy measuring to $$25\,kJ\,mo{l^{ - 1}},$$ by a reversible path and returns from $$Y$$ to $$X$$ by an irreversible path. What will be the net change in internal energy ?
A
$$25\,kJ$$
B
$$ > 25\,kJ$$
C
$$ < 25\,kJ$$
D
$${\text{Zero}}$$
Answer :
$${\text{Zero}}$$
292.
Among the following the state function(s) is (are)
(i) Internal energy
(ii) Irreversible expansion work
(iii) Reversible expansion work
(iv) Molar enthalpy
A
(ii) and (iii)
B
(i), (ii) and (iii)
C
(i) and (iv)
D
(i) only
Answer :
(i) and (iv)
293.
The factor of $$\Delta G$$ values is important in metallurgy. The $$\Delta G$$ values for the following reactions at $${800^ \circ }C$$ are given as :
$${S_2}\left( s \right) + 2{O_2}\left( g \right) \to 2S{O_2}\left( g \right);$$ $$\Delta G = - 544\,kJ$$
$$2Zn\left( s \right) + {S_2}\left( s \right) \to 2ZnS\left( s \right);$$ $$\Delta G = - 293\,kJ$$
$$2Zn\left( s \right) + {O_2}\left( g \right) \to 2ZnO\left( s \right);$$ $$\Delta G = - 480\,kJ$$
$${\text{Then}}\,\Delta G\,{\text{for the reaction :}}$$
$$2ZnS\left( s \right) + 3{O_2}\left( g \right) \to $$ $$2ZnO\left( s \right) + 2S{O_2}\left( g \right)$$
will be :
A
$$- 357\,kJ$$
B
$$- 731\,kJ$$
C
$$- 773\,kJ$$
D
$$- 229\,kJ$$
Answer :
$$- 731\,kJ$$
294. The standard enthalpy of formation $$\left( {{\Delta _f}{H^ \circ }_{298}} \right)$$ for methane, $$C{H_4}$$ is $$ - 74.9\,kJ\,mo{l^{ - 1}}.$$ In order to calculate the average energy given out in the formation of a $$C-H$$ bond from this it is necessary to know which one of the following ?
A
The dissociation energy of the hydrogen molecule, $${H_2}.$$
B
The first four ionisation energies of carbon.
C
The dissociation energy of $${H_2}$$ and enthalpy of sublimation of carbon (graphite).
D
The first four ionisation energies of carbon and electron affinity of hydrogen.
Answer :
The dissociation energy of $${H_2}$$ and enthalpy of sublimation of carbon (graphite).
295. If bond enthalpies of $$N \equiv N,H - H$$ and $$N - H$$ bonds are $${x_1},{x_2}$$ and $${x_3}$$ respectively, $$\Delta H_f^ \circ $$ for $$N{H_3}$$ will be
A
$${x_1} + 3{x_2} - 6{x_3}$$
B
$$\frac{1}{2}{x_1} + \frac{3}{2}{x_2} - 3{x_3}$$
C
$$3{x_3} - \frac{1}{2}{x_1} - \frac{3}{2}{x_2}$$
D
$$6{x_3} - {x_1} - 3{x_2}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{1}{2}{x_1} + \frac{3}{2}{x_2} - 3{x_3}$$
296. An ideal gas occuping a volume of $$2d{m^3}$$ and a pressure of $$5\,bar$$ undergoes isothermal and irreversible expansion against external pressure of $$1\,bar$$ The final volume of the system and the work involved in the process is
A
$$10\,d{m^3},1000\,J$$
B
$$8\,d{m^3},\, - 800\,J$$
C
$$10\,d{m^3}, - 800\,J$$
D
$$10\,d{m^3}, - 1000\,J$$
Answer :
$$10\,d{m^3}, - 800\,J$$
297. Consider the reversible isothermal expansion of an ideal gas in a closed system at two different temperatures $${T_1}$$ and $${T_2}$$ $$\left( {{T_1} < {T_2}} \right).$$ The correct graphical depiction of the dependence of work done $$(w)$$ on the final volume $$(V)$$ is :
A
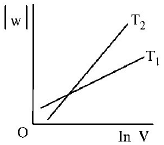

B
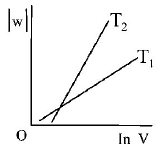

C
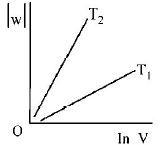

D
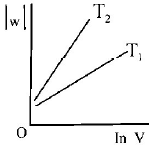

Answer :


298. The latent heat of vapourization of a liquid at $$500\,K$$ and $$1\,atm$$ pressure is $$10.0\,kcal/mol.$$ What will be the change in internal energy $$\left( {\Delta U} \right)$$ of $$3\,moles$$ of liquid at the same temperature
A
$$13.0\,kcal/mol$$
B
$$ - 13.0\,kcal/mol$$
C
$$27.0\,kcal$$
D
$$ - 7.0\,kcal/mol$$
Answer :
$$27.0\,kcal$$
299.
Match the column I with column II and mark the appropriate choice.
| Column I | Column II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| a. | $${H_{2\left( g \right)}} + B{r_{2\left( g \right)}} \to 2HB{r_{\left( g \right)}}$$ | 1. | $$\Delta H = \Delta U - 2RT$$ |
| b. | $$PC{l_{5\left( g \right)}} \to PC{l_{3\left( g \right)}} + C{l_{2\left( g \right)}}$$ | 2. | $$\Delta H = \Delta U + 3RT$$ |
| c. | $${N_{2\left( g \right)}} + 3{H_{2\left( g \right)}} \to 2N{H_{3\left( g \right)}}$$ | 3. | $$\Delta H = \Delta U$$ |
| d. | $$2{N_2}{O_{5\left( g \right)}} \to 4N{O_{2\left( g \right)}} + {O_{2\left( g \right)}}$$ | 4. | $$\Delta H = \Delta U + RT$$ |
A
a - 3, b - 1, c - 2, d - 4
B
a - 3, b - 4, c - 1, d - 2
C
a - 2, b - 1, c - 4, d - 3
D
a - 4, b - 2, c - 1, d - 3
Answer :
a - 3, b - 4, c - 1, d - 2
300.
Given the following entropy values $$\left( {{\text{in}}\,J{K^{ - 1}}\,mo{l^{ - 1}}} \right)$$ at $$298\,K$$ and $$1\,atm:{H_2}\left( g \right):130.6,$$ $$C{l_2}\left( g \right):223.0,$$ $$HCl\left( g \right):186.7.$$ The entropy change $$\left( {{\text{in}}\,J{K^{ - 1}}\,mo{l^{ - 1}}} \right)$$ for the reaction
$${H_2}\left( g \right) + C{l_2}\left( g \right) \to 2HCl\left( g \right),$$ is
A
+ 540.3
B
+ 727.0
C
- 166.9
D
+ 19.8
Answer :
+ 19.8